How to diagnose computer errors through beeps
Every time you turn on the computer, there will be a beep, then the operating system will start. Often beeps will appear only once and start up, so that users know the current status of the computer. If so, when the computer appears unusual beeps, such as long beeps or multiple occurrences, users need to check the hardware.
Each motherboard manufacturer will use a different type of BIOS chip, from which each BIOS chip will have a different way of emitting sound. If you have difficulty detecting a beep error on your computer, you can use the Beep Code Viewer software to diagnose errors through beeps. This software will synthesize all the beeps of existing BIOS chip manufacturers and fully explain how you can correct the errors.
- Instructions to fix blue screen error on computer
- How to fix the screen error of Windows 7/8 / 8.1 / 10 is black
- 5 tips for using the BIOS to help you master your computer
How to diagnose computer errors through beeps
- Beep code and POST of the computer
- Beep code AMI BIOS
- Beep code AWARD BIOS
- Beep code Dell
- Beep IBM BIOS code
- Audio boot Macintosh
- Code Phoenix BIOS code
- How to use Beep Code Viewer to guess PC error via beep
Beep code and POST of the computer
POST (power-on self-test) checks the computer's internal hardware to check for compatibility and connectivity before starting the rest of the boot process. If the computer goes through the POST process, the computer may beep (some computers may beep twice) and then restart. However, if the computer has a POST error, the computer will not beep or create a beep code, to let the user know the cause of the problem.
If your computer has an unusual POST or beep code not mentioned below, follow the POST troubleshooting steps to determine if the hardware component is faulty.
Beep code AMI BIOS
Below are the possible BIOS code for AMI. However, since this BIOS has many different manufacturers, the codes may be slightly different.
Beep Code Description of 1 hour short Error refresh DRAM. 2 short hoursParity circuit error (parity).
3 hours short 64 K RAM base. 4 hours short System timer error. 5 hours short Error process. 6 hours short Error Gate A20 keyboard driver. 7 hours short Virtual mode exception error. 8 short hours Displays the memory read / write test failed. 9 short hours BIOS ROM test error. Short 10 hours Error reading / writing off CMOS. 11 hours short Cache error. 1 hour long, 3 hours short Normal / extended memory error. 1 hour long, 8 hours short Displays / retrieves failed test. Voice alarm with 2 different tones Low CPU fan speed, voltage problems.Beep code AWARD BIOS
Below is the BIOS AWARD code beep that may occur. However, since this BIOS has many different manufacturers, the Beep code may be slightly different.
Beep Code Describing a long sound, 2 short hours Indicates that a video error has occurred and the BIOS cannot initialize the video screen to display any additional information. 1 hour long, 3 hours short No faulty video card (video card reattachment) or video card was detected. Repeated non-stop beep RAM issue. Repeat deafening beep while PC is running. The processor (CPU) is too hot. Repeat the alternating beeping sound at no problem with the processor (CPU). It may be broken.If any other fixable hardware problems are found, the BIOS will display a message.
Beep code Dell
Beep Code Describes a corrupted or defective BIOS ROM. 2 beeps Not receiving RAM 3 beeps Motherboard error 4 beeps RAM error 5 beeps Error CMOS battery. 6 beeps Video card error. 7 beeps The processor (CPU) is poorBeep IBM BIOS code
Below are the possible BIOS code beep. However, since this BIOS has many different manufacturers, the Beep code may be slightly different.
Beep Code Description No beeps No power input, liquid power cord or insufficient power. A normal POST short beep, the computer is fine. 2 short beeps POST error, review the screen to find the error code (error code). Continuous beep No power input, liquid power cord or insufficient power. Repeat short beeps No power input, liquid power cord or insufficient power. 1 long beep and 1 short beep There is a problem with the motherboard. 1 long beep and 2 short beep Video related problems (Mono / CGA display circuit problem). 1 long beep and 3 short beeps Video display circuit (EGA). 3 long beeps Keyboard error or keyboard card. 1 beep, the screen does not display or display incorrectly Video display circuit.Audio boot Macintosh
Negative Error error message (2 different tones) Problems with logic board or SCSI bus. Start-up alarm, drive rotation, no video Problem with video controller. The power is on, there is no alarm signal Logic board problem. High tones, 4 higher tones Problems with SIMM.Code Phoenix BIOS code
Below are the code beeps for Phoenix BIOS Q3.07 or 4.x.
Beep Code Description or section to check1-1-1-1 Beep code has not been confirmed. Reattach RAM chips or replace RAM chips where possible. 1-1-1-3 Verification of real mode. 1-1-2-1 Receive CPU type. 1-1-2-3 System hardware initialization. 1-1-3-1 Initialize chipset registers with initial POST value. 1-1-3-2 Set the flag flag to the position. 1-1-3-3 Initialize CPU registers. 1-1-4-1 Cache initialization to initial POST value. 1-1-4-3 Initialize the I / O value. 1-2-1-1 Initialize the power management process. 1-2-1-2 Load register replaces with initial POST value. 1-2-1-3 Go to UserPatch0. 1-2-2-1 Initialize the keyboard driver. 1-2-2-3 Check BIOS ROM. 1-2-3-1 Timer initialization 8254. 1-2-3-3 Initializing the DMA controller 8237. 1-2-4-1 Resetting the programmable interrupt driver. 1-3-1-1 Check the refreshability of DRAM. 1-3-1-3 Check the keyboard driver 8742. 1-3-2-1 Set the segment to register 4GB. 1-3-3-1 Automation of DRAM. 1-3-3-3 Clear RAM memory 512 K. 1-3-4-1 Check 512 base address lines. 1-3-4-3 Check basic memory 512 K. 1-4-1-3 Check CPU bus clock frequency. 1-4-2-4 Re-initialize the chipset. 1-4-3-1 Protect the system BIOS ROM. 1-4-3-2 Cache reset. 1-4-3-3 Cache automation. 1-4-4-1 Advanced register chipset configuration. 1-4-4-2 Load replacement registers with CMOS values. 2-1-1-1 Set the initial CPU speed. 2-1-1-3 Interrupt vector initialization. 2-1-2-1 Initializing BIOS interrupt processes. 2-1-2-3 Check ROM copyright notice. 2-1-2-4 Initialize the manager for PCI optional ROMs. 2-1-3-1 Check video configuration with CMOS. 2-1-3-2 Initialize the PCI bus and devices. 2-1-3-3 Initialize all video adapters in the system. 2-1-4-1 BIOS video ROM protection. 2-1-4-3 Display copyright notice. 2-2-1-1 Displays the type and speed of CPU. 2-2-1-3 Check the keyboard. 2-2-2-1 Set up keypress operation if activated. 2-2-2-3 Activate the keyboard. 2-2-3-1 Check for unexpected interruptions. 2-2-3-3 Display the prompt Press F2 to enter SETUP . 2-2-4-1 RAM test from 512 to 640 k. 2-3-1-1 Check memory expansion. 2-3-1-3 Check the expanded memory address lines. 2-3-2-1 Go to UserPatch1. 2-3-2-3 Configure the advanced cache register. 2-3-3-1 Activate external cache and CPU. 2-3-3-3 Display external cache size. 2-3-4-1 Display protection notice. 2-3-4-3 Displays non-disposable segments. 2-4-1-1 Displays an error message. 2-4-1-3 Check for configuration errors. 2-4-2-1 Check real-time clock. 2-4-2-3 Check the keyboard error. 2-4-4-1 Set up hardware interrupt vector. 2-4-4-3 Check the remaining processor (if any). 3-1-1-1 Turn off the I / O port on the board. 3-1-1-3 Detect and install external RS232 ports. 3-1-2-1 Detecting and installing external parallel ports. 3-1-2-3 Reset the integrated I / O ports. 3-1-3-1 Initializing the BIOS data area. 3-1-3-3 Initialize the BIOS data area. 3-1-4-1 Initialize the floppy disk controller. 3-2-1-1 Initialize the hard disk controller. 3-2-1-2 Initialize the local bus hard disk controller. 3-2-1-3 Go to UserPatch2. 3-2-2-1 Disable the A20 address line. 3-2-2-3 Delete large segment register ES. 3-2-3-1 Search for optional ROMs. 3-2-3-3 Protect optional ROMs. 3-2-4-1 Set up energy management features. 3-2-4-3 Set hardware interrupt feature. 3-3-1-1 Set the time of day. 3-3-1-3 Check the key lock. 3-3-3-1 Delete the F2 prompt. 3-3-3-3 Scan F2 key stroke. 3-3-4-1 Enter the CMOS setting. 3-3-4-3 Delete flag flag. 3-4-1-1 Error checking. 3-4-1-3 The POST process is finished, prepare to start the operating system. 3-4-2-1 A beep. 3-4-2-3 Password check (optional). 3-4-3-1 Delete the global description table. 3-4-4-1 Delete the parity checker. 3-4-4-3 Clear the screen (optional). 3-4-4-4 Check virus reminders and backups. 4-1-1-1 Try to boot with INT 19. 4-2-1-1 Processor interrupt error. 4-2-1-3 Unidentified interruption error. 4-2-2-1 Pending interrupt error. 4-2-2-3 Initializing an optional ROM error. 4-2-3-1 Shutdown error. 4-2-3-3 Move the extension block. 4-2-4-1 Shutdown error 10. 4-3-1-3 Initialize the chipset. 4-3-1-4 Initialize refresh counter. 4-3-2-1 Flash check required. 4-3-2-2 Check the HW status of the ROM. 4-3-2-3 BIOS ROM stable. 4-3-2-4 Perform a complete RAM test. 4-3-3-1 OEM creation. 4-3-3-2 Initialize the interrupt controller. 4-3-3-3 Read in the startup code. 4-3-3-4 Initialize all vectors. 4-3-4-1 Boot flash program. 4-3-4-2 Initialize boot device. 4-3-4-3 Boot code read is OK. Voice alarm with 2 different tones Low CPU fan speed, there is a problem with the voltage level.How to use Beep Code Viewer to guess PC error via beep
Step 1:
First of all, please access the link below to download the software to your computer, then proceed to extract the zip file with the tool on your computer.
- fshare.vn/file/GHDFUPXGAP/
Step 2:
In the unzipped folder, simply click on the Beep Code Viewer file to run the software without installing multiple steps.
Step 3:
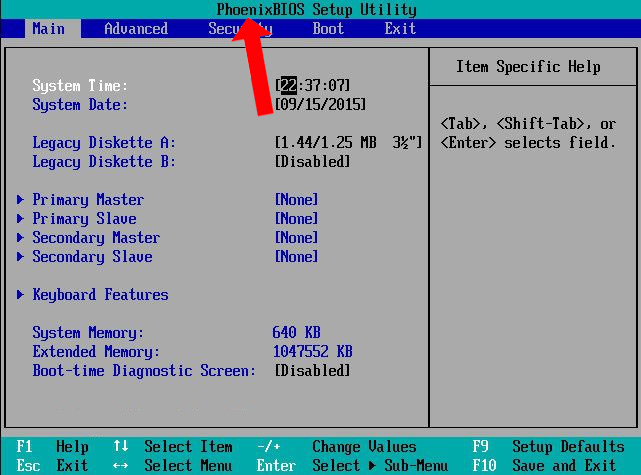
Appearance of the software, very simple for users to follow. To check for errors first you need to know the BIOS vendor Mainborad's computer is using. Click BIOS Information in the interface.

Or users can use the BIOS access keys in the article Instructions on BIOS entry on different computers.
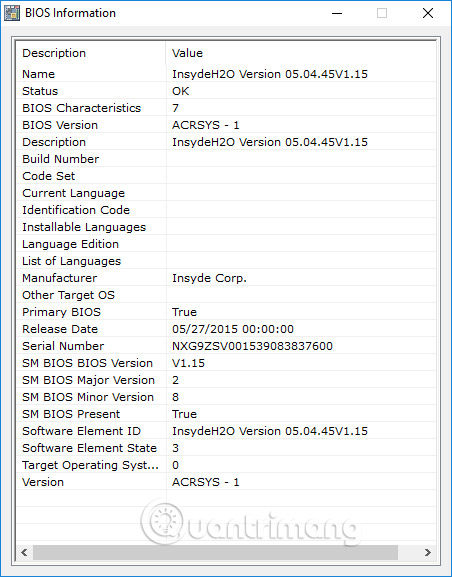
Appear all information of the BIOS.
After you have identified the BIOS vendor and determine the type of beep that appears on your computer, you just need to press the beep type and right below there will be the error name and error correction method.
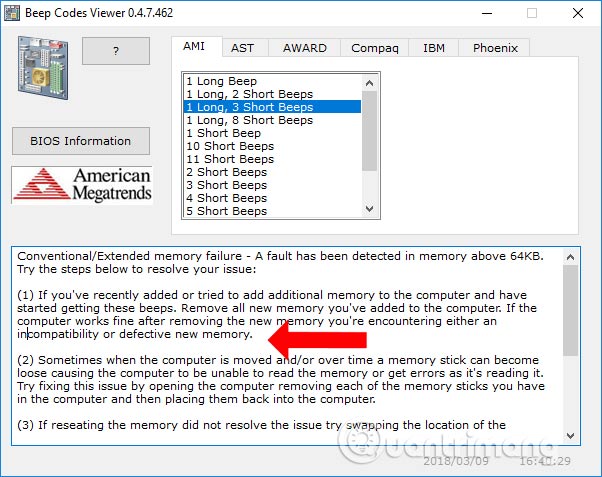
With the Beep Code Viewer tool, we can identify the cause and error of abnormal beeps on the machine. From there, users can rely on the lightness of the machine's error to get a solution.
See more:
- Reset BIOS password or remove BIOS password with CMOS battery
- Enable password in BIOS
- Instructions for accessing BIOS on Windows 8
I wish you all success!