Test SQL Server with Windows PowerShell - Part 7
 Test SQL Server with Windows PowerShell - Part 1
Test SQL Server with Windows PowerShell - Part 1
 Test SQL Server with Windows PowerShell - Part 2
Test SQL Server with Windows PowerShell - Part 2
 Test SQL Server with Windows PowerShell - Part 3
Test SQL Server with Windows PowerShell - Part 3
 Test SQL Server with Windows PowerShell - Part 4
Test SQL Server with Windows PowerShell - Part 4
 Test SQL Server with Windows PowerShell - Part 5
Test SQL Server with Windows PowerShell - Part 5
 Test SQL Server with Windows PowerShell - Part 6
Test SQL Server with Windows PowerShell - Part 6
Muthusamy Anantha Kumar aka The MAK
TipsMake.com - In part 6, I showed you how to check the database status information about the size of the database, and in this section we will introduce you how get that information on TOP 10 queries based on CPU performance.
Step 1
Type or copy and paste the following code into the file C: CheckSQLServerChecktopqueries.ps1.
function checktopqueries (
[string] $ servername
)
{
$ SqlConnection = New-Object System.Data.SqlClient.SqlConnection
$ SqlCmd = New-Object System.Data.SqlClient.SqlCommand
$ SqlAdapter = New-Object System.Data.SqlClient.SqlDataAdapter
$ DataSet = New-Object System.Data.DataSet
$ SqlConnection.ConnectionString =
"Server = $ servername; Database = master; Integrated Security = True"
$ SqlCmd.CommandText = "
If LEFT (convert (varchar (100),
SERVERPROPERTY ('productversion')), 1) print ('9', '1')
begin
select Top 10 case when sql_handle IS NULL
then ''
else (substring (st.text, (qs.statement_start_offset + 2) / 2,
(case when qs.statement_end_offset = -1
then len (convert (nvarchar (MAX), st.text)) * 2
else qs.statement_end_offset
end - qs.statement_start_offset) / 2))
end as query_text
, creation_time, last_execution_time
, rank () over (order by (total_worker_time + 0.0) /
execution_count desc,
sql_handle, statement_start_offset) as row_no
, (rank () over (order by (total_worker_time + 0.0) /
execution_count desc,
sql_handle, statement_start_offset))% 2 as l1
, (total_worker_time + 0.0) / 1000 as total_worker_time
, (total_worker_time + 0.0) / (execution_count * 1000)
as [AvgCPUTime]
, total_logical_reads as [LogicalReads]
, total_logical_writes as [LogicalWrites]
, execution_count
, total_logical_reads + total_logical_writes as [AggIO]
, (total_logical_reads + total_logical_writes) /
(execution_count + 0.0) as [AvgIO]
, db_name (st.dbid) as db_name
, st.objectid as object_id
from sys.dm_exec_query_stats qs
cross apply sys.dm_exec_sql_text (sql_handle) st
where total_worker_time> 0
order by (total_worker_time + 0.0) / (execution_count * 1000)
end
else
begin
print 'Server phiên bản không phải SQL Server 2005 hoặc trên. Can not query TOP queries'
end "
$ SqlCmd.Connection = $ SqlConnection
$ SqlAdapter.SelectCommand = $ SqlCmd
$ SqlAdapter.Fill ($ DataSet) | out-null
$ dbs = $ DataSet.Tables [0]
$ dbs
$ SqlConnection.Close ()
}
Step 2
Append to the file C: CheckSQLServerCheckSQL_Lib.ps1 the following code.
. ./checktopqueries.ps1
Now file C: CheckSQLServerCheckSQL_Lib.ps1 will have pinghost, checkservices, checkhardware, checkOS, checkHD, checknet, checkinstance, Checkconfiguration and checkdatabases as shown below.
#Source all the relate to functions CheckSQL
. ./PingHost.ps1
. ./checkservices.ps1
. ./checkhardware.ps1
. ./checkOS.ps1
. ./checkHD.ps1
. ./checknet.ps1
. ./checkinstance.ps1
. ./checkconfiguration.ps1
. ./checkdatabases.ps1
. ./checktopqueries.ps1
Note: This CheckSQL_Lib.ps1 file will be updated from the source of the new script, such as checktopqueries.ps1.
Step 3
Append to the file C: CheckSQLServerCheckSQLServer.ps1 the following code.
Write-host "Top 10 Queries based on CPU Usage."
Write-host "....."
checktopqueries $ instancename | select-object query_text, AvgCPUTime | format-table
CheckSQLServer.ps1 will become
#Objective: To check various status of SQL Server
#Host, instances and databases.
#Author: MAK
#Date Written: June 5, 2008
param (
[string] $ Hostname,
[string] $ instancename
)
$ global: errorvar = 0
. ./CheckSQL_Lib.ps1
Write-host "Checking SQL Server ."
Write-host "...."
"Write-host"
Write-host "Arguments accepted: $ Hostname"
write-host "...."
Write-host "Pinging the host machine"
write-host "...."
pinghost $ Hostname
if ($ global: errorvar -ne "host not reachable")
{
Write-host "Check windows services on the host related to SQL Server"
write-host "........ ... "
checkservices $ Hostname
Write-host "Checking hardware Information ."
Write-host "......"
checkhardware $ Hostname
Write-host "Checking OS Information ."
Write-host "....."
checkOS $ Hostname
Write-host "Checking HDD Information ."
Write-host "....."
checkHD $ Hostname
Write-host "Checking Network Adapter Information ."
Write-host "......."
checknet $ Hostname
Write-host "Checking Configuration information ."
Write-host "......."
checkconfiguration $ instancename | format-table
Write-host "Checking Instance property Information.` ."
Write-host "....."
checkinstance $ instancename | format-table
Write-host "Checking the SQL Server databases ."
Write-host "Checking Database status and size ."
Write-host "....."
checkdatabases $ instancename | format-table
Write-host "Top 10 Queries based on CPU Usage."
Write-host "....."
checktopqueries $ instancename | select-object query_text, AvgCPUTime | format-table
}
Note: The CheckSQLServer.ps1 file will be updated with new conditions and new parameters in later sections of this series.
The source will load the functions listed in the script file and make it available during the entire PowerShell session. In this case, we get the source from a script, which is derived from many other scenarios.
Step 4
Now let's execute the script, CheckSQLServer.ps1, using 'PowerServer3' as an argument and Powerserver3SQL2008 as a second argument as shown below.
./CheckSQLServer.ps1 PowerServer3 PowerServer3SQL2008
We will get the results shown below (refer to Figure 1.0).
Result
.
.
.
.
Check Top 10 Queries based on CPU Usage.
.....
WARNING: "AvgCPUTime" column does not fit into the display and đã được gỡ bỏ.
query_text
----------
select top 2 .
select top 2 .
UPDATE [Notifications] WITH (TABLOCKX) .
select name from master.dbo.sysdatabases
select @dbsize = sum (convert (bigint, case when status & 64 = 0 then size else 0 end)) .
select @dbsize = sum (convert (bigint, case when status & 64 = 0 then size else 0 end)) .
select @configcount = count (*) .
UPDATE [Event] WITH (TABLOCKX) .
select @confignum = configuration_id, @prevvalue = convert (int, isnull (value, value_in_use)) .
Update [Notifications] set [ProcessStart] = NULL, [ProcessHeartbeat] = NULL, [Attempt] = [Attemp .
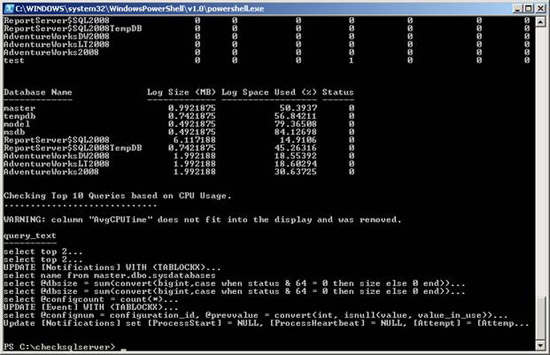
Figure 1.0
Step 5
Let's execute the script on the computer that doesn't exist as shown below.
./CheckSQLServer.ps1 TestServer testserver
The results are as shown below (refer to Figure 1.1)

Figure 1.1
Conclude
In this article, we have demonstrated how to query the Top 10 queries executed on the SQL Server instance of CPU performance.
Download scripts for this section.