Let's Encrypt - Create a free SSL certificate for 'poor people'
What is SSL? What is Let's Encrypt? If you make a website for money, then read this article.
Before going into Let's Encrypt, you need to know what SSL is, its importance to the website, why "poor people" still need SSL for their website?
Specifically: What is SSL? Is SSL important to the website?
At this point, by default, you understand SSL well and are looking for free SSL for your website, so it's time to know about Let's Encrypt.
What is Let's Encrypt?
Let's Encrypt is a free, automated SSL certificate provider that works for the benefit of the community. It is managed by Internet Security Research Group (ISRG).
Let's Encrypt provides website administrators with a digital certificate required to activate HTTPS (SSL or TLS) for their website, completely free of charge, and in the most friendly way possible. All based on the goal of creating a secure, private and respectful Web environment.
Let's Encrypt provides SSL certificate of Domain Validation, ie after installing, your website will have a green lock in the address bar of the browser, when users access.
- What types of SSL Certificates are there?

Benefits of using Let's Encrypt
- Free: Just own a domain name, you can use Let's Encrypt to get a trusted certificate without spending a penny.
- Automatic: The software runs on Let's Encrypt web server that can be interacted to get a certificate quickly, safely configured to be ready to use and automatically renewed when needed.
- Safety: Let's Encrypt will act as a platform to promote the best TLS, both on the CA side (Certificate Authority) and help website operators secure the server properly.
- Transparency: All certificates issued or revoked will be publicly recorded and anyone can check.
- Unrestricted: Automatic release and renewal protocols will be published as a public standard and others may apply.
- Let's Encrypt : Like other basic Internet protocols, Let's Encrypt strives to benefit the community and is not under the control of any organization.
How does Let's Encrypt create free SSL certificate?
Let's Encrypt's goal and the ACME protocol is to set up HTTPS server and let it automatically get reliable certification in the browser without any human intervention. This is done by running a certificate manager on the web server.
To understand how Let's Encrypt technology works, let's find out the process of setting up https: .// example.com/ with the certificate manager for Let's Encrypt support.
There are 2 steps in this process. First, the manager will prove to the CA that the web server is controlling a domain name. After that, the manager can request, renew or revoke the certificate for that domain name.
Domain name verification:
Let's Encrypt determines server administration rights by public key. For the first time, management software for Let's Encrypt interaction, it created a new key pair and proved Let's Encrypt CA that the server is controlling one or several domains. This is similar to the traditional CA process that creates an account and adds a domain name to that account.
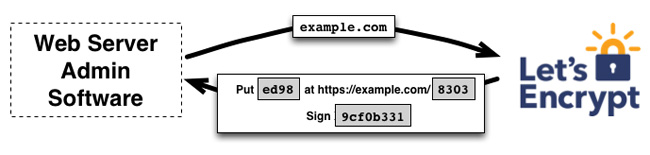
To start this process, Let's Encrypt CA request manager provides the necessary information to prove that it is controlling example.com. Let's Encrypt will review and make requests, you need to complete it to prove you have domain control. You have two options:
- Provide a DNS record under the name example.com
- Provide an HTTP source under a URL known on https://example.com/
After completing the requirements, Let's Encrypt will give the certificate manager a private key pair to prove that it controls the key pair.
At this point, the manager places a file on the path specified on the website https://example.com. The manager also signs a private key, after it will notify the CA that it has completed validation.
The next job of CA is to check if the requests are satisfied. CA verifies the signature, tries to download the file from the web server and make sure it obtains the desired content.
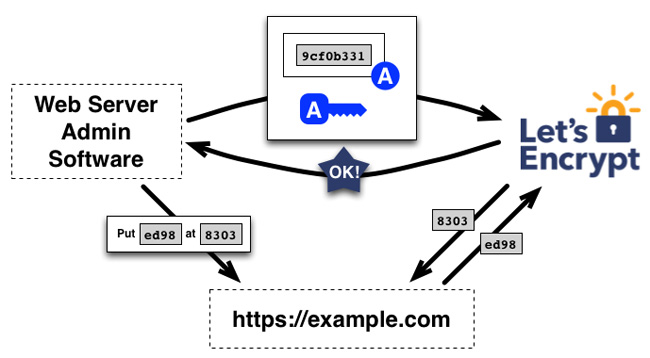
If the signature is valid, the requests have been met, the manager is identified by the authorized public key as the certificate manager for example.com. The key pair that the manager uses for example.com is called "authorization key pair".
Certification and withdrawal
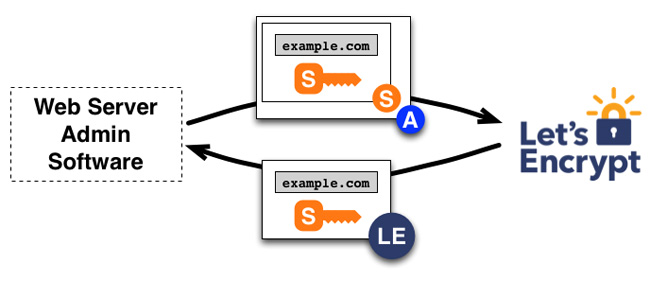
When the manager has obtained the "authorization key pair", the request, renewal, revocation of SSL certificate becomes simple, just send the certificate of management certificate and sign with the authorization key pair.
To obtain a domain certificate, the PKCS # 10 Certificate Signing Request manager, requires Let's Encrypt CA to issue a certificate for example.com with a specified public key. As usual, CSR includes signatures with private keys corresponding to public keys in CSR. The manager also signed CSR with the authorization key for example.com so Let's Encrypt CA knew it was authorized.
When Let's Encrypt CA receives the request, it will verify both signatures. If everything looks good, it gives a certificate to example.com with the public key from CSR and returns it to the manager.
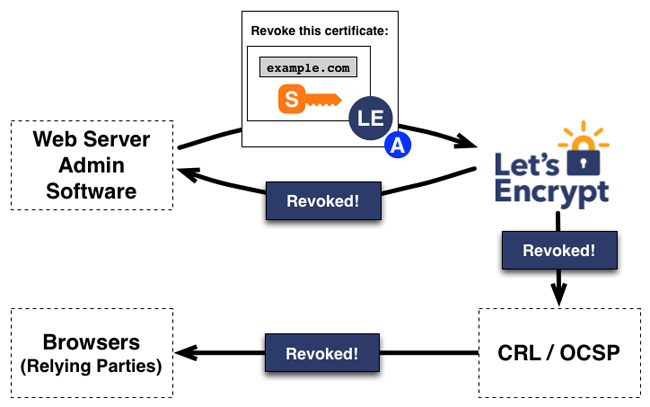
Certificate revocation works in the same way. The manager signing a request to revoke the authorization key pair for example.com and Let's Encrypt CA verifies that the request is indeed authorized. Then, it will export certificate revocation information to regular recovery channels (such as CRL, OCSP), based on third parties, such as browsers so that they do not accept the revoked certificate.
Software for managing SSL certificates on Windows servers - Certify
Let's Encrypt is a free service to create trusted SSL certificates for your domain name, but most tools are just command line. If you are using a Windows server, install Certify. This software provides a simple user interface to manage SSL certificates. Just turn on Certify on the IIS web server to get started.
Download Certify for free
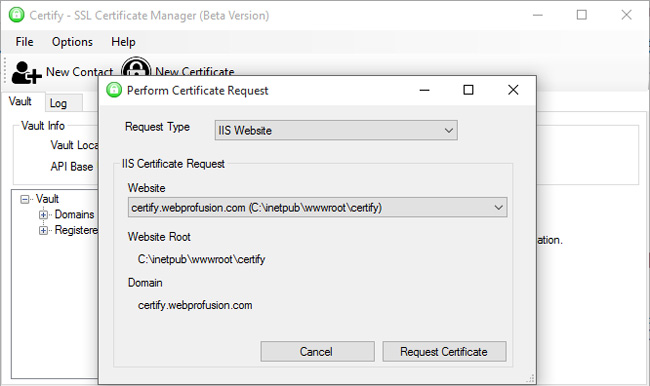
Main features of Certify:
- Easy to install
- Easily create new certificate, authorization, and certificate requests
- Manage certificates and related information
- The IIS Lockdown feature makes it easy to track the best SSL for disabling unsafe protocols and passwords.
Hopefully the information in this article will be helpful to you as a web site to earn extra income as well as other website administrators.
Also you can refer to:
- How to host different SSL on an IP address using IIS 8 SNI?
- How to view SSL certificate details on Chrome browser?
You should read it
- ★ Learn about DNS Over HTTPS
- ★ Let's Encrypt expires root certificate, many devices and websites have problems accessing it
- ★ Instructions for setting up HTTPS for simple websites
- ★ What kind of SSL certificate does your website need?
- ★ Activate the mechanism to automatically encrypt websites into Firefox