Instructions on how to use PowerShell in Windows Server 2012
What is PowerShell?
Windows PowerShell is a command-line shell language interpreter and scripting language specifically designed for system administrators. It is similar to Bash Scripting in Linux. Built on the .NET Framework, Windows PowerShell helps IT professionals control and automate Windows operating system administration tasks as well as applications running on Windows Server environments.
PowerShell commands are called cmdlets, which allow computer management with the command line. The tools in PowerShell allow access to data warehouses such as Registry and Certificate Store as easily as accessing file systems.
In addition, PowerShell has a rich display parser and a fully developed scripting language. Simply put, you can complete all tasks like working with the user interface and more.
The PowerShell icon can be found in the taskbar and in the Start menu. You can open it by clicking on this icon.
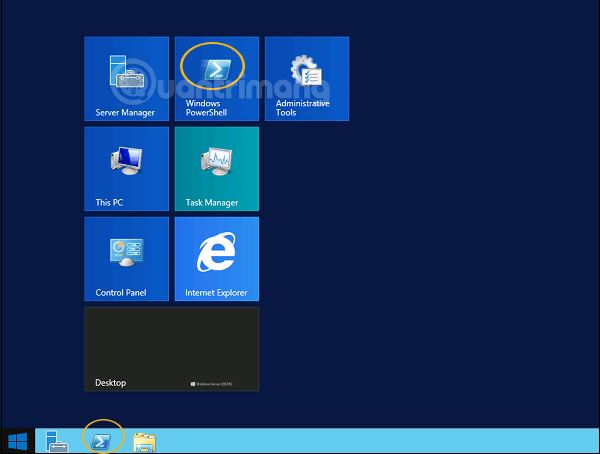
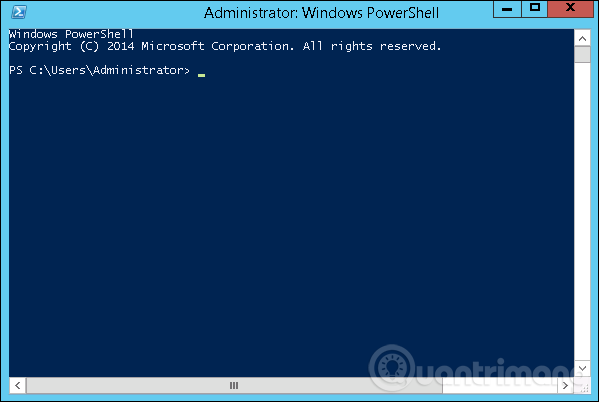
When the screen below appears, Windows PowerShell is ready to work.
The latest version of PowerShell is 5.0 and to check which version of PowerShell is installed on the server, you only need to enter the command:
:$PSVersionTable In the results returned, look for the PSVersion line in the Name column and look at the corresponding row in the Value column. As shown below, we see the version of PowerShell currently installed as 4.0.

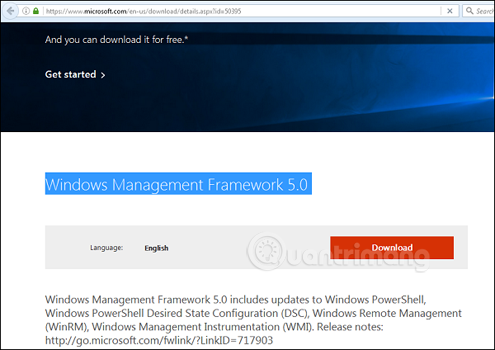
To update to the latest PowerShell with more cmdlets, you must download Windows Management Framework 5.0 and install it.
Learn about PowerShell ISE
Windows PowerShell Integrated Scripting Environment (ISE) is a host application for Windows PowerShell. In PowerShell ISE, you can run the command line, write, test and debug scripts in a graphical user interface with multi-line editing, tab completion, syntax coloring, make selections, help contextual and support for right-to-left language.
You can use menu objects or keyboard shortcuts to perform many of the same tasks as you do in the Windows PowerShell console. For example, when debugging a script in PowerShell ISE, to set a line break in the script, simply right-click on the code, and select Toggle Breakpoint.
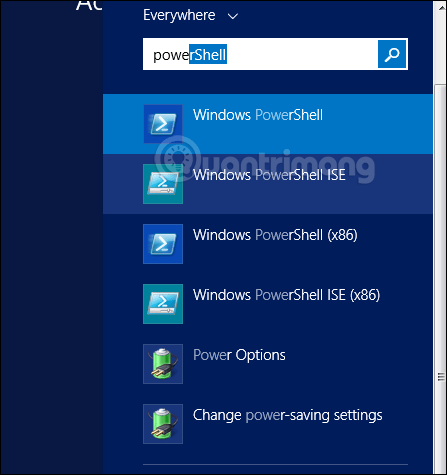
To open PowerShell ISE, just go to Start > Search > and enter PowerShell , in the search results that appear, you just need to click PowerShell ISE as shown:
The other way is to click the down arrow as shown below:
It will list all applications installed on the server and you just need to click on Windows PowerShell ISE.

PowerShell ISE interface will look like this:
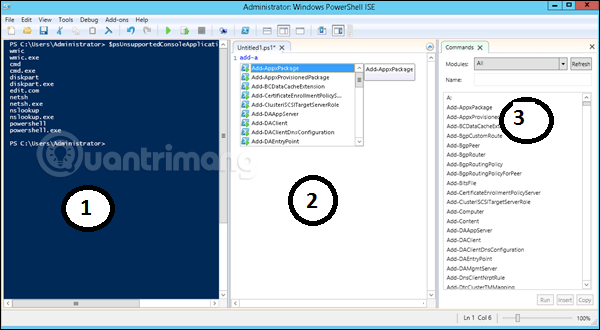
It has 3 parts, 1 is PowerShell Console, 2 is Scripting File, 3 is Command Module. While creating the script, you can run it directly and see the result:
Basic commands in PowerShell
There are many PowerShell commands and it is difficult to list them all in this tutorial, we will only focus on PowerShell's basic and most important commands.
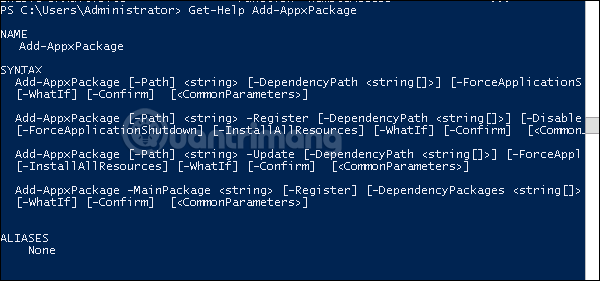
The first is the Get-Help support command, explaining to you how to create commands and its parameters.
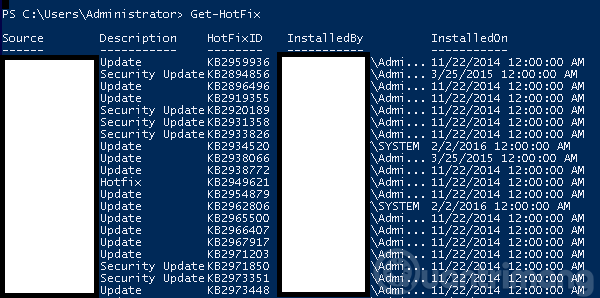
To get the update list, use the Get-HotFix command and to install a hot fix, say KB2894856, enter the following command: Get-HotFix -id kb2894856 .
Previous lesson: Install Role, configure role on Windows Server 2012