Test SQL Server with Windows PowerShell - Part 5
 Test SQL Server with Windows PowerShell - Part 1
Test SQL Server with Windows PowerShell - Part 1
 Test SQL Server with Windows PowerShell - Part 2
Test SQL Server with Windows PowerShell - Part 2
 Test SQL Server with Windows PowerShell - Part 3
Test SQL Server with Windows PowerShell - Part 3
 Test SQL Server with Windows PowerShell - Part 4
Test SQL Server with Windows PowerShell - Part 4
Muthusamy
Network Administration - Part 1 of this series introduced the first check on SQL Server - ping a host. Part 2 is an introduction to how to check all Windows services related to SQL Server, part 3 is how to check hardware and software information, part 4 is an introduction to collecting information. about network card and hard drive from server. In this part 5, we will check whether we can connect to SQL Server and see if we can query some properties related to SQL Server.
Step 1
Type or copy and paste the following code into C: CheckSQLServerCheckinstance.ps1 file.
function checkinstance (
[string] $ servername
)
{
$ SqlConnection = New-Object System.Data.SqlClient.SqlConnection
$ SqlCmd = New-Object System.Data.SqlClient.SqlCommand
$ SqlAdapter = New-Object System.Data.SqlClient.SqlDataAdapter
$ DataSet = New-Object System.Data.DataSet
$ SqlConnection.ConnectionString =
"Server = $ servername; Database = master; Integrated Security = True"
$ SqlCmd.CommandText = "
create table #serverproperty (varchar (100) property,
value varchar (100))
insert into #serverproperty values
('MachineName', convert (varchar (100),
SERVERPROPERTY ('Machinename'))))
insert into #serverproperty values
('Servername', convert (varchar (100),
SERVERPROPERTY ('ServerName'))))
insert into #serverproperty values
('InstanceName', convert (varchar (100),
SERVERPROPERTY ('ServerName'))))
insert into #serverproperty values
('Edition', convert (varchar (100), SERVERPROPERTY ('Edition')))
insert into #serverproperty values
('EngineEdition', convert (varchar (100),
SERVERPROPERTY ('EngineEdition'))))
insert into #serverproperty values
('BuildClrVersion', convert (varchar (100),
SERVERPROPERTY ('Buildclrversion'))))
insert into #serverproperty values
('Collation', convert (varchar (100), SERVERPROPERTY ('Collation')))
insert into #serverproperty values
('ProductLevel', convert (varchar (100),
SERVERPROPERTY ('ProductLevel'))))
insert into #serverproperty values
('IsClustered', convert (varchar (100), SERVERPROPERTY ('IsClustered')))
insert into #serverproperty values
('IsFullTextInstalled', convert (varchar (100), SERVERPROPERTY
('IsFullTextInstalled'))))
insert into #serverproperty values
('IsSingleuser', convert (varchar (100),
SERVERPROPERTY ('IsSingleUser'))))
đặt nocount trên
select * from #serverproperty
drop table #serverproperty
"
$ SqlCmd.Connection = $ SqlConnection
$ SqlAdapter.SelectCommand = $ SqlCmd
$ SqlAdapter.Fill ($ DataSet)
$ DataSet.Tables [0]
$ SqlConnection.Close ()
}
Step 2
Type or copy and paste the following code into the file C: CheckSQLServerCheckconfiguration.ps1.
function checkconfiguration (
[string] $ servername
)
{
$ SqlConnection = New-Object System.Data.SqlClient.SqlConnection
$ SqlCmd = New-Object System.Data.SqlClient.SqlCommand
$ SqlAdapter = New-Object System.Data.SqlClient.SqlDataAdapter
$ DataSet = New-Object System.Data.DataSet
$ SqlConnection.ConnectionString = "Server = $ servername; Database = master; Integrated Security = True"
$ SqlCmd.CommandText = "
exec master.dbo.sp_configure 'show advanced options', 1
reconfigure
"
$ SqlCmd.Connection = $ SqlConnection
$ SqlAdapter.SelectCommand = $ SqlCmd
$ SqlAdapter.Fill ($ DataSet)
$ SqlCmd.CommandText = "
đặt nocount trên
create #config table (varchar (100) name, bigint minimum, maximum bigint, config_value bigint, run_value bigint)
insert #config exec ('master.dbo.sp_configure')
đặt nocount trên
select * from #config as mytable
#config drop table
"
$ SqlCmd.Connection = $ SqlConnection
$ SqlAdapter.SelectCommand = $ SqlCmd
$ SqlAdapter.Fill ($ DataSet)
$ SqlConnection.Close ()
$ DataSet.Tables [0] .rows
}
Step 3
Attach to the file C: CheckSQLServerCheckSQL_Lib.ps1 the following code.
../checkinstance.ps1
../checkconfiguration.ps1
Now file C: CheckSQLServerCheckSQL_Lib.ps1 has pinghost, checkservices, checkhardware, checkOS, checkHD, checknet, checkinstance and Checkconfiguration as shown below.
#Source all the relate to functions CheckSQL
. ./PingHost.ps1
. ./checkservices.ps1
. ./checkhardware.ps1
. ./checkOS.ps1
. ./checkHD.ps1
. ./checknet.ps1
. ./checkinstance.ps1
../checkconfiguration.ps1
Note: This CheckSQL_Lib.ps1 file will be updated with the source from the new script file, such as checkinstance.ps1 and checkconfiguration.ps1
Step 4
Append to the file C: CheckSQLServerCheckSQLServer.ps1 the following code.
Write-host "Checking Instance property Information ."
Write-host "....."
checkinstance $ instancename
Write-host "Checking Configuration information ."
Write-host "......."
checkconfiguration $ instancename
Now the file will have both checkinstance and checkconfiguration scenarios as shown below. We have added some write-host commands to display the entire process. You should also keep in mind that we have added $ instancename as an additional parameter to the checksqlserver script.
#Objective: To check various status of SQL Server
#Host, instances and databases.
#Author: MAK
#Date Written: June 5, 2008
param (
[string] $ Hostname,
[string] $ instancename
)
$ global: errorvar = 0
. ./CheckSQL_Lib.ps1
Write-host "Checking SQL Server ."
Write-host "...."
"Write-host"
Write-host "Arguments accepted: $ Hostname"
write-host "...."
Write-host "Pinging the host machine"
write-host "...."
pinghost $ Hostname
if ($ global: errorvar -ne "host not reachable")
{
Write-host "Check windows services on the host related to SQL Server"
write-host "........ ... "
checkservices $ Hostname
Write-host "Checking hardware Information ."
Write-host "......"
checkhardware $ Hostname
Write-host "Checking OS Information ."
Write-host "....."
checkOS $ Hostname
Write-host "Checking HDD Information ."
Write-host "....."
checkHD $ Hostname
Write-host "Checking Network Adapter Information ."
Write-host "......."
checknet $ Hostname
Write-host "Checking Configuration information ."
Write-host "......."
checkconfiguration $ instancename | format-table
Write-host "Checking Instance property Information ."
Write-host "....."
checkinstance $ instancename | format-table
}
Note: This CheckSQLServer.ps1 file will be updated with new conditions and new parameters in later sections of the series.
Loading basically loads the functions listed in the scripts and makes it available during the entire PowerShell session. In this case, we source a scenario, which is sourced from many other scenarios.
Step 5
Now let's execute the script, CheckSQLServer.ps1, by passing 'PowerServer3' host as an argument as shown below.
./CheckSQLServer.ps1 PowerServer3 PowerServer3SQL2008
We will see results as shown below (Figure 1.0).
.
.
.
two digit year cutoff 1753 9999 2049
user connections 0 32767 0
user options 0 32767 0
xp_cmdshell 0 1 0
Checking Instance property Information .
.....
11
value property
-------- -----
MachineName POWERSERVER3
Servername POWERSERVER3SQL2008
InstanceName POWERSERVER3SQL2008
Edition Enterprise Evaluation Edition
EngineEdition 3
BuildClrVersion v2.0.50727
Collation SQL_Latin1_General_CP1_CI_AS
ProductLevel RTM
IsClustered 0
IsFullTextInstalled 1
IsSingleuser 0
.
.

Figure 1.0
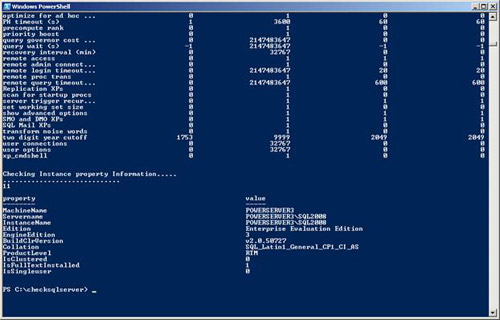
Figure 1.1
Step 6
Now let's execute the script on the machine that doesn't exist as shown below.
./CheckSQLServer.ps1 TestMachine
The results will be as below (refer to Figure 1.3)
Result
Checking SQL Server .
....
Arguments accepted: TestMachine
....
Pinging the host machine
....
TestMachine is NOT reachable

Figure 1.3
Conclude
Part 5 of this series showed you how to access SQL Server instance attributes and its configuration details using Windows PowerShell.
Download the script for this article.