Commands in CMD are common and useful in Windows 10
CMD - Command Prompt is a command-line interface application used to execute batch files, perform tasks quickly, help you troubleshoot and solve some Windows problems when the system crashes. However, not all Windows commands are useful and often must be done. In this article, TipsMake.com will summarize for you some of the common and useful CMD commands in Windows 10, please refer.
To open Command Prompt, press Windows + R to open the Run dialog box, then type cmd and press Enter.

Here are the common commands in CMD:
1. PING command.
Uses : Use up Ping to check whether a computer has no network connection. The PING command sends packets from your computer to the destination computer, you can determine the connection status or determine whether the computer is connected or not.

Syntax : ping ip / host / [/ t] [/ a] [/ l] [/ n]
- Ip: IP address of the machine to be checked; host is the name of the computer to check the network connection (can use the IP address or the name of the computer).
- / t: used to keep the computer "ping" to the destination computer, press Ctrl + C to stop.
- / a: get the IP address from the computer name (host).
- / l: specify the width of the sending packet to check.
- / n: Specify the number of packets to send.
2. Tracert command.
Usage : Command helps you see the path of packets from your computer to the destination computer, see which packets go through which servers or routers .
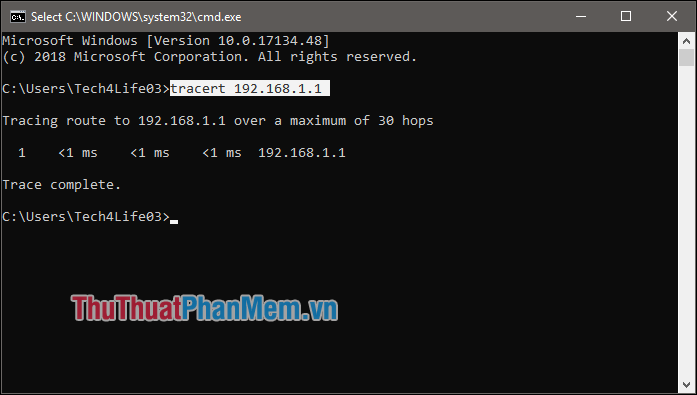
Syntax : tracert ip / host
- ip / host: IP address / computer name.
3. Netstat command.
Uses : List outbound connections to your computer.
Syntax : Netstat [/ a] [/ e] [/ n]
- / a: Displays all connections and ports that are listening.
- / e: Ethernet statistical information.
- / n: Display the address and port numbers.
You can refer to other parameters by typing Netstat /?
4. Ipconfig command.
Uses : Display the IP configuration of the computer you are using (host name, IP address, DNS .).
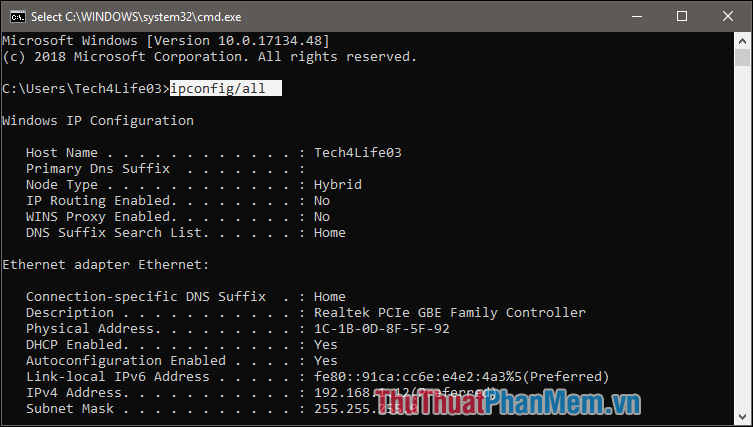
Syntax : ipconfig / all
5. Shutdown command.
Uses : Turn off and restart the computer.
Syntax (Windows 7):
- Shutdown: Shutdown -s -t [a]
- Restart computer: Shutdown -r -t [a]
+ a: shutdown time (units seconds).
6. The DIR command.
Uses : View files, folders.
Syntax : DIR [drive:] [path] [filename]
- Path: Path to file, folder.
- Filename: File name.
7. DEL command.
Uses : Delete files.
Syntax : DEL [/ p] [/ f] [/ s] [/ q] [/ a [[:] attributes]] "file name to delete"
- / p: Display file information before deleting.
- / f: Delete files with read-only attribute.
- / s: Delete the file in all directories that contain it.
- / q: Delete without asking.
- / a [[:] attributes]: Delete by file attributes (R: Read-only files, S: System files, H: Hidden files).
Delete all files *. *
8. COPY order.
Uses : Copy files from one folder to another in the computer.
Syntax : COPY "address to copy" "address of file copy" / y
- / y: Copy without asking.
9. RD command.
Uses : The RD command helps you delete directories.
Syntax : RD / s / q "directory to delete"
- / s: Delete the entire directory.
- / q: Delete without asking.
10. MD command.
Use : Create a new folder.
Syntax : MD "path to save the file to create" "directory name to create"
For example: md "C: tailieu" (create tailieu directory in drive C).
11. TASKKILL command.
Uses : Turn off a running application.
Syntax : taskkill / f / im "application name" .exe.
For example taskkill / f / im Skype.exe (disable Skype application).
12. REG ADD command .
Uses : Create, edit the Registry.
Syntax : REG ADD KeyName [/ v ValueName] [/ t Type] [/ s Separator] [/ d Data] [/ f]
- KeyName: Path to the Key.
- / v ValueName: The value name to create.
- / t Type: Data type.
- / d Data: Value value.
13. REG DELETE command.
Uses : Delete the value in the Registry.
Syntax : REG DELETE KeyName [/ v ValueName] [/ f]
- [/ v ValueName]: The value name to delete.
14. REGEDIT.EXT command.
Uses : Run the .reg file.
Syntax : Regedit.exe / s "where the .reg file is not"
- / s: No need to ask.
15. ATTRIB command.
Uses : Set properties for files and folders.
Syntax : ATTRIB -a -s -h -r "file, directory" / s / d
or ATTRIB + a + s + h + r "files, directories" / s / d
- + sign: Add the attribute.
- Mark -: Remove the attribute.
- a: Archive (storage properties).
- s: System (system property).
- h: Hidden (hidden attribute).
- r: Read- only (attribute read only).
- / s: Perform with all files located in the directory and subfolders.
- / d: Set properties for directories and subfolders.
Above are some useful and common CMD commands Thuthuatphanmem.vn introduce to you. Thank you for watching the article!
 How to schedule a computer to shutdown by Internet Download Manager
How to schedule a computer to shutdown by Internet Download Manager How to time off the computer very quickly and easily by the command CMD, no need to install additional software
How to time off the computer very quickly and easily by the command CMD, no need to install additional software Create USB Boot with Hiren's Boot
Create USB Boot with Hiren's Boot How to take a laptop screen, take a screenshot of the computer screen
How to take a laptop screen, take a screenshot of the computer screen Instructions on how to rename files in batches very quickly
Instructions on how to rename files in batches very quickly