What are files and folders in the computer?
This article helps beginner computer users have more knowledge to access and use the computer in the best way. Let's find out "What are the files and folders on the computer?"
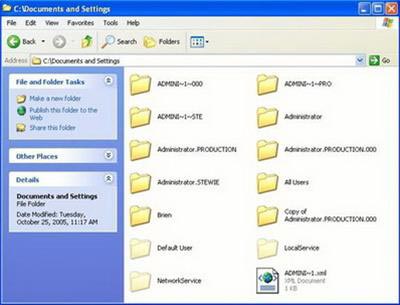
1. What is a file? (File)
a) Concept:
File (File) is a collection of related information together stored on external memory. Specific files are programs and data stored on disk. To distinguish between files , each file has a name.
b) File naming rules: The file name looks like this.
- Where the main name of the file (file name) is required.
- Extensions are used to define file types and may or may not.
- The file extension is separated by a name by a period (.)
For example: 1.xls Quyet (EXCEL file), Tong-ket-quy1-2004.doc, Turbo.exe
Attention :
- Characters cannot be used to name files as / *? <>;
- Files with extensions of EXE, COM, BAT are usually program files.
- Files with the extension SYS are usually system files containing information related to hardware, device declaration, etc.
- Files with extensions of DOC, TXT, HTM are usually text files.
- PAS, PRG, C file extensions are source program files of PASCAL, FOXPRO, C.
In the main name or file extension can use * or? to refer to a file family instead of a file.
- The * character represents an arbitrary group of characters from the position of *.
- Character ? Represents an arbitrary character at the position of?.
For example: * .PAS is a group of files with the extension PAS , and the main name is optional. DATA? .DOC is the name of the file with an arbitrary 5th character, it is a group of files with names such as: DATA1.DOC, DATA2.DOC, DATAT, .
- MS-DOS and Windows reserved the following names for some peripheral devices, do not use these names for the file name.
Reserved name CON device Keyboard, monitor (Console) LPT1 (PRN) Parallel Port 1 (Parallel printer 1) LPT2, LPT3Parallel Port 2,3 (Parallel printer 2, 3) COM1 (AUX) Serial Port 1 (Serial port 1) COM2 Serial Port 2 (Serial port 2) CLOCKS NUL 's clock Dummy Device clock
2. What is a directory? (Folder / Directory)
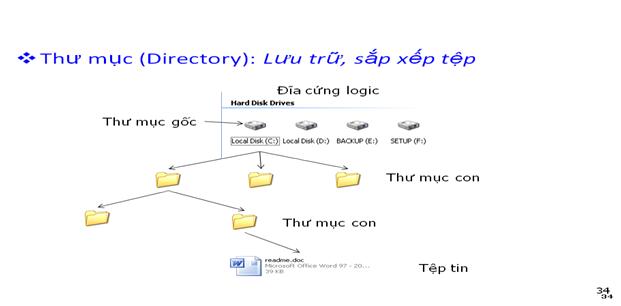
- A folder is a formatted partition on disk to store systematic files. Users can divide a disk into separate areas, each of which can be a storage of certain software or individual files of each user . Each area is called a directory .
- Each disk on the machine corresponds to a directory and is called the root directory (Root Directory) . The root directory may contain files or subdirectories (Sub Directory). Each subdirectory may contain other files or subfolders . This structure is called a directory tree.
- The name of the directory (Directory Name) is set according to the naming rules of the file, usually the directory name does not place the extension.
- The root directory is the highest directory organized on the disk and is created during formatting the disk using the Format command, so we cannot delete this directory.
- Current directory (Working Directory) is the directory in which we are currently selecting or working.
- Empty Directory (Empty Directory) is a directory in which does not contain files or subfolders.
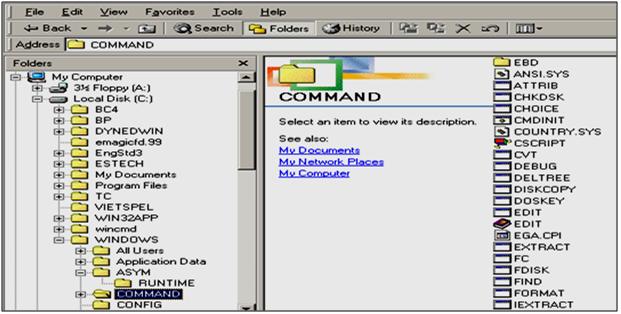
For example: According to the structure diagram of the directory tree above, we see:
- C root folder : contains folders BC4, BP, DYNEDWIN, .
- In sub-level directory 1 WINDOWS contains sub-folders ALL USERS, APPLICATION DATA, .
- In level 2 subdirectory COMMAND contains sub-level 3 sub-directory EBD and files ANSI.SYS, ATTRIB.EXE,…
3. Path (Path):
- Once there is a folder organization on the disk, it's easier to manage the files . However, when the user wants to access an object (a file or a subfolder), it is not simply a matter of naming it (since there may be multiple files or subfolders with the same name on the different folders) that must be very clear about the location of the object to access.
For example : The location of the ANSI.SYS file is fully defined as follows:
C: WINDOWSCOMMANDANSI.SYS
Where : Drive letter is C, folder name is WINDOWS , COMMAND . The file name to access is ANSI.SYS.
Path: A string of folders that we need to go through to get to the file we are using . In the path the directory names are separated by a slash (left slash), where the folder right after is the child of the folder immediately preceding it.
For example:
- C: WINDOWSASYMRUNTIME is the path to the RUNTIME folder in the directory
C: WINDOWSASYM.
- C: WINDOWSCOMMANDANSI.SYS is the path to the ANSI.SYS file in the C: WINDOWSCOMMAND directory .
You should read it
- How to extract a file or folder from a TAR or TAR.GZ file
- How to synchronize files and folders on Linux
- Instructions for setting password to protect files and folders in Windows
- Manage files and folders in Python
- How to Create and Delete Files and Directories from Windows Command Prompt
- File Management in Unix / Linux
 How to insert comments in Excel
How to insert comments in Excel 10 tips for using Windows XP
10 tips for using Windows XP Quickest Tips to Copy Data In Windows with FastCopy
Quickest Tips to Copy Data In Windows with FastCopy Private Annotations, a new feature is about to be added on Microsoft Word
Private Annotations, a new feature is about to be added on Microsoft Word Tips for adding in Excel you need to know
Tips for adding in Excel you need to know How to Use Solver in Microsoft Excel
How to Use Solver in Microsoft Excel