Why does Chrome ask users to update or delete incompatible applications?
Many applications running on Windows platforms, such as antivirus software, put code into Chrome to modify the operation of this application.This leads to more frequent browser crashes, so Google is taking corrective actions by blocking code injection applications into Chrome.
Why do some applications inject code into Chrome?
Some applications put code into other running applications to modify the application's behavior. On Windows, this technique is called code injection, has existed for a long time and is used by many Different types of applications, from anti-malware tools to dangerous malware.This concept is also commonly referred to as DLL injection on Windows.

In other words, these applications will put code into Chrome to modify Chrome's behavior.Assuming a security program wants to add some additional checks to Chrome's browsing feature or some malware may want to track your browsing, they will send the code to your Chrome. .
Even if applications are using this code injection feature with good intentions, they can still cause problems for the browser because these code will interfere with Chrome's code.Chrome developers do not know exactly how these 3rd party codes will work.As Chrome developer, Chris H. Hamilton said: 'These types of code injection software appear rampant on Windows platforms and cause significant problems for maintaining stable operation of Chrome (crashes) '.
When will Chrome completely block these codes?

Google has officially announced plans to prevent this phenomenon in November 2017. The giant technology firm also noted that Windows users that contain code injection software in Chrome are at risk of encountering these errors. Chrome is 15% higher than usual.Google says there are better blocking techniques for applications that require this type of code injection function, such as installing extensions for Chrome browsing, which will use Chrome's Native Messaging to Communicate with another program on the system.
In its official announcement, Google also said Chrome 69 will start blocking all code injection behavior into Chrome from September 2018. However, according to the test, the beta version of Chrome 69 only shows the scene. notice that the 3rd party application's code may have been sent to Chrome when your browser has trouble, and does not support blocking the code injection.Chrome developers regularly test new features in this way.In other words, they will introduce different features to different Chrome users to see how people respond, so maybe some users have seen similar warnings right from the session. Chrome version 68.
Google has announced plans to block all code injection behavior of applications starting from January 2019. According to Hamilton, Google still plans to block these codes from afar, when warnings will stop appearing. because Chrome will silently block the application's code injection efforts.Microsoft Edge is the first browser on Windows to make these changes.Microsoft Edge has been blocked from code injection since 2015.
Are applications really causing problems on Chrome?
Even if Chrome gives you warnings about incompatible applications it is unlikely that these applications will cause the problem, unless your browser has an error.
Hamilton noted that Chrome merely gave warnings about any software that uses code injection without giving 'valuable evaluations'.The software you have installed may still work correctly and does not cause any problems, but Google simply doesn't like code injection and is trying to block it.
How to check incompatible applications
If Chrome encounters a problem, you will see a message asking you to Update or deleteincompatible applications(Update or remove incompatible applications)or Update or delete problematic applications (Update or remove problem applications).These notifications will then take you to a list of applications that use the code injection feature on your system.
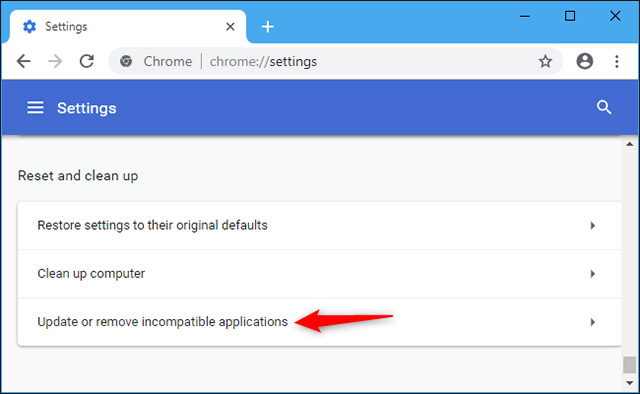
Alternatively, you can access this list even before Chrome has a problem by visiting Menu> Settings> Advanced, scrolling to the bottom of the screen and clicking 'Update or delete incompatible apps 'in the reset and cleaning section.If you don't see this option here, then there is no application on your system that is injecting code into Chrome.
You can also enter the addresses chrome: // settings / IncompatibleApplications into the search address bar and press Enter.If you do not see a list of incompatible applications, you have not installed any incompatible applications.
(Note: This option only started to appear from Chrome 69. The stable version of Chrome 69 is scheduled to be released on September 4, 2018).
Chrome will list all applications that use the code injection feature that you have installed.There will be many anti-virus applications, including Avast, AVG, Bitdefender, Emsisoft, Eset, IObit, Norton Security, Malwarebytes and WinPatrol that appear on this list.Other applications that will appear in this list include Acronis True Image, Dropbox and RocketDock.Overall this list may be surprising to many, but any application that uses the code injection feature will also appear in the list.
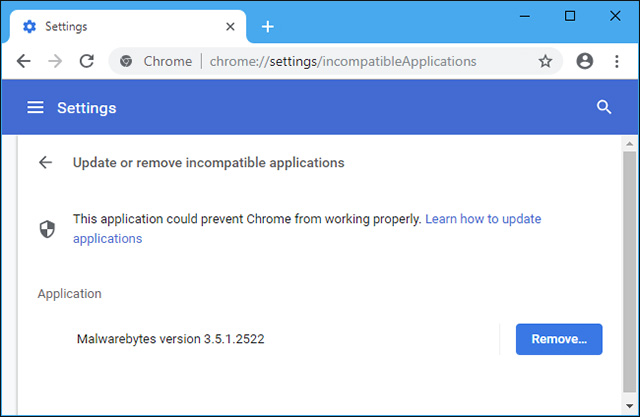
The ' Remove ' button next to each application will take you to the Settings or Control Panel window, where you can uninstall these applications if you want.
If you do not encounter any problems with Chrome, you do not need to uninstall applications in the list, anyway, Google will block the code injection feature of that application after a few months.

Google is clearly hoping that application developers will update their applications to no longer depend on code injection techniques.After all, developers certainly don't want Chrome to encourage people to uninstall their applications.Either way, these errors won't last long.
However, removing software using code injection is probably not a big loss.As Chrome developers have said, code injection contributes to the problem, and it is best not to have many problems occurring on your browser.
see more
- How to select and move multiple tabs simultaneously on Chrome
- How to fix SSL connection errors on Chrome and Firefox
- To speed up Chrome browser, apply these tricks
- How is Chromium and Chrome different?