How to disable automatic workspace in GNOME
Better performance, more customization and integration features. However, there are still some aspects that annoy users with GNOME. One great example is how to manage workspaces - GNOME creates and deactivates workspaces, but many users prefer to have a certain amount of virtual workspaces that remain unchanged when the window is added.
Here, TipsMake will guide you how to disable automatic workspace in GNOME.
Install GNOME Tweak tool
The GNOME Tweak tool is essential for anyone who wants to change the default settings in GNOME, right down to things like setting a dark theme and the inclusion of minimize / zoom buttons. The GNOME Tweak tool is included in most repos, so you just need to use your package manager.
# Debian / Ubuntu
sudo apt install gnome-tweaks# Fedora
sudo dnf install gnome-tweaks# Arch
sudo pacman -S gnome-tweaksOnce it's installed, you should be able to find it in your 'Utilities' folder by default.

Disable automatic workspace
To disable automatic workspace, open the GNOME Tweaks tool and navigate to 'Workspaces'.
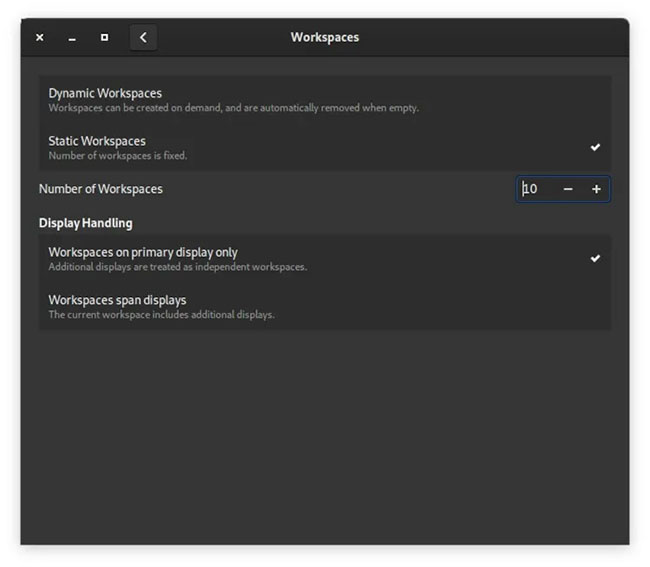
At the top, click 'Static Workspaces'. You will be able to set as many workspaces as you want, from 4 or more. Then, when you enter the Activities Overview , you'll see all of the workspaces arranged for you.
Other tweaks
The GNOME Tweak tool has a lot to offer beyond setting up a static workspace. Some things to keep in mind are in 'Window Titlebars' , where you can add zoom and zoom buttons, and switch buttons from a Windows-like layout on the right to a macOS-like layout on the left.
Alternatively, under 'Top Bar' , you can turn off the Activities Overview Hot Corner in the upper left corner of the screen. This is extremely useful if you are not a fan of hot-corner.

Extensions
Extensions are community-developed additions to GNOME Shell that aim to bring or add new functionality that users are looking for.
To get started with GNOME Shell Extensions, visit https://extensions.gnome.org and start looking around. If something needs to be installed (most distributions have extensions enabled by default), the page will tell you how to do that.

To manage extensions, you should use the Extensions application . This application is usually included in the repos for most distributions, but if you are using GNOME Shell versions prior to 3.36, you can find it in the Tweaks Tool.
To install the Extensions application, use one of the following commands:
# Debian / Ubuntu
sudo apt install gnome-extensions-app# Fedora
sudo dnf install gnome-extensions-app# Arch
sudo pacman -S gnome-extensions-appIt's a much more intuitive interface for managing extensions.