Wireless LAN security (Term 3)
Wireless LAN security (Term 1)
Wireless LAN security (Term 2)
6. Encryption
Encryption is a data transformation so that only confirmed components can decode it. The encoding process is to combine several plaintext with a key to form a secret text (Ciphertext). The decoding by combining the Ciphertext with the key to reconstruct the original plaintext is shown in Figure 5. The process of arranging and distributing keys is called key management.
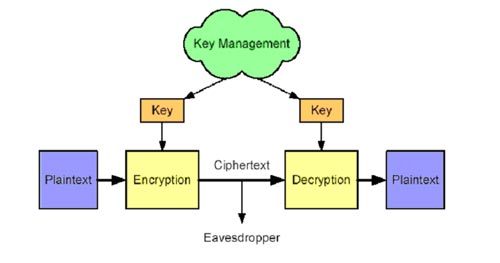
Encryption and decoding process
If the same key is used for both encoding and decoding, then the keys are interpreted as 'symmetric'. If different keys are used, this process is interpreted as 'asymmetrric'. Asymmetric keys are widely used in PKIs (Public Key Infrastructures), where a key is 'public' and the rest are 'private'.
There are two encryption methods : Cipher block and Cipher string. Block cipher works on plaintext in bit groups called blocks, typically 64 or 128 bits long. Typical examples of block Cipher such as: DES, triple DES (3DES), AES and Blowfish. Chain Cipher transforms a key into a random 'keystream' (typically 8 bits), then combines with the plaintext to encrypt it. Chain Cipher is used more than block Cipher. Examples of string cipher are: RC4 (used in 802.11 wireless LANs).
7. Confirm wireless
Confirmation is the provision or cancellation of a confirmation by someone or something. Normal validation is a one-way process, such as a log on user with a computer and provides their identity with the username and password. In wireless networks, mutual authentication should be used where the network authenticates the Client and the Client to authenticate the network. This prevents fake devices from disguising themselves as network devices to access important data on wireless clients.
The 802.11 wireless LAN standard does not have intelligent validation, so the industry standard has adopted 802.1x protocol for its validation. 802.1x offers a way to control port-based network access, which uses EAP (Extensible Authentication Protocol) and RADIUS server. 802.1x does not provide a specific validation protocol but specifies EAP in supporting the number of authentication protocols such as CHAP-MD5, TLS and Kerberos. EAP can be extended so new authentication protocols can be supported as in later versions. EAP is provided to operate on Point-to-Point (PPP) protocol; It is compatible with other data link layer protocols (such as Token Ring 802.5 or Wireless LANs 802.11) EAP Over LANs (EAPOL) has been developed. The final confirmation model is shown in the figure below:
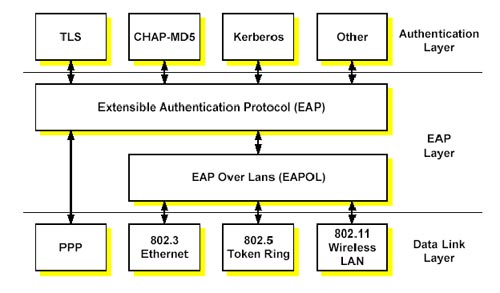
Confirmation model
802.1x EAP-TLS is used in high security and native field models. Exchange of EAP-TLS messages provides mutual validation, handshake of the encryption protocol and the exchange of security keys between a wireless client and the network. EAP-TLS is a technique that provides dynamic encryption keys for users and sessions. This greatly improves and overcomes many weaknesses in wireless networks.
The following figure shows a sequence of events that occur when a Client is authenticated by EAP-TLS 802.1x. Two digital certificates are required here: one on RADIUS server (eg EAS) and one on the Wireless Client. Note that wireless access is provided until the successful validation and dynamic WEP keys have been set.
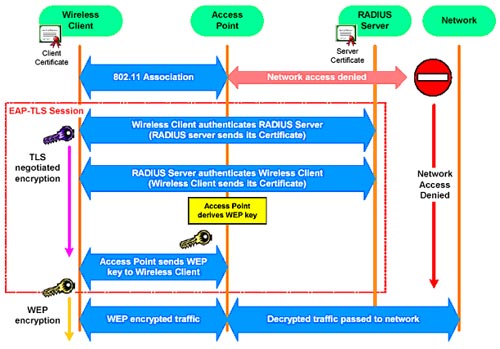
Confirm EAP-TLS 802.1x
802.1x EAP-TLS with EAS in Controller Mode is shown in Figure 8. Wireless client with digital certificate (pre-installed). Wireless client communicates with EAS via AP. All three components (Wireless client, AP and EAS) support the EAP-TLS 802.1x process. Wireless clients can use Windows XP (built to support 802.1x EAP-TLS) or Windows 98 / Me / 2000 using Madge Wireless LAN Utility (WLU). When verified, user data can also be used for EAS that has been configured in Gateway Mode.
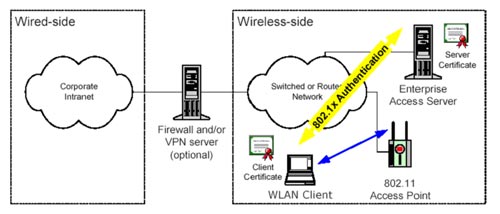
802.1x EAP-TLS in Controller Mode
Pham Van Linh
Email: vanlinh@quantrimang.com