How to use ChatGPT API
With the release of the API, OpenAI has opened up the possibility of bringing ChatGPT to everyone. Now you can seamlessly integrate ChatGPT features into your app.
Follow these steps to get started, whether you're looking to integrate ChatGPT into your existing app or develop new ones with it.
1. Get the OpenAI API key
To start using the ChatGPT API, you need to get an API key.
- Register or log in to the official OpenAI platform.
- Once logged in, click the API keys tab on the left.
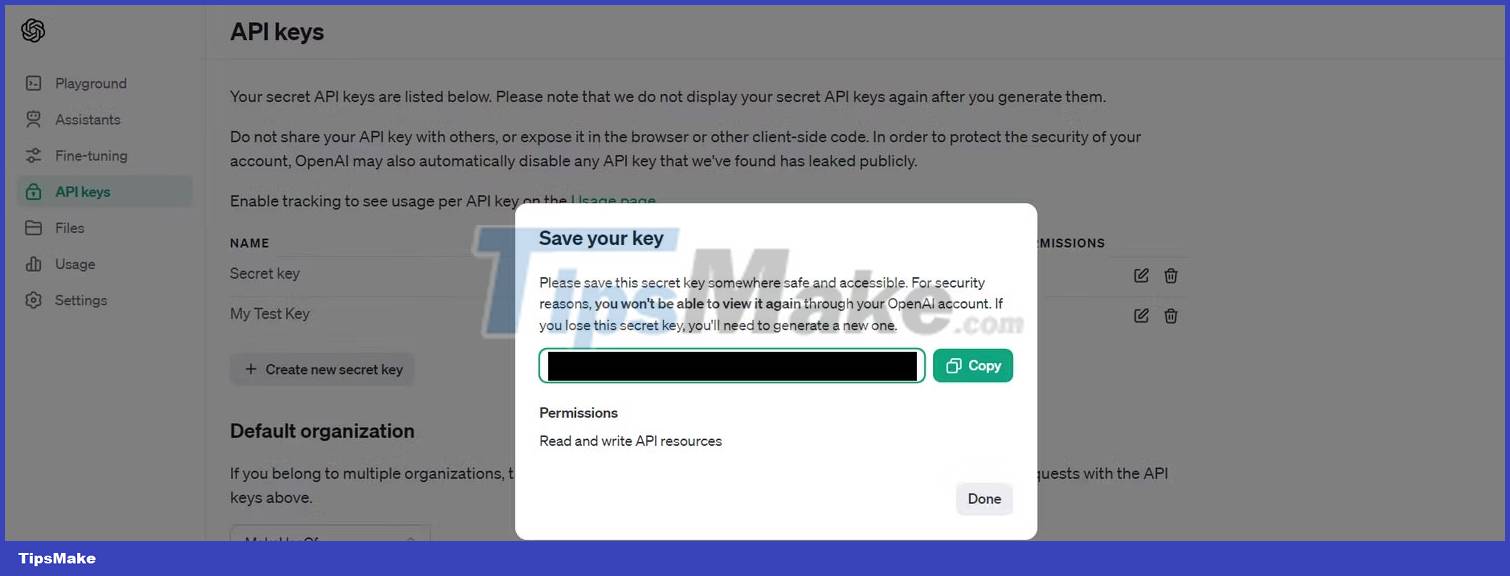
- Next, click the Create new secret key button to generate the API key.
- You will not be able to review the API key, so please copy it and store it in a safe place.
Note: The code used in this project is available in the GitHub repository and can be used for free under the MIT license.
2. Set up the development environment
You can use the API endpoint directly or leverage the openai Python/JavaScript library to start building applications that support the ChatGPT API. This tutorial uses Python and the openai-python library.
To begin:
- Create a Python virtual environment
- Install openai and python-dotenv libraries via pip:
pip install openai python-dotenv
- Create an .env file in the project's root directory to safely store the API key.
- Next, in the same file, set the OPENAI_API_KEY variable with the key value you copied earlier:
OPENAI_API_KEY="YOUR_API_KEY"
Warning: Make sure you don't accidentally share your API key through version control. Add the .gitignore file to your project's root directory and add ".env" to it to ignore the dotenv file.
3. Make a ChatGPT API request
The OpenAI API's GPT-3.5 Turbo, GPT-4, and GPT-4 Turbo are the same models that ChatGPT uses. These powerful models are capable of understanding and generating natural language text and code. GPT-4 Turbo can even process image input, opening the door to a number of uses including image analysis, metric document analysis, and copying text from images.
Please note that the ChatGPT API is a generic term for OpenAI APIs that use GPT-based models, including the GPT-3.5 Turbo, GPT-4, and GPT-4 Turbo models.
ChatGPT API is primarily optimized for chat but also works well for text completion tasks. Whether you want to create code, translate languages, or draft documents, this API can handle it all.
Note: To gain access to the GPT-4 API, a successful payment of $1 or more is required. Otherwise, you may get an error similar to "The model `gpt-4` does not exist or you do not have access to it".
Use the API to complete the conversation
You need to configure the chat model to be ready for API calls. Here is an example:
from openai import OpenAI from dotenv import load_dotenv load_dotenv() client = OpenAI() response = client.chat.completions.create( model = "gpt-3.5-turbo-0125", temperature = 0.8, max_tokens = 3000, response_format={ " type": "json_object" }, messages = [ {"role": "system", "content": "You are a funny comedian who tells dad jokes. The output should be in JSON format."}, {"role" : "user", "content": "Write a dad joke related to numbers."}, {"role": "assistant", "content": "Q: How do you make 7 even? A: Take away the s ."}, {"role": "user", "content": "Write one related to programmers."} ] ) ChatGPT API sends responses in the following format:

You can extract the content from the response as a JSON string using this code:
print(response.choices[0].message.content)
Running this code will produce the following output:

This code illustrates calling the ChatGPT API in Python. Note that the model understands the context ("dad joke") and the type of response (question-and-answer format) we expect, based on the prompts provided to it.
The most important part of the configuration is the messages parameter which accepts an array of message objects. Each message object contains a role and contain. You can use 3 types of roles:
- system sets the context and behavior of the assistant.
- The user gives instructions to the assistant. The end user will typically provide this information, but you can also provide some default prompts to the user in advance.
- assistant can include sample answers.

You can further customize the model's temperature and max_tokens parameters to get the output according to your requirements.
The higher the temperature, the higher the randomness of the output and vice versa. If you want your answer to be more focused and decisive, choose a lower temperature value. And if you want it to be more creative, use a higher value. Temperature values range from 0 to 2.

Like ChatGPT, the API also has a word limit. Use the max_tokens parameter to limit the length of the response. Please note that setting a lower max_tokens value may cause problems as it may interrupt the output mid-stream.
At the time of writing, the gpt-3.5-turbo model has a token limit of 4,096, while the gpt-4's is 8,192. The latest gpt-3.5-turbo-0125 and gpt-4-turbo-preview models have limits of 16,385 and 128,000 respectively.
After high demand from developers, OpenAI introduced a JSON mode that instructs the model to always return a JSON object. You can enable JSON mode by setting reply_format to { "type": "json_object" }. Currently, this feature is only available on the latest models: gpt-3.5-turbo-0125 and gpt-4-turbo-preview.
You can further configure the model using other parameters provided by OpenAI.
Use ChatGPT API to complete text
In addition to multi-turn conversation tasks, the chat completion API (ChatGPT API) also does a great job with text completion. The following example illustrates how you can configure the ChatGPT API for text completion:
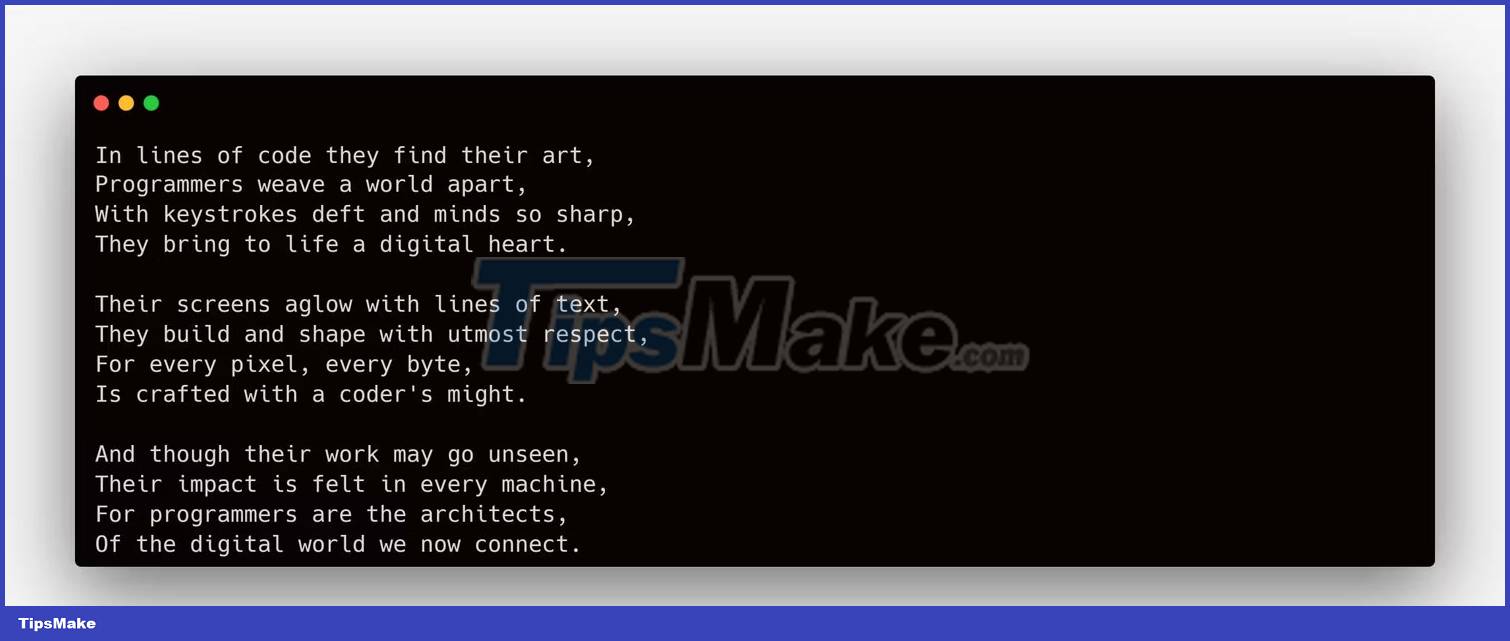
from openai import OpenAI from dotenv import load_dotenv load_dotenv() client = OpenAI() response = client.chat.completions.create( model = "gpt-3.5-turbo", temperature = 0.8, max_tokens = 3000, messages = [ {"role ": "system", "content": "You are a poet who creates poems that evoke emotions."}, {"role": "user", "content": "Write a short poem for programmers."} ] ) print(response.choices[0].message.content) You don't even need to provide the system role and its contents. Providing only user prompts will do the job for you.
messages = [ {"role": "user", "content": "Write a short poem for programmers."} ] Running the above code will create a poem for the programmer, for example: