How to control WiFi network in Linux using Evillimiter
Is your WiFi connection too slow? Are you having persistent network problems while surfing the web? Chances are, your wireless network is handling more traffic than usual. Fortunately, controlling a WiFi network in Linux is pretty easy. You can use Evillimiter - an open source application - to monitor and control your device's bandwidth. This tutorial illustrates how to do this using a step-by-step approach.
What is Evillimiter?
Evillimiter is a free and open source monitoring tool that can limit bandwidth usage for devices connected to LAN. Evillimiter runs on Linux and Windows, and can work without admin access to the network.
Note : You should not use this tool on other people's networks, avoid possible legal troubles.,
How to install Evillimiter
You need to install Evillimiter before use. Fortunately, installation is very simple if you already have the dependencies installed. It requires Python 3, which will be available on most Linux installations by default. To install Evillimiter, activate Terminal and enter the commands below:
# Retrieve the source code
git clone https://github.com/bitbrute/evillimiter.git# Navigate to source directory
cd evillimiter# Install Evillimiter
sudo python3 setup.py installHow to control a WiFi network with Evillimiter
Once the installation is finished, you can begin monitoring the devices connected to your personal WiFi. To do this, first start the application by running the following command:
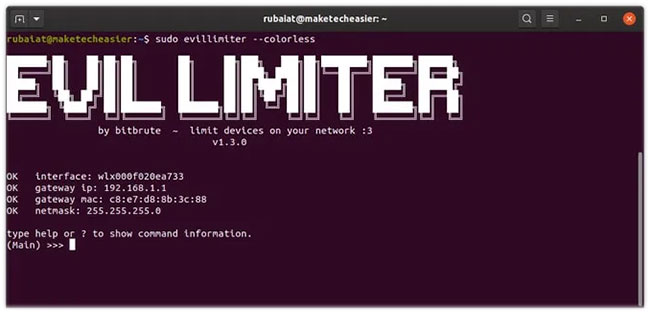
sudo evillimiterNote that you will need sudo / root privileges to run and use Evillimiter. This is because it handles the network controller and needs access to low level kernel parameters. When you run Evillimiter for the first time, it will display some information about the WiFi network. This includes interface name, port IP, MAC and netmask.

The interactive dashboard is where you enter commands to monitor bandwidth usage. Evillimiter provides a number of commands for ease of control. You can see a list of available commands by typing ? or help in the interactive dashboard.
(Main) >>> helpYou need to scan your local network before you can monitor connected devices. Use Evillimiter's scan command to do this.
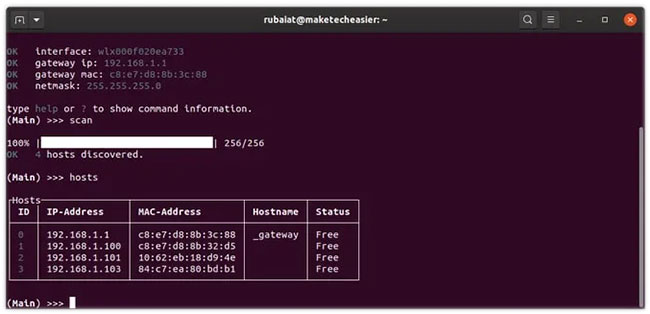
(Main) >>> scanThis will scan all hosts connected to WiFi and report the number of active devices. Now, you can view the hosts and limit their bandwidth usage. Use the hosts command to view all active hosts.
(Main) >>> hostsThis will display a list of devices connected to your WiFi network. Evillimiter will assign an ID to each device, displaying its IP and MAC information. A status field indicates whether bandwidth has been limited for a single device.
Now, you can limit the bandwidth for a device using the limit command .
(Main) >>> limit 2 100kbitThis command limits the bandwidth of the second device ( ID = 2 ) to 100 kilobits. You can limit multiple devices at once using a comma separated list.
(Main) >>> limit 2,3 50kbitThis command will limit the bandwidth of the second and third device to 50 kbit.
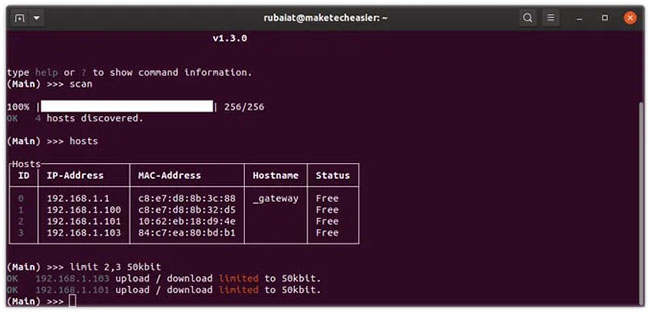
Bandwidth limits are set for both upload and download speeds. But you can also limit upload / download speeds separately. The next command limits the second device's download speed to 100 kbit per second.
(Main) >>> limit 2 100kbit --downloadYou can also block the Internet connection for the host device using the block command. That way, you can control WiFi users directly from Terminal.
(Main) >>> block 2This command will block the second device from using network resources. Use the --upload and --download flags to block one-way traffic.
(Main) >>> block 2 --downloadLet's say you want to stream gaming sessions. You can block all other WiFi devices with the command below.
(Main) >>> block all 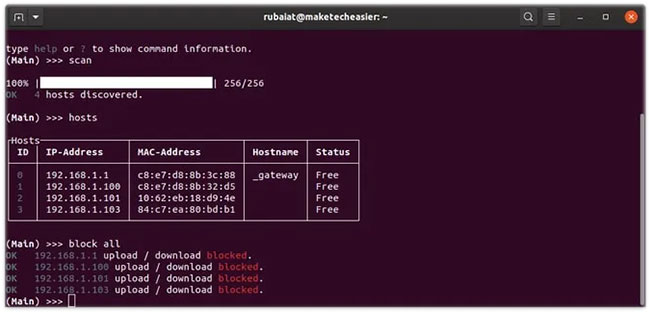
So far, this article has shown how to scan, limit, and block devices using Evillimiter in Linux. However, don't forget to free these devices after you are done. Use the free command followed by the host ID to do this.
(Main) >>> free 1,2,3 (Main) >>> free all 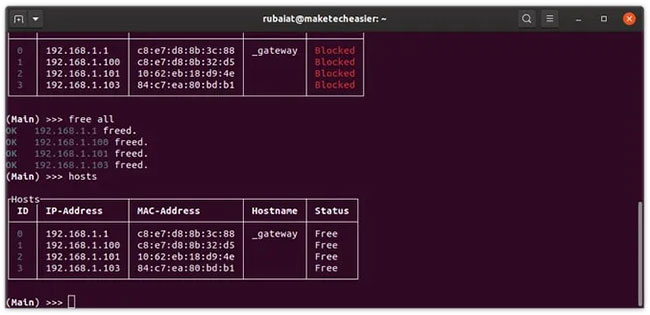
To exit the interactive console, enter quit or exit in the command prompt .
(Main) >>> quitIt will exit the current session and return you to the Terminal.
Next up are two other features of Evillimiter. Because the interactive panel is colored, it may not run properly in some environments. You can install the packages needed for color coding or use the --colorless option in such cases.
sudo evillimiter --colorlessIf you run this command in Terminal, it will initiate a colorless interactive session for Evillimiter. People can use this mode whenever they have a problem with the ASCII color.
Finally, the -f option solves problems with the Linux iptables configuration or network parameters.
sudo evillimiter -f