How to create new files in Linux
We'll cover creating files both in the Terminal and on the Linux desktop.
Create file on desktop
If you are uncomfortable using Terminal, creating new files in a desktop environment is straightforward, using a few basic everyday applications.
File browser
Most file browsers like Thunar and Dolphin will allow you to create an empty file by right clicking on the desired folder and pressing Create empty file or a similar option from the drop-down menu.
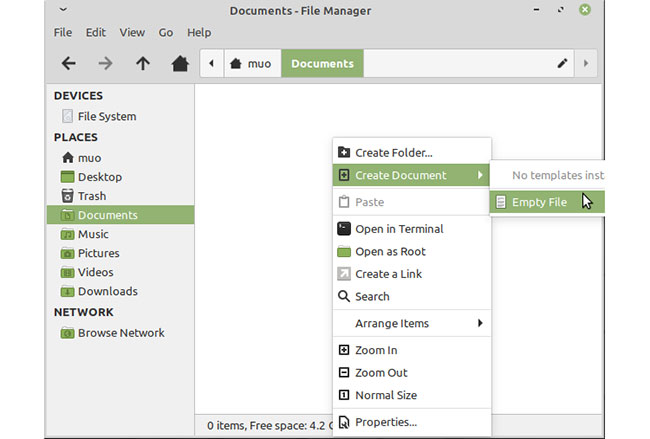
Alternatively, in the apps menu, you can often click File> Create New for options to create new files.
Text editor
Your Linux distribution will certainly include a basic text editor application. You'll start with a blank file when you open it and pressing Ctrl + S will give you a dialog to save the file at a specific location.
Create file in Terminal
Many Terminal commands in Linux allow you to create files quickly and efficiently. We will discuss some of these commands below.
touch
One of the most basic Linux commands, touch, will create a new file or if the filename you specified already exists, update the file's last modified date.
In the directory where you want to save your file, type:
touch filename.txtAlternatively, create multiple files with one command by simply placing a space between each filename:
touch filename1.txt filename2.txt filename3.txtYou can check if the file you created exists or not with this command:
lsSince you cannot edit files with the touch, this command is better suited for quickly creating multiple files for later editing.
Redirect operator (>)
Right braces are used in many commands to redirect output to a specific file. You will see it used with other commands later in this article.
However, you can import it without a specific command to create an empty file.
> filename.txtNote, however, that the redirect operator itself will overwrite any existing files that used that name.
echo
The echo command will output in Terminal any input you give it. However, it is also possible to create a new file and (optionally) save a line of text inside it.
To create a new blank file, use the following command:
echo -n > filename.txtTo create a new file with a single line of text use:
echo "File text" > filename.txtBe sure to put quotes around your text!
cat
The cat command (short for concatenate) is most commonly used to combine or read files. However, it can also easily create new files with text in it.
cat > filenname.txtThe redirect operator is here to redirect the cat's output to the specified file, the output is whatever you enter next. When you've finished writing the contents of the new file, press Ctrl + D to save it.
printf
The printf command is similar to the echo command, but has a bit more formatting capabilities.
For example, you can create a file with two lines of text using the following single command:
printf 'Some text Some more text' > filename.txtfallocate
Fallocate allows you to create a file in Linux of a specific size. It is mainly useful for test purposes, such as assessing hard drive write speed.
Use fallocate with the following command:
fallocate -l 10MB filenameReplace "filename" with whatever name you want to call your file.
The "-l" option indicates that you want a specific capacity and the "10MB" argument indicates what the size is. You can also use larger byte capacities, like GB and TB. You can also use M instead of MB to specify mebibyte instead of mega byte.
vim
Vim is a Terminal-based text editor that will launch when you specify a filename:
vim filename.txtWhile vim is running, press the I key to start typing. When you're done, press Esc and type : wq , then press Enter to save and exit.
nano
GNU nano is another text editor similar to Vim, but is probably a bit more user-friendly.
You can quickly create and start editing files with the following command:
nano filename.txtType whatever you want into the file, then press Ctrl + S to save and Ctrl + X to exit.