Comprehensive guide to Windows 7 security - Part 1
In this article we will show you how to secure Windows 7 and introduce some of the lesser known security features that this operating system provides.
 Windows 7 is Microsoft's latest desktop computer operating system, built on the strengths and weaknesses of its predecessors, Windows XP and Windows Vista. Every aspect of the operating system like, how to run services and how to load applications will make this operating system more secure than ever. All services are enhanced and there are more reliable security options available. However, the fundamental improvements to new systems and services, Windows 7 also provides better security functions, improved authentication and test features, and encryption capabilities. Remote connection and data, this operating system also has many improvements for protecting internal components, ensuring system safety such as Kernel Patch Protection, Service Hardening, Data Execution Prevention, Address Space Layout Randomization and Mandatory Integrity Levels.
Windows 7 is Microsoft's latest desktop computer operating system, built on the strengths and weaknesses of its predecessors, Windows XP and Windows Vista. Every aspect of the operating system like, how to run services and how to load applications will make this operating system more secure than ever. All services are enhanced and there are more reliable security options available. However, the fundamental improvements to new systems and services, Windows 7 also provides better security functions, improved authentication and test features, and encryption capabilities. Remote connection and data, this operating system also has many improvements for protecting internal components, ensuring system safety such as Kernel Patch Protection, Service Hardening, Data Execution Prevention, Address Space Layout Randomization and Mandatory Integrity Levels.
It can be said that Windows 7 is designed to be safer. First, it was developed on the basis of Microsoft's Security Development Lifecycle (SDL). Secondly, it is designed to support the general standard requirements for certification Evaluation Assurance Level (EAL) 4, to meet the information processing standards Federal Information Processing Standard (FIPS) # 140-2. When used as a standalone operating system, Windows 7 will protect individual users well. It has many useful security tools inside, but only when used with Windows Server 2008 (R2) and Active Directory, protection will be more effective. By raising the level of security from tools like Group Policy, users can control all aspects of desktop security. If used for personal or small office, the operating system still appears to be quite secure in preventing multiple attack methods and can be recovered quickly in case of a disaster, so although there will be more advantages if Windows 2008 is available, this is not necessary to get a high level of security for Windows 7.
However, even though it may be assumed that Windows 7 is itself a secure operating system, that doesn't mean that you rely solely on the default configuration but forget about making some adjustments to reinforce. his security capabilities. Be aware that you are the target of some form of malware or Internet attacks when your computer is used in public networks. Be aware that if the computer is used for public Internet access, your system and the network it connects to will be a good bait for attackers.
In this article, I will show you some basic knowledge needed to secure Windows 7 properly, help you achieve basic security, consider some advanced security configurations as well as go explore some of the lesser known security features in Windows to prevent and protect against possible attacks. Introducing a number of ways to ensure data security, perform backup and run quickly if you encounter some attacks or system malfunctions in a catastrophic way beyond your ability to handle. Then there are some security concepts, how to 'solidify' Windows 7, how to install and provide security for running applications, how to manage security on a Windows 7 system and prevent problems. threads caused by malware.
The article also introduces data protection, operating system backup and restore features, how to restore the operating system back to its previous operating state, some ways to protect data and system state. If disaster happens. We also introduced a number of strategies for quickly implementing those tasks. The topics covered in this article also include how to work safely while online, how to configure biometric controls for advanced access control, how and when to use them with Windows Server 2008 (and Active). How to Directory), how you can safely integrate options for control, management and testing. The goal of this article is to introduce you to the security features of Windows 7, the enhancements and their applications, and to provide you with the knowledge of planning, using the right features. This security feature. The concepts that we introduce will be broken down and organized by block method.
Note : If you work in a company or other professional environment, you should not make adjustments to your company's computer. Follow the published security plan (or policy), as well as the best practices, principles, and guidelines published in the organization. If you're not familiar with security topics and Microsoft products, read the product documentation before applying any changes to the system.
Basic security issues
Before diving into the details of Windows 7, I want to introduce you to some basic concepts about security and how to plan for its applications. You also need to know why testing to maintain security is so important and how to correctly check security services to find the problem. More importantly, we also need to know how to check and discover if we have to open the door for easy attacks. Security is not something you can plan arbitrarily and then quickly apply. It is a concept that must be applied to every technical aspect in deployment as well as in practice. It is also something that needs to be considered carefully before being deployed and then tested and managed after application. It is required that you conduct an analysis to make appropriate adjustments to the current security architecture, as well as discover potential attacks. Most need to be tested by a malicious program or an attacker to find access in this process; Then you can pioneer in protecting yourself if you see any attempts and actions that are invasive. Take notes and then verify, you will find interesting information about what is querying your router login prompts, administrator account login attempts, .
Logs and warnings are very useful because, when something goes wrong, you can respond quickly and accurately by analyzing source IP addresses, or login attempts are caught by assessment. Responding to an attack with a detailed plan is called incident incident. Preparation will be the main key to the act of 'responding to the incident', so having a pioneering plan and a response plan is important to have before the disaster happens. The Disaster Recovery Plan (sometimes used in conjunction with the work continuation plan, BCP), will include a recovery strategy from incidents. Some IT units also have IT experts dedicated to responding to the case, this is the group that will take responsibility according to the plan set out to overcome and solve important issues that may cause a halt The system works significantly, or worse, data loss, network and system attacks, etc.
For home users and independent systems, you need to follow such a strategy but at a simplified level. Because you still need to protect everything, you need to react to the disaster, so a good plan created in advance for disaster recovery will do the right thing for you. A good example of such a simple plan would be, if your system is infected with malware (such as a Trojan), chances are you'll have to reinstall the operating system if all attempts are made. restore and fix failure. If this is the case, you need to assign the team members, detailed steps and pre-prepared disaster procedures to be able to respond correctly and a test process to ensure that everything is done right after recovery takes place. Being able to access, or have a copy of the installation files or any other program and application in hand now saves you time troubleshooting, and if set up correctly, it can show you the right direction you need to take.
Note : To help you plan and know more about security issues, you can search the checklists and plans in the referenced links section of this article.
Also review your plans on a regular basis, especially after a serious problem has occurred and have additional action items if needed. Once you have the right plan, you need to consider building on the platform with many functions and services.
Tip : Security needs to be reviewed and applied to which systems or services are used to mitigate the risks involved while working. And if security is applied in such a way as to prevent an attack or a disaster, what you have to spend will be much less expensive. Security, even at its most basic level, needs to be applied to keep personal data safe, but make sure that if you need to completely reinstall Windows from the rubble, you can still reuse their data and can access and use this data. Security cannot be ignored.
Consideration should also be given to implementing security in both conceptual and technical uses of the Defense in Depth security concept. Security needs to be considered and applied to all network systems, services, applications and devices, which need to keep your system up and running with the Internet. Published policies and plans have been developed to help users gain high productivity in using the systems, along with general understanding of the use of policies. Continuous maintenance will increase your investment. But to prevent vulnerabilities in security architecture, you must consider planning and applying security models that use the concept of 'Defense in Depth'. Figure 1 shows the 'Defense in Depth' application at the simplest level, you can add other classes, depending on how your family or corporate network is set up.
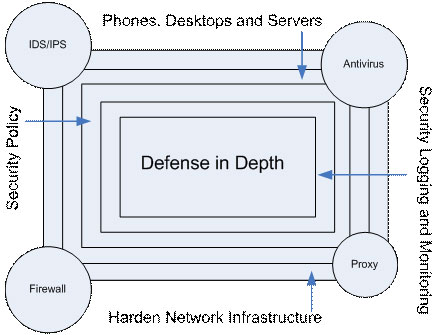
Figure 1: See how Defense in Depth is focused and deployed
Defense in Depth as you can see, can be customized to suit your needs. In this example, the security policy is to provide security and communication direction to users in the system and the network. In addition, it should be considered to solidify your systems, phones, desktops, services, applications, servers, routers, switches and PBXs, all, to ensure that all The entrances are well shielded. Obviously, there are still some forms of public Internet protection (such as firewalls) that need to be used during the usage process, but always have to extend this issue and add other items such as polling sets. , filtering, scanning to get more sophisticated support. In addition, you should also have a way to check and record all this information for purposes of reviewing and reviewing if necessary.
Windows 7 is designed to be integrated into any environment that conforms to a high level of security, such as the US government and the US military. When considering the basic security principles of Windows, you need to remember that any enterprise-level system must be certified at C2 security level from the gold book. Microsoft Windows also needs to follow the general standard certificate. For more information on these topics, you can find other articles and other information at the end of the reference links. Windows 7 is quite flexible, with many options that allow you to configure a system with complete functionality (minimum security), or a basic-level configuration, with only the operations you configure for permission to use (maximum security). With Windows 2008 and Windows 7, the security function will increase tenfold when used together properly.
Note : Remember that denying a problem (or a potential problem) is not an option. Previous problems can be used later, or omitted completely. Lazy just makes you spend a lot of time. Even so, obscure security is not confidential. Failure to follow a strict rule will only cause many problems later. A security deployment throughout home computers or within a business (both important) will prevent detection and attacks, providing multi-layer security to help the status quo. Your security is at a high level of security, but not all of them will be avoided. You need to know the basics of security, how to prepare ahead and how to cope with attacks if you want to be safe.
So far you have become familiar with some of the basic security concepts, let us take a look at what we have studied in the process of configuring Windows 7 security settings. The point of looking at how we gain knowledge begins with why we want to apply security, when to apply it, as well as the reasons for managing, testing and upgrading it, all What we need to do is dig more into those security concepts while configuring a basic Windows 7 system. This problem will be done quite easily if you know what you want to accomplish. If a new Windows user or someone who is very difficult to adapt to this new operating system (you probably missed Vista) then you will probably need to spend a lot of time learning the tools and Study them on online websites to get a deeper understanding. For example, you can find many online templates and checklists from Microsoft.com, which will give you the ability to step-by-step apply security issues on Windows systems. You can also find useful tools in the reference links at the end of this article.
Templates are not always the answer, sometimes it can cause unwanted consequences if not used properly (or properly configured), always observe the notes - even Releases download directly from Microsoft.com. Another important thing that you need to do is always read the documentation that comes with the template to be able to use it correctly. It must be emphasized that, without a basic platform for an operating system itself, or the basic principles that the operating system operates, you will not be able to maintain a high level of security in one. long time. Knowledge of the core operating system and its translations is also essential if you want to maintain a high level of security, even after properly configuring the security on your base system. Event Viewer logging is extremely useful, because you can configure the audit action (for example) and get detailed information about what's going on inside your systems. Most (but not all) of the records are intrinsically incomprehensible and interpret problems in the most basic terms or with a set of machine languages. You will need online to remove your problems, this is a way to make your work easier. And you'll see a lot of things I don't know and will find a lot of tools that I want to add to my kit for future deployments when tested carefully.
There is also a degree of flexibility when applying security, which allows you to achieve the goals and requirements of your business (such as Internet access) without having problems. What, while still maintaining the high level of security needed. A great example is the User Account Control (UAC) tool, which is a tool when adjusted, can provide a high level of security, or can be turned off completely. You will have to restart your system if you turn off UAC.
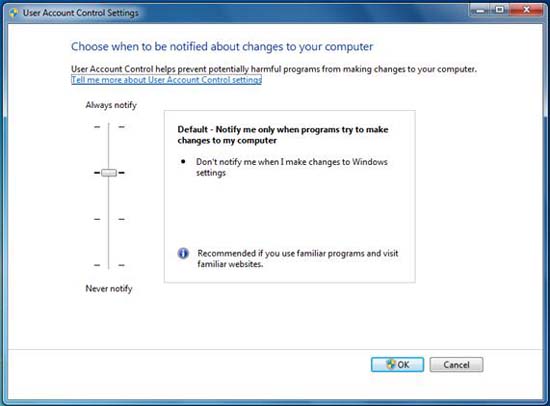
Figure 2: Adjusting the Level of Security by adjusting UAC settings
UAC is used to prevent programs and applications from making changes to your operating system. It works by restricting access within the operating system core, then providing detailed information to the user about the programs that are trying to install or interfere with the operating system configuration. This is a very useful tool, it gives you the opportunity to assess what programs are working and can interfere if that's what you don't want. UAC has been introduced since Windows Vista, but since Vista users cannot turn off this utility, it seems to be an annoyance for most. In Vista, UAC also annoys users because they can't seem to find a way to solve those problems. Windows developers also have a lot of trouble writing the code because of UAC limitations and some related but necessary issues. Now, with Windows 7, UAC can be turned off completely, which is an insecure level of security configuration, but it provides users with flexibility and an additional choice.
Note : It is important to protect your system safely, not completely turn off UAC or if you turn it off for some reason, you need to turn it on immediately.
Install and 'solidify' Windows 7
It can be said that Windows 7 is a safe design. When deploying it, you should perform a fresh installation on a newly purchased computer, need to have the required hardware configuration and then 'solidify' it. Enabling the system is a process that increases the security level for a newly installed computer by configuring necessary security settings, removing unnecessary software and making adjustments. some advanced policy settings.
Note : You need to create a plan when selecting hardware for Windows 7, because if you want to use virtualization, or the Windows Trusted Platform Module (TPM) Management feature as well as other features such as BitLocker, you need to must buy the right hardware that it supports these features.
When your operating system is properly installed and basically configured, it is time to do the "solidify" process. Is it necessary to have a new Windows installation or can it "solidify" a system already in use? Technically, you can 'solidify' any system that is already installed and being used, but before you do it, you should do research, analyze, test and verify the levels. Current security is configured in use. Not "solidifying" something was compromised. You also do not know how security applications will affect the production system when used in the home or corporate environment. Some cloning systems set up to test will cost you a bit of time and resources, but this is worth doing because it can find out and avoid some problems that may appear with the device. Your design and deployment. You can do more damage than do it better if you don't know how changes in security settings or templates will affect services on the production system. For example, it is possible to apply security to a system and limit changes to the firewall's filtering features, remove functionality from a program that you have installed and used - it can use one certain ports are currently closed by the firewall and this will result in a connection error. This problem can cause undesirable effects if the application is used for business, necessary for production and may need a lot of time to search and fix. That's why it is simpler to install fresh Windows 7 operating system, then 'solidify' it quickly, you can verify that security will remain in place until deploy it. In addition, you can also make the process faster, especially if you are using a virtual machine (VM) or VHD file, these are things that give you many options to create multiple instances of the desktop to be able to manually virtual failover or restore quickly if there are no reserve options. Virtualization simplifies the installation process when creating asexual images for backup purposes, so you can restore your desktop easily and within a few minutes. We will introduce virtualization in the later part of this series. If automatic failover is enabled and configured, desktop users may not even notice a stop on the device at all if they are virtualized.
You can 'solidify' the system and then access your secure data through drives, databases and shared repositories - all done at high speeds, with options. Select failover not only makes it safe, but also separates the data you access. If you plan correctly, you can create a complete snapshot of the configured, safe, and updated Windows version, and when disaster strikes, you can restore the system quickly. Then, after restoring the basic operating system, you can re-mount the shared drive to access the data.
So when installing Windows, what steps do you need to take to 'solidify' it? And is there a certain order to choose? If there are some installation steps and 'solidify' they will be the basic installation order, removing some unused things, updating the system, applying basic security, then creating a backup to restore quickly when needed, see list below:
- Step 1 - Install the basic operating system by selecting the options during the installation process to increase security, not selecting unnecessary services, options and programs.
- Step 2 - Install the Administrator toolkit, security tools and necessary programs.
- Step 3 - Remove unnecessary services, programs and software. Disable or remove unused user or group accounts.
- Step 4 - Upgrade service packages, patches, as well as all installed programs.
- Step 5 - Perform security audits (scans, samples, MBSA, .) to assess the current security level.
- Step 6 - Run System Restore and create a restore point. Backup and restore application for disaster recovery.
- Step 7 - Backup the operating system in some way to quickly recover it in case of a disaster.
This is just a simple list. Bạn có thể bổ sung thêm một số bước và mở rộng danh sách này hơn nữa. Rõ ràng nó không phải là một danh sách bắt buộc, tuy nhiên danh sách này là một điểm khởi đầu khá tốt khi áp dụng bảo mật vào Windows 7 sau khi đã cài đặt cơ bản. Nếu hoàn tất một cài đặt fresh cho Windows 7, bước tiếp theo là gỡ bỏ phần mềm, dịch vụ, giao thức và chương trình mà bạn không muốn hay không cần chạy nó. Công việc này có thể thực hiện dễ dàng trong Control Panel.
Tiếp đến, bạn có thể vào Control Panel và thiết lập xem ai được phép sử dụng máy tính trong User Accounts applet. Ở đây bạn nên remove các tài khoản không cần thiết, hoặc vô hiệu hóa nó. Rõ ràng, nên cẩn thận với người dùng và nhóm người dùng mặc định, một số tài khoản đó sẽ được thắt chặt với các dịch vụ đang chạy, cách truy cập dữ liệu của bạn và ,. Bạn có thể vô hiệu hóa cũng như remove tài khoản một cách dễ dàng. Một kỹ thuật khác được sử dụng bởi hầu hết các chuyên gia bảo mật là để tài khoản quản trị viên nội bộ ở một nơi thích hợp và thẩm định nó cho các cố gắng sử dụng. Một cách làm chung là không sử dụng các tài khoản mặc định khi quản lý một mạng Microsoft với số lượng lớn các hệ thống và thiết lập các tài khoản quản trị viên mới có thể được lần vết nếu cần. Bằng cách thẩm định các tài khoản mặc định này và sử dụng tài khoản được tạo mới với các đặc quyền quản trị viên có liên quan với nó, bạn sẽ tăng được độ bảo mật lên gấp hai. Một là bạn sẽ phát hiện ra ai đó đang cố gắng truy cập vào máy tính của mình bằng các tài khoản mặc định khi mà lẽ ra không ai được làm việc đó. Nếu được thẩm định, bạn có thể thấy các cố gắng và thời điểm chúng diễn ra. Ứng dụng bảo mật cho tài khoản được biết đến như một honeypot và hữu dụng trong việc tìm kiếm các cố gắng gây ra bởi những người dùng đang cố gắng truy cập vào hệ thống của bạn. Hai, bạn có thể bỏ được một nửa phương trình khi ai đó cố gắng crack tài khoản của bạn thông qua các chứng chỉ cơ bản, chẳng hạn như sự kết hợp của username và password. Nếu bạn lấy đi các thông tin dễ đoán về username, thì bạn chỉ còn lại mật khẩu, thứ có thể được cấu hình theo cách nào đó để không thể bị crack. Nếu đã thiết lập các tài khoản mặc định như một honeypot thì bạn có thể tạo một mật khẩu gần như không thể crack và hạn chế nó để không thể thực hiện thứ gì nếu có bị thỏa hiệp (hạn chế được ảnh hưởng khi bị thỏa hiệp). Bạn nên thay đổi tất cả mật khẩu cho các tài khoản mặc định. Sử dụng mật khẩu theo cách có thể làm cho mật khẩu được khỏe nhất để bảo mật cho các tài khoản và cần thẩm định chúng . Bạn cũng nên cấu hình chính sách để người dùng cần thay đổi mật khẩu qua một quá trình mà ở đó họ chỉ được phép thay đổi nó nếu chọn mật khẩu mới mạnh và không dễ bị hack. Đây chỉ là một mẹo 'làm vững chắc' mang lại nhiều lợi ích, chẳng hạn như khả năng phát hiện các tấn công thông qua việc ghi chép và thẩm định.
Mẹo : Trong Windows Server 2008, bạn có thể cài đặt chức năng 'core' (lõi), một quá trình 'làm vững chắc' được áp dụng cho hệ thống trong giai đoạn cài đặt thực sự. Khi cài đặt, máy chủ chỉ chạy với những chức năng tối thiểu mà bạn cần đến, vì vậy sẽ giảm được bề mặt tấn công. Windows 7 có thể được 'làm vững chắc' nhưng không có tùy chọn cài đặt giống như ở Windows Sever 2008. Để 'làm vững chắc' Windows 7, bạn cần áp dụng các chính sách, các template hoặc phải tự cấu hình các thiết lập bảo mật cần thiết.
Nói là vậy nhưng cách mà bạn bắt đầu để khóa chặt và bảo mật cho Windows 7 như thế nào? Một cách dễ dàng nhất để bắt đầu quá trình 'làm vững chắc' hệ thống của bạn là sử dụng menu Start để tìm kiếm bất cứ thứ gì có liên quan đến vấn đề bảo mật được lưu bên trong hệ thống và đã được đánh chỉ số. Để thực hiện điều đó, hãy kích nút Start để mở Start menu. Sau đó đánh vào từ khóa ' security' trong trường Search Programs and Files . Hình 3 bên dưới hiển thị các tùy chọn của Start menu dựa trên từ khóa tìm kiếm 'Security'.
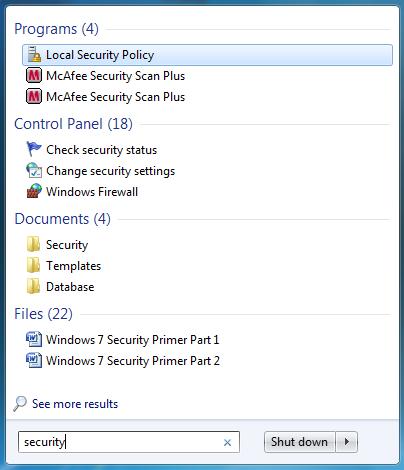
Hình 3: Tìm và sau đó xem các tùy chọn bảo mật bên trong menu Start
Ở đây bạn có thể thấy các chương trình, Control Panel applet (hay các action), tài liệu và file đã được chọn và được tổ chức theo cách dễ xem và truy cập. Local Security Policy (nếu được chọn) là bộ chỉnh sửa chính sách, cho phép bạn xem và cấu hình các chính sách bảo mật cho hệ thống. Local Security Policy editor có thể thấy như trong hình 4. Ở đây bạn có thể thực hiện một số điều chỉnh cho tất cả các thiết lập dựa trên chính sách trên hệ điều hành của mình.
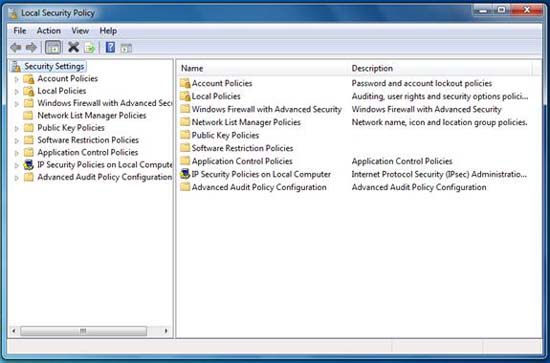
Hình 4: Xem và cấu hình bảo mật với chính sách bảo mật nội bộ
Mẹo – để có quyền điều khiển toàn bộ chính sách, bạn nên sử dụng Windows 7 với các sản phẩm Windows Server, chẳng hạn như Windows Server 2008 R2. Nếu thực hiện như vậy, bạn có thể sử dụng Active Directory (AD) và Group Policy.
Nếu muốn thiết lập cục bộ hành động thẩm định cho một sự kiện nào đó (chẳng hạn như sự kiện đăng nhập và đăng xuất), bạn có thể chỉ định hành động đó trong cửa sổ Local Security Policy (hình 4). Trong Control Panel, bạn có thể vào Administrative Tools applet để tìm Local Security Policy editor, hoặc tìm kiếm nó trong Start menu. Khi Windows 7 được sử dụng với Active Directory, bạn có thể sử dụng Group Policy, một dịch vụ mạnh cho phép bạn tùy chỉnh, quản lý và triển khai các thiết lập cũng như sự ưu tiên trong triển khai phần mềm một cách dễ dàng, tuy nhiên bạn cần kết nối Windows 7 với miền tích cực và quản lý nó đúng cách.
Nếu cần cấu hình bảo mật theo chính sách thì đây là cách làm đơn giản nhất. Tuy nhiên ngoài ra bạn cũng có thể thấy nhiều công cụ cần thiết cho việc cấu hình bảo mật trong Control Panel hoặc trong MMC mà bạn thiết kế và triển khai. Microsoft Security Center (Windows Vista, XP) đã được sử dụng để tập trung hầu hết các chức năng bảo mật trước đây. Đây là thứ được thay thế bằng Action Center, và các hành động bảo mật hiện dễ tìm hơn nhiều, được quan sát và được chọn dựa trên sự cho phép của bạn. Cho ví dụ, như thể hiện trong Start menu (hình 3), hành động 'Check security status' khi được chọn sẽ tạo một danh sách các cấu hình bảo mật mà Windows 7 khuyến khích, chẳng hạn như nâng cấp hệ thống, hay một chương trình như antivirus (AV). Khi được chọn, bạn sẽ được gửi đến Action Center để bạn biết thêm các vấn đề cần quan tâm.
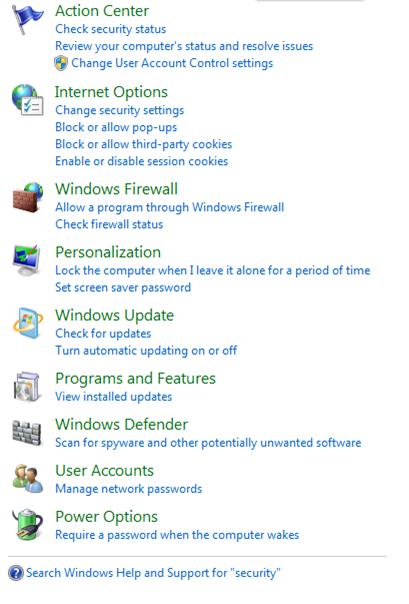
Hình 5: Cấu hình các hành động bảo mật và các tùy chọn trong Control Panel
Mẹo : Hình 5 hiển thị các hành động có trong Control Panel mà bạn có thể lựa chọn. Nếu kích Start menu, đánh ' security ' và kích liên kết Control Panel, bạn sẽ nhận được một danh sách các hành động và cấu hình bảo mật, đây là danh sách bạn có thể tùy chỉnh ngay lập tức với các tùy chọn dễ tìm và dễ truy cập.
Khi ở trong Action Center (hoặc nếu đang xem danh sách các hành động), bạn có thể chuyển xuống phần dưới danh sách và cấu hình những gì phù hợp với mình. Đây là những giới thiệu vắn tắt về các tùy chọn có thể được cấu hình trong danh sách của Action Center:
- Action Center – Action Center thay thế cho Security Center. Action Center là nơi bạn có thể chỉ định các hành động mà hệ điều hành có thể thực hiện. Với sự cho phép của bạn, các hành động có thể diễn ra. Ở đây bạn sẽ được thông báo rằng chưa thực hiện nâng cấp phần mềm Antivirus (ví dụ như vậy). Bạn có thể truy cập vào thành phần trung tâm để thực hiện các hành động có liên quan đến bảo mật cần thiết.
- Internet Options – Duyệt web với bất cứ hình thức nào cũng đều mở cửa cho các rủi ro Internet. Nếu sử dụng máy chủ proxy, sử dụng hành động lọc và kiểm tra web, cập nhật các bản vá lỗi mới nhất cho hệ điều hành, bạn vẫn có thể rơi vào tình huống mà ở đó bảo mật của bạn bị thỏa hiệp. Bên trong Internet Options Control Panel applet, bạn có thể chỉ định các vùng an toàn, chỉ cho phép các URL nào đó được phép truy cập, triển khai các thiết lập bảo mật nâng cao trong tab Advanced và,. Bản thân trình duyệt cũng có tính năng lọc Phishing để ngăn chặn các tấn công Phishing và các tùy chọn cấu hình khác chẳng hạn như InPrivate Browsing, tính năng ngăn chặn việc lưu lại các thông tin cá nhân của ban sau khi duyệt web, đặc biệt hữu dụng khi sử dụng một máy tính dùng chung.
- Windows Firewall – Giống như bất cứ phần mềm nào hoặc tường lửa phần cứng nào, Windows Firewall có thể làm chệch hướng các tấn công cơ bản và có thể được cấu hình ở 'mức tinh hơn' đạt mức kiểm soát cao cho những gì vào ra khỏi hệ thống máy tính của bạn khi kết nối với một mạng public hay private. Bằng cách vào Control Panel và chọn Windows Firewall, bạn có thể truy cập đến hầu hết các thiết lập cấu hình của tường lửa. Có thể kích liên kết Advanced settings trong hộp thoại để truy cập Firewall with Advanced Settings và các tùy chọn cấu hình. Với Windows 7, bạn còn có thể triển khai nhiều chính sách tường lửa đồng thời và sử dụng thứ bậc miền mới để cấu hình và quản lý tường lửa Windows dễ dàng hơn.
- Personalization – Tùy chọn Personalization là nơi bạn có thể thay đổi diện mạo bề ngoài của Windows, tuy nhiên nó cũng là nơi bạn cấu hình mật khẩu screensaver nếu muốn. Nếu chạy Windows 7 trong doanh nghiệp, người dùng nên biết cách khóa các máy trạm làm việc của họ bất cứ khi nào họ rời bàn làm việc hoặc sử dụng một thiết lập chính sách để thực hiện việc đó một cách tự động sau một khoảng thời gian không hoạt động nào đó, mặc dù vậy nếu quên, bộ bảo vệ màn hình đã được cấu hình sẽ yêu cầu đăng nhập lại có thể khá hữu dụng. Tại nhà, đây sẽ là tuyến phòng chống nếu bạn rời hệ thống của mình và quên khóa nó.
- Windows Update – Tất cả các phát hành phần mềm đều yêu cầu một số mức vá nhất định. Bạn có thể chuẩn bị, test và phát triển phần mềm hoàn hảo nhưng không thể tính toán hết được mọi thứ. Cũng vậy, các nâng cấp và phát hành mới cũng yêu cầu các nâng cấp cho hệ điều hành qua thời gian tồn tại của phiên bản hệ điều hành hiện hành. Do có nhiều tiến bộ trong hệ thống, nhiều yêu cầu cần thiết cho các kỹ thuật phát triển, nhiều lỗ hổng bảo mật mới được phát hiện theo thời gian, các nâng cấp driver cho hiệu suất và chức năng tốt hơn nên sẽ luôn có một nhu cầu cho Windows Update. Windows (và Microsoft) Update, hoặc các phiên bản quản lý bản vá của doanh nghiệp (WSUS,.) được sử dụng để kiểm soát và triển khai các nâng cấp. Các công cụ này được sử dụng để điều khiển, theo dõi và kiểm tra các nâng cấp hiện hành và tương lai cần thiết. Cấu hình sao cho nó có thể thực hiện nhiệm vụ này một cách tự động, hoặc bạn phải có thói quen thực hiện nó vì đây là một vấn đề thực sự quan trọng. Nếu bạn không vá hệ điều hành của mình những gì khuyến khích (đôi khi là yêu cầu), bạn có thể sẽ là đối tượng tấn công.
- Programs and Features – Ngoài việc kiểm tra và thấy những gì Windows Updates cài đặt, bạn cũng cần kiểm tra để xem những gì mình đã cài đặt vào hệ thống của mình một cách thường xuyên, đặc biệt nếu làm việc trên Internet hoặc download phần mềm từ các máy chủ web trên Internet. Cho ví dụ, bằng việc cài đặt một nâng cấp Java, nếu bạn không đọc các thông tin hiển thị trên màn hình một cách cẩn thân trong quá trình cài đặt, bạn có thể sẽ cài đặt cả toolbar trên hệ thống của mình, thứ sẽ được tích hợp vào trình duyệt web của bạn. Giờ đây, dù có được sự kiểm soát chặt chẽ hơn về điều đó, tuy nhiên vẫn nên kiểm tra một cách định kỳ để thấy những gì hiện được cài đặt vào hệ thống của mình.
- Windows Defender – Spyware là phần mềm được sử dụng chủ yếu cho các mục đích thương mại trái phép, nó sẽ thực hiện những thứ như phân phối một tải trọng trực tuyến, redirect trình duyệt của bạn hoặc gửi lại các thông tin trên hành động của bạn. Mặc dù phần mềm Antivirus có một số tùy chọn để chống lại hành vi này nhưng Windows Defender (hoặc các ứng dụng remove Spyware khác) có thể là một lựa chọn để dọn dẹp phần còn lại. Các Cookie mặc dù vô hại theo bản tính của nó, nhưng đôi khi lại bị thao túng với một vài lý do không đúng. Cần phải bảo đảm nâng cấp Windows Defender thường xuyên với các file định nghĩa mới và các nâng cấp cần thiết của nó để bảo đảm bạn có thể quét tất cả Spyware mới nhất. SpyNet cũng là một cộng đồng mà Microsoft nói về cách ngăn chặn các mối hiểm họa gây ra bởi Spyware.
- User Accounts – Việc quản lý các tài khoản người dùng là cốt lõi của việc truy cập an toàn máy tính cũng như mọi thứ chạy bên trong nó. Cho ví dụ, nếu tạo một tài khoản người dùng mới và gán nó cho nhóm Administrators, bạn sẽ có quyền truy cập toàn bộ vào hệ thống máy tính. Nếu cấu hình tài khoản đó là người dùng chuẩn thì các điều khoản mà được phép sẽ rất hạn chế và người dùng chỉ được phép thực hiện một số thứ cụ thể nào đó. Bạn cũng có thể cấu hình mật khẩu với chính sách mật khẩu tối thiểu để bắt buộc người dùng phải tạo một mật khẩu khó bị crack. Khi Windows Server 2008 và Active Directory được triển khai, bạn có thể truy cập một vào một miền nào đó mà khi truy cập sẽ cho phép cấu hình các điều khoản NTFS 'tinh hơn' cho thư mục và file cũng như các nguồn chia sẻ khác như máy in chẳng hạn.
- Power Options – Power Options Control Panel applet là nơi bạn có thể cấu hình các hành vi mặc định cho hệ điều hành khi không được cắm nguồn trực tiếp, đóng hoặc chuyển sang chế độ 'ngủ'. Cấu hình bảo mật để thiết lập là một mật khẩu được yêu cầu khi máy tính thức giấc từ trạng thái ngủ. Bất cứ khi nào có thể truy cập, bạn cũng cần xem xét một cách kỹ lưỡng.
Lưu ý : Start menu cũng có thể cung cấp nhiều thông tin về tài liệu có liên quan đến bảo mật trên hệ thống. Đây là một địa chỉ hữu dụng khi tìm kiếm tài liệu chẳng hạn như một chính sách bảo mật,.
Bạn có thể 'làm vững chắc' một cách nhanh chóng Windows bằng cách download các công cụ và tài liệu trực tiếp từ Microsoft. Cho ví dụ, nếu muốn cấu hình mức bảo mật cơ bản cho Windows 7, bạn có thể dễ dàng download template bảo mật cơ bản để sử dụng, chạy nó và có được hầu hết các thiết lập bảo mật đã được điều chỉnh. Hình 6 cung cấp một Windows 7 Security Baseline Settings template với các entry được chia tab cho việc thẩm định tài khoản người dùng, BitLocker và . Tìm hiểu thêm trong phần các liên kết tham chiếu ở cuối bài để tăng truy cập vào nó.
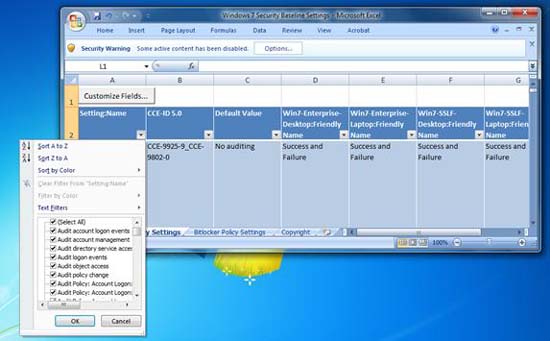
Hình 6: Cấu hình bảo mật cơ bản từ các Template của Microsoft
Lưu ý tùy chọn 'Security Warning' ở phía trên toolbar (ribbon) của Microsoft Office Excel 2007, đây là tùy chọn ngăn chặn bạn sử dụng template bằng cách vô hiệu hóa Macro cho tới khi bạn chú tâm đến Security Warning (xem trong hình 6). Ở đây, Security Macros đã bị vô hiệu hóa và được yêu cầu cho ứng dụng của template này. Đây là một ví dụ hoàn hoản cho bảo mật và sự linh hoạt. Để có được sự linh hoạt trong ví dụ này, bạn cần tắt bỏ hoặc hạn chế mức bảo mật được áp dụng cho nó. Chọn thủ công tùy chọn này để chạy, hoặc vô hiệu hóa sự bảo vệ, chạy Macro sau đó nâng mức bảo mật một lần nữa để giữ bảo mật đúng cách sẽ có được cài đặt mẫu.
Hệ thống của bạn đã sẵn sàng và bạn đã cấu hình một số tính năng bảo mật cơ bản, lúc này bạn nên xem xét cách quản lý nó, cũng như kiểm trra sự xâm nhập, malware và các vấn đề khác được phát hiện thấy trong các bản ghi sự kiện.
Lưu ý : Bạn nên lưu ý rằng Windows 7 có một tùy chọn mang tên XP-mode, đây là tùy chọn được sử dụng cho việc giải quyết các vấn đề liên quan đến sự tương thích ứng dụng cho các ứng dụng XP cũ. Như những gì chúng ta đã thảo luận về chủ đề ảo hóa bên trên, khi xem xét việc sử dụng chế độ XP-mode, bạn hiện đang cài đặt Virtual PC trên Windows 7 và chạy một instance của XP trên Virtual PC. Nếu sử dụng XP-mode, hãy bảo đảm làm vững chắc bất cứ VM nào đang chạy trên các máy ảo theo cách mà bạn làm với hệ điều hành cơ bản. Các hành động gồm có bảo vệ AV, chính sách khóa, gói dịch vụ, nâng cấp phần mềm,. Bạn có thể cung cấp mức bảo mật qua ảo hóa nhưng mức bảo mật đó là không hoàn tất, vì vậy bạn vẫn cần đến một số bước 'làm vững chắc', thậm chí nếu ảo hóa được sử dụng.
Conclude
Hệ thống Windows 7 gia đình có thể được khóa chặn và quản lý một cách dễ dàng. Bạn có thể cấu hình nó một cách an toàn để được truy cập trên Internet từ một vị trí từ xa. Windows 7 có thể được trang bị một lá chắn nếu bạn thực sự muốn 'làm vững chắc' để khóa chặn hoàn toàn các điểm có thể xâm phạm. Tuy nhiên nó có thể vẫn trở thành đối tượng tấn công và chắc chăn sẽ là vậy nếu bạn sử dụng máy tính trên Internet, một ví dụ như vậy. Do đó chúng ta cần lập kế hoạch cho những khả năng có thể xảy ra và làm vững chắc Windows 7 theo đó.
Khi xem xét đến việc sử dụng Windows 7, trong tình hình các tấn công và khai thác ngày nay, các tùy chọn bảo mật và sự linh hoạt là ưu tiên hành đầu cho việc tạo quyết định. Windows 7 rất an toàn nhưng không phải an toàn 100%. Bạn cần phải biết áp dụng kiến thức, các công cụ khác và các cấu hình nâng cao để bảo mật mọi khía cạnh của nó và sau đó nâng cấp và kiểm tra chúng một cách thường xuyên. Đây là một công việc rất quan trọng và đáng giá nếu bạn muốn tránh tấn công. Thêm vào đó Windows 7 cũng có nhiều cải tiến về bảo mật và có thể được cấu hình để khôi phục nhanh chóng.
Các nguyên lý bảo mật cơ bản chẳng hạn như Defense in Depth phải được áp dụng kết hợp với những hướng dẫn bảo mật và các hành động tốt nhất để không chỉ áp dụng cho việc bảo vệ mà nó còn là nhiều lớp che đậy toàn bộ kiến trúc và mã chương trình.
Trong phần này chúng ta mới chỉ đụng chạm đến bề mặt trong phần này, có rất nhiều kiến thức khác mà chúng ta cần phải nghiên cứu thêm, tuy nhiên hy vọng những thông tin này sẽ giúp ích cho bạn. Để tìm hiểu thêm, bạn có thể đọc các liên kết tham chiếu bên dưới, đây là các thông tin chi tiết về các công cụ miễn phí, các template và hướng dẫn. Và không quên theo dõi đón đọc phần 2 và 3 sẽ được chúng tôi phát hành tới đây.
Các liên kết tham chiếu
- Windows 7 Security Features
- Windows 7 Security Enhancements
- target=_blankWindows 7 Security TechNet Blog
- target=_blankWindows 7 Security Checklist
- Ten Things IT Professionals Should Know About Windows 7
- Microsoft Malicious Software Removal Tool and Safety Assessment Scan
- Windows 7 System Requirements
- Virtual PC and XP-Mode
- Windows 7 Compatibility Center
- Windows Performance and Hardware Compatibility
- AppLocker
- Download and Install Microsoft Security Essentials for Windows 7
- BitLocker Drive Encryption Step-by-Step Guide for Windows 7
- Windows Trusted Platform Module Management Step-by-Step Guide
- Microsoft Security Compliance Management Toolkit
- Windows Server 2008 Security Compliance Management Toolkit
- Enterprise Security Management with Forefront
- Network Access Protection (NAP)
- Cisco Network Admission Control (NAC)
- Introduction to DNSSEC
- DNSSEC Components and Terminology
- The Trustworthy Computing Security Development Lifecycle (SDL)
- Common Criteria Certification: Microsoft Windows Platform Products
- Responding to IT Security Incidents (Incident Response Planning)
- An Introduction to Kernel Patch Protection
- Data Execution Prevention
- Windows Integrity Mechanism Design
- Understanding and Working in Protected Mode Internet Explorer
- Strategies for Managing Malware Risks
- Security Risk Management Guide and Toolkit
- Security Monitoring and Attack Detection
- Windows 7 and Windows Server 2008 R2: Controlling Communication with the Internet
- Leverage Windows 7 Security in Business Environments
- Windows 7 Security in the Enterprise
- Request for Comments (RFC) Search