5 tips to troubleshoot network connectivity issues in Windows Vista
In this article, I will show you five tips that you can take to fix some network problems in Windows Vista; includes automatic diagnostics, command line tools and powerful troubleshooting methods.
Introduce
Windows Vista is no different than other operating systems, whether sooner or later you will experience network problems. These problems can be caused by the operating system, user or administrator configuration errors, network problems, or other problems. So it is impossible to ask whether you need to perform Vista network troubleshooting, but you need to ask when you need to perform troubleshooting for this network. In this article, I will show you five tips that you can use to troubleshoot network problems in Windows Vista. Begin with the first tip:
1. Using the 'Bottom Up' method to temporarily translate as 'overturning'
If you look at the OSI 7-layer reference model, you will see that it is the class model that represents all the different components that make up a network. The bottom layer 'bottom' is the physical layer. This class is shown in reality that is the cable, NIC interface, switch and electrical signal running on the wire. If you start troubleshooting your problem in this last layer (physical layer) and move up to the upper layers in the model, then you will go through other layers like the Data-Link layer (usually Ethernet). protocol), Network Layer (IP Network), Transport Layer (TCP), . and finally the Application layer application layer (layer 1).
Our tip is to start troubleshooting by checking the physical connection. Here are some questions for you to check your connection:
- Is your network cable connected?
- Do you see a signal light on the NIC?
- Does Windows see your NIC?
- Is the Ethernet switch powered and shows the light on?
Whether you use a wired or wireless connection, the questions are similar. Get an example of the wireless network connection state in Vista:
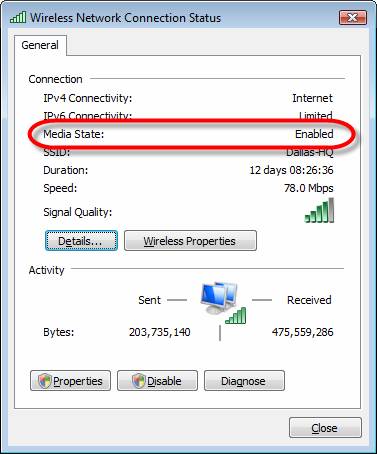
Figure 1: Wireless network connection status in Vista
Pay attention to the 'media state' section. In this case, the transmission environment is wireless but the important thing here is that it is activated.
If you want to make a connection to a wireless network, make sure that you are actually connected to a network. You can click Connect to a Network to connect or disconnect from a wireless or dialup network.
On a computer with a physical Ethernet connection, you will see similar things. See the following example of Windows 2008 Server with an Ethernet NIC:
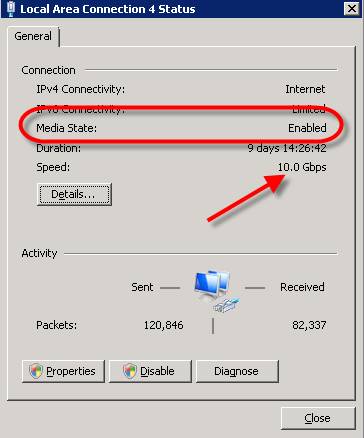
Figure 2: Windows 2008 Media Stat
On this server, you can see that the Ethernet environment on the wired LAN connection is activated and you can see that its speed is 10.0 Gbps.
If you can verify those things, proceed to verify the OSI model until you find the problem. Network administrators often joke about the OSI model that there is an 8th class in this model that is the 'end user' class and they need a lot of time for this problem.
However, many of those things will need to be included in the category for testing different classes in the reference model as with most network tools, they are used to test the relevant Network & Transport classes. to TCP / IP.
2. IP addressing
To advance to this step, you need to clearly identify the state of the environment and the link signaling and your physical network connection are currently working. When you first transition to the higher layer in the reference model, we will skip the layer datalink layer (layer 2) and go straight to layer 3 (IP addressing) because the Ethernet MAC address usually does not cause problems in the network.
In this step, you need to check IP addressing to ensure that:
- You have a real IP address (not an automatically assigned IP address)
- Your address is correct and valid for network addresses and gateways
- You have defined gateway addresses and DNS Server IPs
To do this, open the Network and Sharing Center and if you have a connection, click View Status to see your connection network interface.
Figure 3: Observe the state of the connection
Then click Details to see the IP address, subnet mask, default gateway and DNS Servers. If you look at the details in Figure 4, then you will see that the connection does not have a gateway or DNS servers.
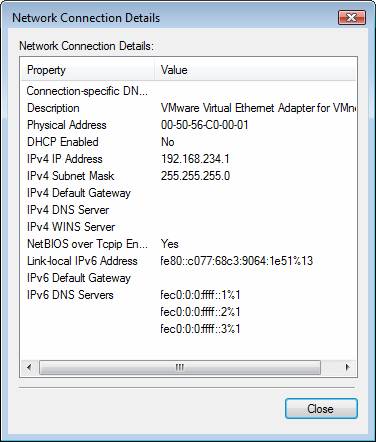
Figure 4: Connection without a default gateway or DNS Servers
Missing one of these components will not allow you to have the network connection as usual. Obviously not all of them are required but most of us want to communicate outside of our LAN. A default gateway must be needed for that. On the other hand, we also want to communicate with multiple servers by name (such as www.quantrimang.com instead of 222.255.28.220) and the name of DNS Server IP is also required for that.
There is another way that you can execute the IPCONFIG / ALL command to check all IP configurations as follows:
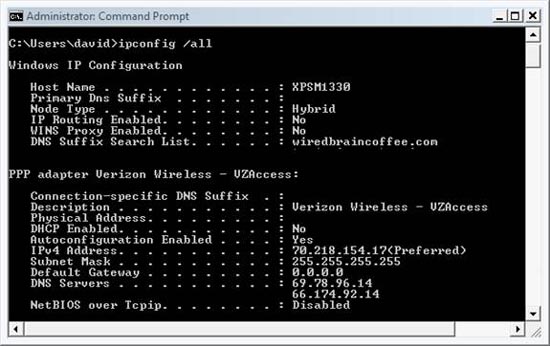
Figure 5: Result of IPCONFIG / ALL command
You may not receive the settings because your adapter is not currently using DHCP.
Even if you don't have a valid IP address, default gateway and DNS Servers, you need to ping them to ensure that you can really communicate with them.
3. Diagnostic tool and error correction
If you do not want to start troubleshooting, Vista also provides you with a Diagnose and Repair tool to automatically diagnose and repair network connectivity problems. IT administrators can use this tool as a 'way to protect themselves with pistols' to solve problems faster without having to try everything. To use this tool, simply open the Network and Sharing Center and click Diagnose and Repair.
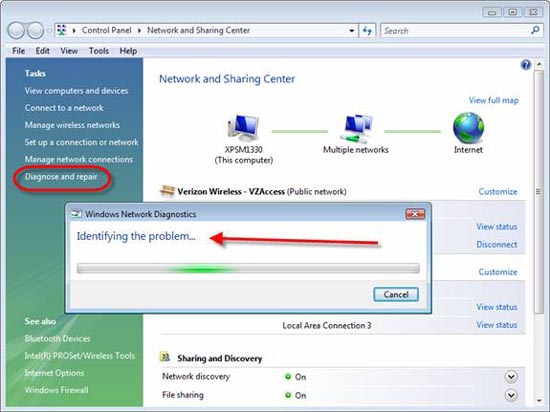
Figure 6: Diagnosis and error correction
Note :
Vista also helps you call the diagnostic tool and fix 'Network Diagnostics' errors. This tool will check your network connection to determine the problem. It will tell you basically what is wrong in the network connection but if you want to get detailed information you need to check Event Viewer .
4. Filtering and Discovery networks
As we continue to go up in the reference model, we will now meet the TCP layer and application layer filtering. Firewalls are used to filter incoming and outgoing network connections. They may be located locally on a Vista computer or may be located outside the network, filtering incoming and outgoing connections to the Internet. We will not mention the case where a firewall is located outside the LAN. If firewalls are on a Vista computer, you can have more than just one (if you install other third-party firewalls). However, the first thing you need to check is Windows' own firewall, which is installed by default when installing Windows Vista.
It is not that the Windows firewall blocks all your network access, but rather it is blocking certain inbound and outbound connections with certain applications. Since this is always a risk if the network is in a public network, one thing you often have to do while in this network is to turn off the firewall to check if your problem is resolved. is not. If the problem is there, you can reactivate your firewall and then troubleshoot it to indicate which port should allow your network traffic through.
To disable or add exceptions to the firewall, simply click Windows Firewall inside the Network and Sharing Center . Here, you can see its status.
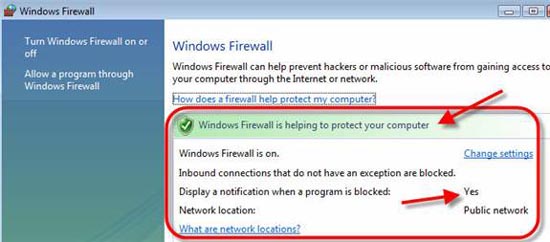
Figure 7: Check the Windows firewall
We can see that the Windows Firewall is enabled and that means that incoming connections without exception will be blocked. There is also no notification here when a certain program is blocked.
To disable the firewall or create an exception, simply click Change Settings and see the following:
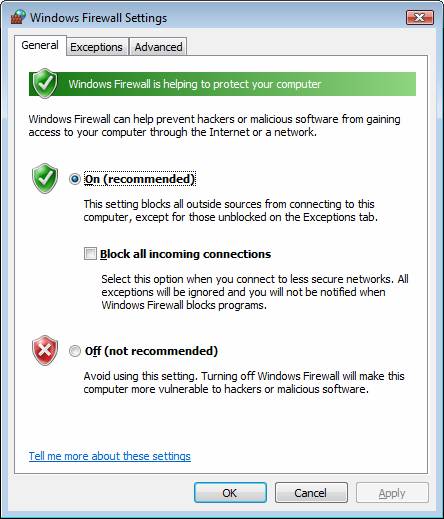
Figure 8: Change the firewall settings in Windows
Here you can turn off the firewall, view or change exceptions in the Exceptions tab, or see advanced features.
Besides Windows Firewall, if you have any problems accessing computers on the local network, you need to check the Network Discovery settings. To do that, go to the Network and Sharing Center and go to Sharing and Discovery . Check your settings for things like Network Discovery, File Sharing, .
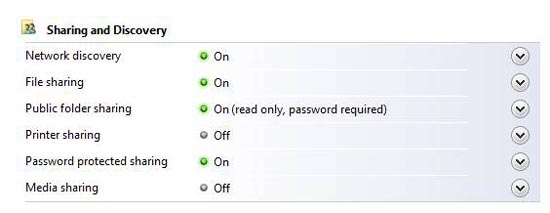
Figure 9: Sharing and Discovery
5. Use senses
Although we have provided you with some troubleshooting tools, there is another trick here that is 'sense' at work. These are necessary perceptions:
- Did you or someone change something from there causing problems with your network connection?
- Did you even connect to the network?
- Do you assume that all network connections are lost when it is actually just an inactive server or application? (it's easy to check that out)
- Check each one then move on to another. Without changing the three things, then maybe your network will work, but you won't know where your resolved problem is (it is likely that there will be many other problems and occurrences. confusion between changes. If you only change something that your problem still exists, then change it back to the previous state.
Conclude
Through this tutorial, you can definitely fix network problems in Vista if you use this operating system. This is obviously not a matter of whether or not it is a matter of when. Not only that when the incident occurs, you can overcome it quickly with the thinking method equipped in the lesson (like the 'bottom up' method) and another factor that you have practiced and have encountered those problems before.