How to Use Windows Command Prompt to Run a Python File
Part 1 of 3:
Finding the Python File Path
-
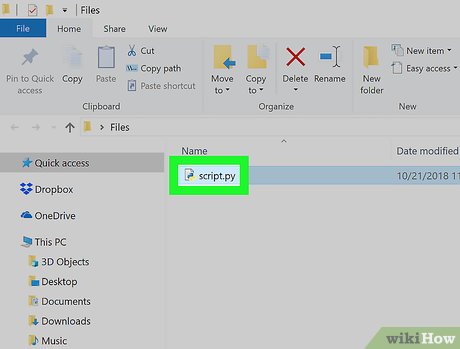
 Go to the Python file's location. Find the Python file that you want to open in Command Prompt.
Go to the Python file's location. Find the Python file that you want to open in Command Prompt.- If you already know the folder path to the Python file you want to open, skip ahead to opening the file in Command Prompt.
-
 Select the Python file. Click once the Python file for which you want to see the folder path.
Select the Python file. Click once the Python file for which you want to see the folder path. -
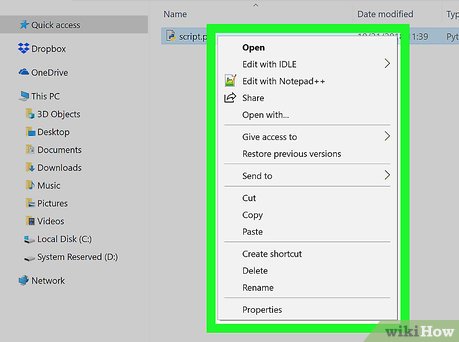
 Right-click the Python file. Doing so prompts a drop-down menu to appear.
Right-click the Python file. Doing so prompts a drop-down menu to appear. -
 Click Properties. It's in the drop-down menu. The properties window will open.
Click Properties. It's in the drop-down menu. The properties window will open. -
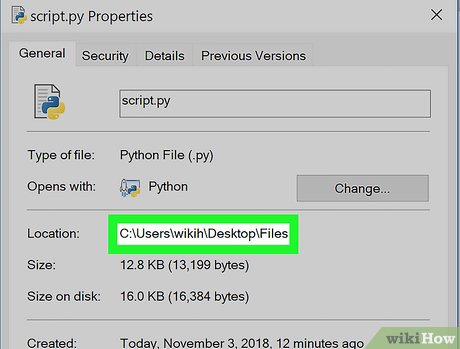
 Note the "Location" value. The folder address (or "path") to the right of the "Location" heading is what you'll need to enter into Command Prompt when switching to the directory in which your Python file is stored.
Note the "Location" value. The folder address (or "path") to the right of the "Location" heading is what you'll need to enter into Command Prompt when switching to the directory in which your Python file is stored.- You can copy the location by highlighting it (click and drag your mouse across the "Location" value) and then pressing Ctrl+C.
Part 2 of 3:
Running a Python File
-
 Open Start. Click the Windows logo in the bottom-left corner of the screen. The Start menu will pop up.
Open Start. Click the Windows logo in the bottom-left corner of the screen. The Start menu will pop up.
-
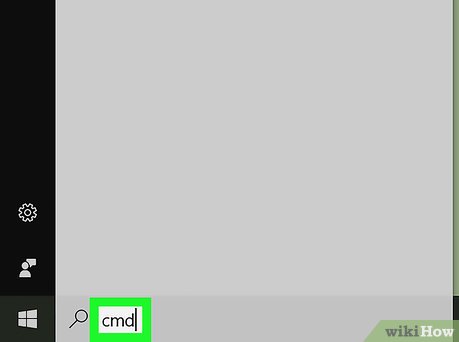
 Search for Command Prompt. Type in cmd to do so.
Search for Command Prompt. Type in cmd to do so. -
 ClickCommand Prompt. It's at the top of the Start menu. Doing so will open Command Prompt.
ClickCommand Prompt. It's at the top of the Start menu. Doing so will open Command Prompt.
-
 Switch to your Python file's directory. Type cd and a space, then type in the "Location" address for your Python file and press ↵ Enter.
Switch to your Python file's directory. Type cd and a space, then type in the "Location" address for your Python file and press ↵ Enter.- For example, to open a Python file in a folder named "Files" on your Desktop, you would enter cd desktop/Files here.
- If you copied the path to the file, you can type in cd and a space and then press Ctrl+V to paste in the path.
-
 Enter the "python" command and your file's name. Type in python file.py where file is your Python file's name.
Enter the "python" command and your file's name. Type in python file.py where file is your Python file's name.- For example, if your Python file is named "script", you would type in python script.py here.
- If your Python file has one or more spaces in its name, you'll place quotation marks around the file name and extension (e.g., python "my script.py").
-
 Press ↵ Enter. Doing so runs your command and opens your Python file via your computer's installed Python program.
Press ↵ Enter. Doing so runs your command and opens your Python file via your computer's installed Python program.- If you encounter an error that says
'python' is not recognized as an internal or external commandafter pressing Enter, you'll need to add Python to the PATH list before retrying this part.
- If you encounter an error that says
Part 3 of 3:
Adding Python to the PATH List
-
 Enable viewing for hidden folders. Since one of the folders that contains your Python installation folder is most likely hidden, you'll have to unhide it before proceeding:
Enable viewing for hidden folders. Since one of the folders that contains your Python installation folder is most likely hidden, you'll have to unhide it before proceeding:- Open File Explorer .

- Click the View tab.
- Check the "Hidden items" box.
- Open File Explorer
-
 Navigate to your Python folder. In some cases, the Python path is "C:Python27"; however, if you've installed the most recent version of Python using the default settings, it's tucked away in a hidden folder. You can copy the proper file path by doing the following:
Navigate to your Python folder. In some cases, the Python path is "C:Python27"; however, if you've installed the most recent version of Python using the default settings, it's tucked away in a hidden folder. You can copy the proper file path by doing the following:- Click This PC on the left side of the File Explorer.
- Double-click your hard drive in the "Devices and drives" section.
- Scroll down and double-click the "Users" folder.
- Double-click the folder with your username on it.
- Scroll down and double-click "AppData".
- Double-click "Local".
- Scroll down and double-click "Programs".
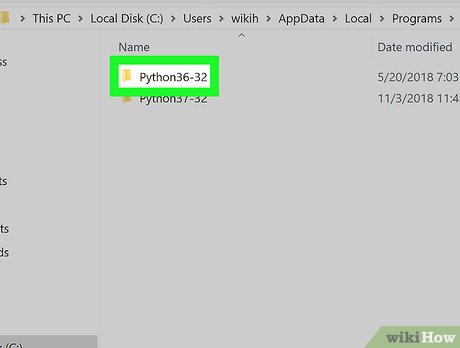
- Double-click the "Python" folder.
- Double-click the Python folder with your preferred version number (e.g., "Python36").
-
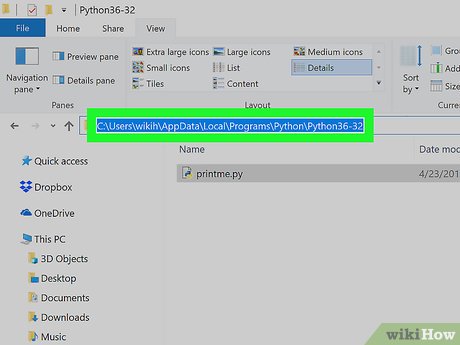
 Copy the path to the Python folder. Click once the address bar at the top of the File Explorer to highlight its contents, then press Ctrl+C to copy the highlighted address.
Copy the path to the Python folder. Click once the address bar at the top of the File Explorer to highlight its contents, then press Ctrl+C to copy the highlighted address. -
 Open the Power User menu. Right-click the Starticon to do so. You should see a pop-up menu appear.
Open the Power User menu. Right-click the Starticon to do so. You should see a pop-up menu appear.
- You can also press ⊞ Win+X to open the Power User pop-up menu.
-
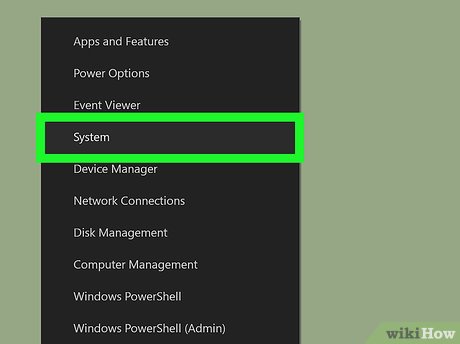
 Click System. It's in the pop-up menu. A new window will open.
Click System. It's in the pop-up menu. A new window will open. -
 Click System info. This is a link in the upper-right corner of the window. Doing so opens the System Information window.
Click System info. This is a link in the upper-right corner of the window. Doing so opens the System Information window. -
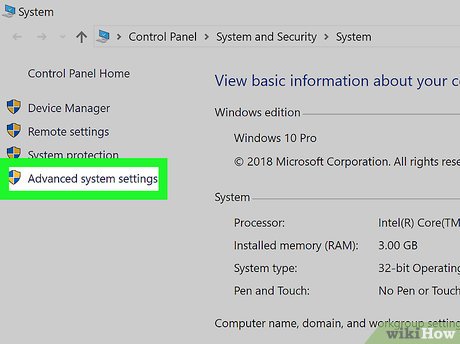
 Click the Advanced system settings link. You'll see this in the upper-left side of the System Information window. Yet another window will pop up.
Click the Advanced system settings link. You'll see this in the upper-left side of the System Information window. Yet another window will pop up. -
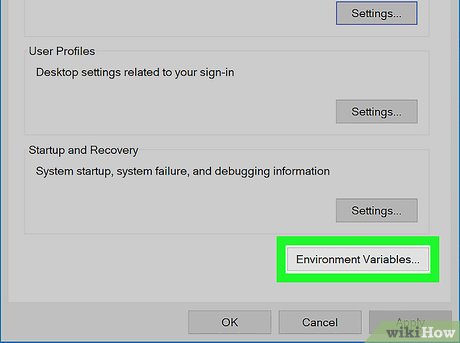
 Click Environment Variables…. It's in the bottom-right corner of the pop-up window.
Click Environment Variables…. It's in the bottom-right corner of the pop-up window. -
 Find the "Path" heading in the "User variables" pane. This window is at the top of the Environment Variables window.
Find the "Path" heading in the "User variables" pane. This window is at the top of the Environment Variables window.- You may have to scroll up or down with your mouse cursor hovering over the "User variables" pane to find the "Path" variable.
-
 Double-click the "Path" heading. Doing so opens a pop-up window.
Double-click the "Path" heading. Doing so opens a pop-up window. -
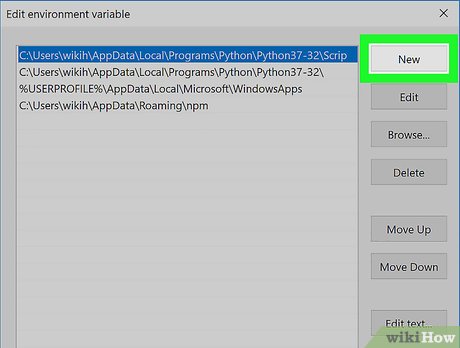
 Click New. It's on the right side of the window. A text field will open in the middle of the window.
Click New. It's on the right side of the window. A text field will open in the middle of the window. -
 Paste in your copied path. Press Ctrl+V to do so. Your copied path will appear in the text field in the middle of the window.
Paste in your copied path. Press Ctrl+V to do so. Your copied path will appear in the text field in the middle of the window. -
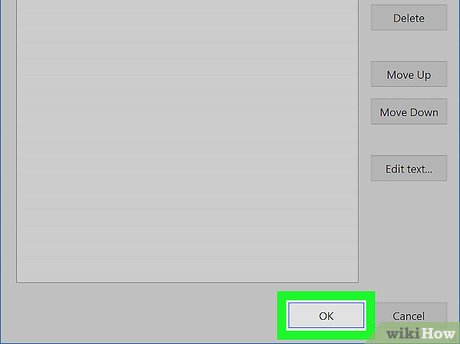
 Click OK on the three open windows. This will save your changes and close the "Path" window, the "Environmental Variables" window, and the "System Properties" window.
Click OK on the three open windows. This will save your changes and close the "Path" window, the "Environmental Variables" window, and the "System Properties" window.
Share by
Lesley Montoya
Update 04 March 2020