How to Uninstall Ubuntu Operating System
Uninstall Ubuntu Installed Parallel to Windows

Run the Windows installation disc on your computer, alternatively you can use the Recovery disc (recovery disc). If you don't have an installation disc or recovery disc, you can create a recovery disc in Windows.
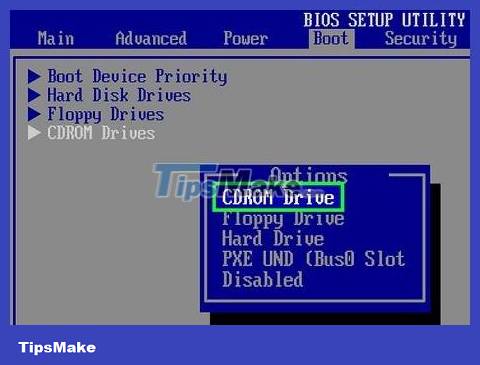
Boot from CD. To boot from the recovery disc, you need to set the BIOS to boot from your CD/DVD drive. When the computer begins to boot, press the BIOS setup key, usually one of the F2, F10, F12, or Del keys. Navigate to the Boot menu and select the CD/DVD drive. Once you've made your selection, save and restart your computer.
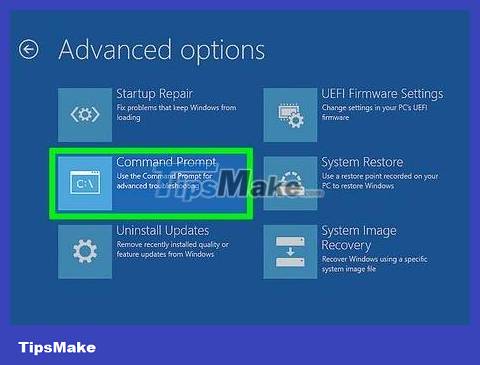
Open Command Prompt. From the Recovery Disc main menu, select the Command Prompt option. If you are using the installation disc, select "Repair your computer" to open Command Prompt.

Edit Master Boot Record. Executing this command, you can remove the parallel boot option when you start the computer, and boot directly into Windows. Enter the following command into Command Prompt:bootrec /fixmbr

Restart the computer. Upon reboot, the Ubuntu option will no longer appear. Instead, you will access Windows directly.

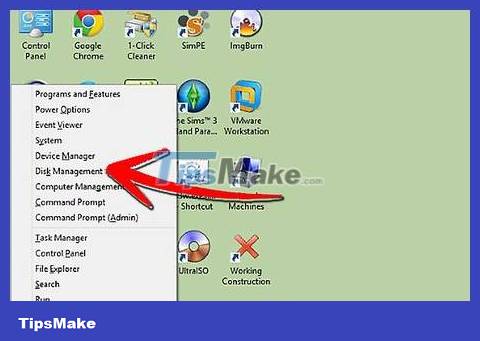
Open Disk Management (Hard drive space management tool). In Windows, it's time to uninstall the old Ubuntu and reclaim hard disk space. Click Start, and right-click Computer/My Computer. Select Manager and then click Disk Management in the left pane of the Computer Management window.
In Windows 8, press the Windows + X key combination and select Disk Management from the menu.
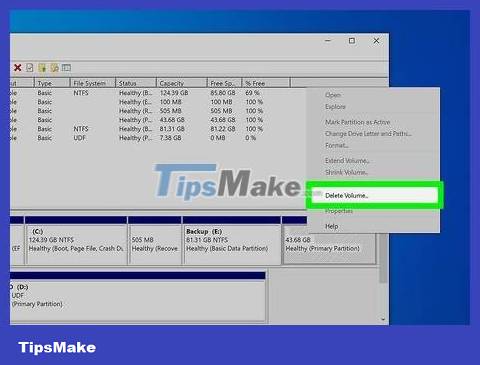
Delete your Ubuntu partition. Right-click the Ubuntu partition and select Delete. Make sure you delete the Ubuntu partition correctly. Once deleted, the partition becomes empty, unallocated space. Right-click your Windows partition and select Extend partition. Select the free space you just created to add to your Windows installation.
Uninstall Ubuntu from Single Boot System

Run the disc of the operating system you want to install on your computer. When Ubuntu is the only operating system on your computer, you can remove it by using another operating system installation disc. Once you have run the disc, restart your computer and choose boot from CD mode, as shown in Step 2 above.
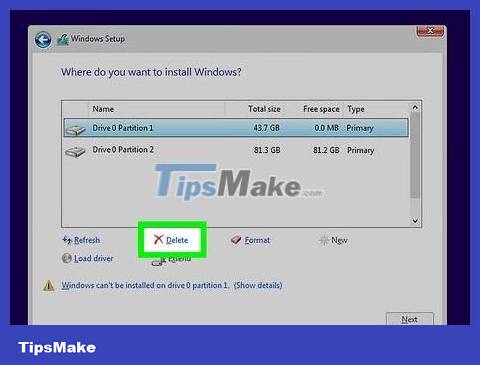
Delete the Ubuntu partition. When you begin the process of installing a new operating system, you can create and delete partitions on your hard drive. Choose to delete the Ubuntu partition. Thus, the Ubuntu partition will become an empty partition.

Continue installing the operating system, or remove the disc and turn off the computer. Once the partition is deleted, Ubuntu has been successfully removed. You can now install a new operating system like Windows 7 or Windows 8.
Note, your computer will not be usable until you install a new operating system.
