Troubleshoot Wi-Fi connectivity problems in iPad and iPhone
Like it or not, but with the increase in the number of iPhone and iPad devices being used, more and more problems are related to Wi-Fi connectivity .
In the wireless LAN troubleshooting tips, I showed you how to troubleshoot Windows, router and physical connectivity issues. However, if you are experiencing WLAN issues with your iPhone or iPad, you can follow the connection troubleshooting steps we provide in this article.
1. Start by rechecking the physical connections . Always start from here and follow the instructions in the Wireless network troubleshooting step, step 1.
2. Next, verify that the iPad or iPhone Wi-Fi adapter is installed and working properly . Because iPhones, iPads and iPod touches have internal 802.11 chipsets, you don't need to verify the installation, but still need to check if the system has Wi-Fi enabled. Tap (tap) on Settings / Wi-Fi . If Wi-Fi is in the OFF state, touch the slider to set the ON status. When Wi-Fi is ON , the Wi-Fi signal strength indicator will appear in the upper left corner of the device's home screen.
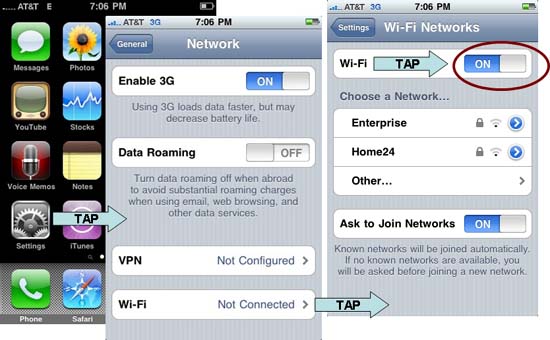
Figure 1: Verify that the client's Wi-Fi is turned on
3. Verify that the wireless router's LAN settings are correct . Follow the instructions in the Wireless network troubleshooting step, step 3 to access the router's administrative utility and determine if the IP address range and subnet are being assigned to the clients.
4. Verify the client's TCP / IP settings to ensure the iPhone's Wi-Fi connection . Return to the Settings / Wi-Fi section on your iPhone, iPad or iPod and find your network name (SSID) on the "Choose a Network" list.
- If your network name is not on the list, your router may be hidden in SSID mode. Click " Other " and enter the network name manually.
- If your network appears in the list without a check mark next to it, the iPhone OS client is not connected. Touch the network name to make the connection. You will be prompted for a password; Enter the password and tap " Join ". If you have tried repeating but the process still fails, go to step 8.
- If the check mark appears to the left of the network name, continue the steps in order.
When you connect to a network, the spinning wheel will appear to the right of the target network on your iPad or iPhone. When this wheel disappears, tap the right-pointing arrow after the network name to see the IP address assigned to the client.
- If the IP address of the connected client is set to " Static " but not within the router's LAN IP range (see step 3), tap " DHCP " to set an automatic IP address and tap " Renew Lease ".
- If the client's IP address is blank or the client repeatedly connects but then quickly disconnects, go to step 8.
- If the client's IP address is in the router's LAN IP range, continue.
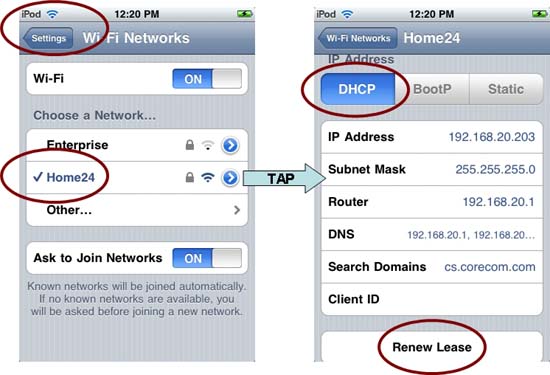
Figure 2: Verifying the client's IP address
5. When your iPhone client has a valid IP address within the router's LAN IP range, use the 'ping' command to authenticate the connection . This step is different when done on iPhone, iPad or iPod because Apple does not include a specific 'ping' application for these devices. However, you can still verify your network connection as shown below.
- If you have not installed the ping application, start by using Safari to check Internet access. You can start by browsing, for example, to Bing.com, for example. If you successfully open this website, then you are happy: You are connected!
- If there is an error message " Cannot Open Page ", then you need to do some other action. Browse to the router's administrative utility (such as http://192.168.1.1). If you can open this page, then you can connect to the router but the router has a problem. Refer to our wireless troubleshooting tips for more details.
- If you cannot access the router's administrative utility or another device that is connected to the router's LAN, you need to troubleshoot connectivity by other means. Use iTunes to download and install the 'ping' application, such as the Network Ping Lite application provided by MochaSoft. Use that application to ping the router's LAN IP address as shown below. If the ping to the router fails, skip step 6.
- If the ping to the router is successful, continue to perform this action with other wireless and wired clients in the network you want to communicate with. If the ping action fails, the AP isolation may be triggered or the destination may use a firewall to block incoming information. Follow the instructions given in the Wireless network troubleshooting article, step 5.
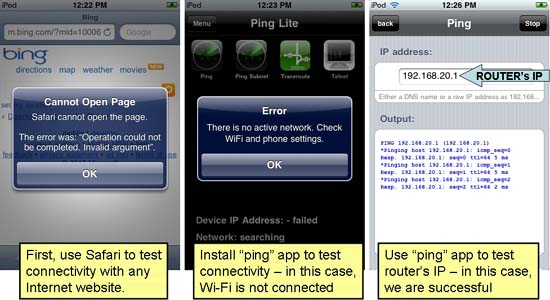
Figure 3: Sending test traffic using Safari or Bing
6. If the iPhone OS wireless client still can't connect, get a valid IP address or ping your router, it's time to look for specific issues. Routers and clients must use compatible 802.11 standards. Detail:
- With older iPhones and iPod touches, integrated 802.11bg is included. They can connect to 802.11b, 11g or 11n (one or dual band bands) but cannot connect to router 11a.
- Third-generation iPod touches have integrated single-band 802.11n but work as 802.11bg clients. They are compatible with routers that work with older devices.
- The new iPad has integrated dual band 802.11n standard and can connect to 802.11 routers (including 11a). However, earlier iPads experienced WLAN problems for iPads, especially in reconnecting with 11n routers.
To determine which 802.11 standards your router supports, search for Wi-Fi-certified logos below in the instructions, search for Wi-Fi-certified products at the Wi-Fi Alliance website. . Once you have confirmed that your router and client are compatible, check the router's wireless settings as described in the Wireless troubleshooting article, step 6.
7. If a compatible wireless client and router can 'listen' to each other but cannot connect or exchange traffic, look for a security type error . The client must support the security mode required by the router: Open, WEP, WPA, or WPA2. Unless the WLAN is in Open mode (insecure mode), the router and client must be configured with the same keys to encrypt traffic between them. Compare router WLAN security settings with the client's wireless connection properties and try to match them.
- To reconfigure security parameters for a network to which you are connected, tap the pointing arrow to the right after the network name, and then tap " Forget this Network ".
- To reconfigure security parameters for other networks, select the network name (or tap " Other " and enter the network name manually).
- If your router uses WEP, set security mode to WEP and copy the router's first WEP key into the " Password " field of the client.
- If your router WPA-Personal, set the client's Security mode to WPA and copy the router's password to the " Password " field of the client.
If your router uses WPA2-Personal encryption, set the client's Security to WPA2 and copy the router's password into the client's " Password " field.
If your router uses WPA or WPA2-Enterprise encryption, set the client's Security to WPA-Enterprise or WPA2-Enterprise and continue the 802.1X installation in step 8.
If you choose the wrong security type or enter the wrong password, when you tap " Join " will usually generate an error message. However, type errors may appear when the router you connected to is reconfigured. In that case, it's best to select " Forget this Network " and start again connecting from the beginning.
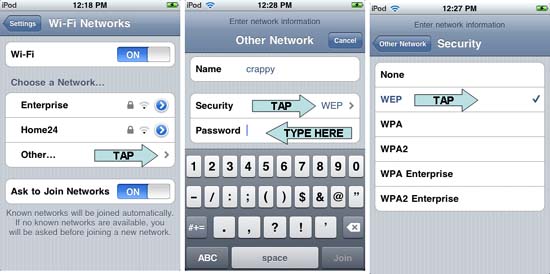
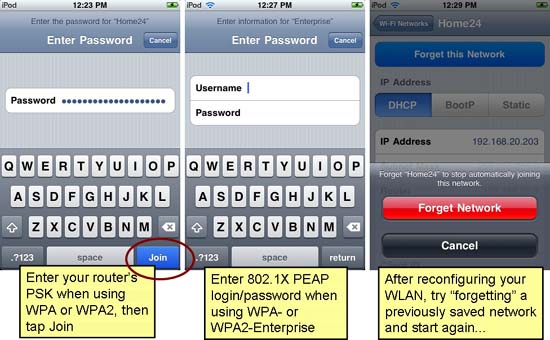
Figure 4: Matching security settings between the client and the router
8. Ensure RADIUS is working. WPA and WPA2-Enterprise write clients to the network and distribute the encryption key using the 802.1X-capable RADIUS server. Refer to Wireless Troubleshooting tips, step 8, to check the router's RADIUS settings.
9. If RADIUS works but client access requests are denied, find out about 802.1X Extensible Authentication Protocol (EAP) issues. Your client must support one or more EAP required by the RADIUS server and must provide a valid login.
- If your RADIUS server requires PEAP, simply set up the client's Security WPA-Enterprise or WPA2-Enterprise and enter the password as well as the assigned username.
- If the RADIUS server requires another EAP type, you must complete the WPA2-Enterprise / 802.1X installation using the configuration utility or configuration profile.
10. If the iPhone OS client still seems to be unable to connect, it seems to be always very slow, or losing connectivity often, you may be experiencing lower-level wireless problems . Refer to our network troubleshooting tips, steps 10 and 11 for more detailed instructions on this issue. To further support debugging, you can install some free applications. For example:
- Ookla SpeedTest - Useful for measuring slow connections
- Bitrino WifiTrak - View current security, channel and credit / security settings
- 10base-t IP Scanner Lite - Access client computers on your network
You should read it
- ★ How to create a new Apple ID on iPhone or iPad
- ★ Apple's new iCloud feature for iPhone, iPad and Mac will have you kissing Dropbox goodbye
- ★ Apple released a list of devices upgraded to iOS 11
- ★ Launched for 6-7 years, iPhone 5s and iPhone 6 have just been updated to the new iOS by Apple
- ★ Apple unveiled the new 10.2-inch iPad model, price unchanged