When should I use Wi-Fi and when should I use wired networks?
Choosing between Wi-Fi and wired LAN (Ethernet) is the choice between convenience and speed / stability for your connection. In some cases, the difference will be enough for you to choose Ethernet.
7 things to do immediately with newly purchased computers
Obviously, you cannot connect a smartphone or tablet to the Internet via . network cable. However, choosing Wi-Fi or network ( Ethernet ) can offer a different experience for devices such as desktops, desktops, game consoles ( Xbox, PlayStation ), and video signal players. other types of large smart devices.
The difference when surfing the web, playing YouTube and downloading files is not much
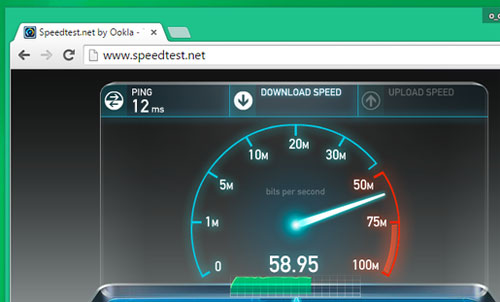
Speedtest.net testing on Wi-Fi and Ethernet will give similar results
It is clear that carrying wires is faster than Wi-Fi. But, in terms of actual use, the difference may not mean much to you. Thanks to the recently released Wi-Fi standards such as 802.11n or 802.11ac, wireless networks can reach a maximum speed of up to 150 Mb / s ( standard ) or 866.7 Mb / s ( ac standard ). . Note that these are theoretical numbers, but the fact is that you no longer need to worry about Wi-Fi data download speeds when using smartphones and tablets.
However, even 802.11ac Wi-Fi networks are still significantly slower than wired networks: the high-end Cat-6 Ethernet wire can deliver a maximum connection speed of 10 Gb / s, while the wired network The common Cat-5e can carry up to 1 Gb / s connection speed.
But if you only use your devices to surf the web or even to download digital content, the difference between Wi-Fi and Ethernet will be negligible. The reason is that connecting a router / modem to the Internet will always play the " bottleneck " role in your network. Almost certainly, your Internet can't reach the 150 Mb / s limit of the 802.11n Wi-Fi standard, and so changing from Wi-Fi to a wired network won't be much different. . Tests to measure Internet speed from speedtest.net or other speed measurement applications will all confirm this.
Copy files between local machines

You should not use Wi-Fi to copy files from one PC to another
If you often have to copy files between computers / devices in the same network, choosing Ethernet instead of Wi-Fi will save you a lot of time. For example, when copying from a laptop's hard drive to a desktop hard drive via an Ethernet network using a regular Cat-5e cable, in 1 second you will copy about 125 MB of data. The copy speed in this case will actually be determined by the read / write speed of the hard drive. Obviously, the Internet connection does not play any role in this case at all.
Conversely, if you use 802.11n Wi-Fi, you will only copy over 18 MB of data. The difference here is very clear.
Gaming
The latency (latency) of the connection network is a different factor that needs to be taken into account when installing the computer network in the room. The latency parameter ( often called a "ping" name ) will have the most impact on gamers. In the game, you will need to minimize the delay from doing the action until your action is recorded by the game ( for example, since you clicked until the gun in the game is pulled ). .
In this case, you should also prioritize the wired network. If you use a Wi-Fi network, you will lose additional delay from your device to the Wi-Fi router. Network cables often have significantly lower latency and therefore will be a better choice for gamers on PC, Xbox and PlayStation.
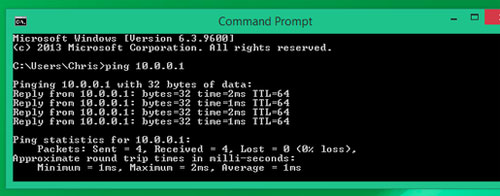
If you check that the latency ('time') difference is too large between Wi-Fi and Ethernet, gamers should switch to using a wired network.
To accurately measure the difference in latency between Wi-Fi and home wiring, you can use Windows 'ping' command. First, connect to the router via Wi-Fi and ping the router's IP address ( usually 192.168.1.1 or 192.168.0.1 ). Then, connect to the router via the network wire and repeat the ping test. You will measure whether the delay caused by Wi-Fi is significant.
Another point to keep in mind is that, like all types of radio waves, Wi-Fi may experience interference, especially in apartment buildings with many adjacent apartments. You will also have to find reasonable locations for your router to have as wide a coverage as possible, while avoiding objects that may interfere / interfere. Different locations in the house will obviously give different Wi-Fi wave quality.
VnReview once had an article to help you improve the quality of Wi-Fi in the house. However, the fact remains that we can hardly measure the latency when using Wi-Fi to play games, and therefore the choice for users who need stable network quality will still be Ethernet.
Increase the level of convenience and aesthetics for the house

Choosing between Wi-Fi and wired LAN (Ethernet) is the choice between convenience and speed / stability for your connection. In some cases, the difference will be enough for you to choose Ethernet.
The only reason why Wi-Fi becomes the most popular intranet choice today is clear: usability. Conventional routers can cover most of your home, allowing you to connect smartphones, tablets and laptops from dining tables, beds or even toilets. On the contrary, most users will not want to go to the network from room to room. The limited number of Ethernet ports ( typically 4-5 ports ) on the router will also be another factor that users need to consider when connecting home computers.
Security
Another reason to prioritize Ethernet is security. Even the most popular Wi-Fi encryption standards such as WPA2-PSK can still be hacked. If you need absolute protection for your communications, stick with wireless routers.
Conclude
It is undeniable that the Wi-Fi connection will give you the most comfortable experience, helping to reduce the number of necessary wiring in the house and expand the range of smart devices. But, in some cases, you still need the speed and stability of the network wire.
With large devices, rarely needing to move positions such as desktops, game consoles or set-top boxes ( TV signals ), you can connect to the network to enjoy the experience. more stable number. Network devices now also allow you to use a combination of Wi-Fi and Ethernet, so you can wire your PC to your PC and enjoy the convenience of Wi-Fi with your smartphone, tablet.
In short, Ethernet and Wi-Fi all have their own strengths, but sometimes the difference may not be much - consider your use cases and perform speed / latency measurements to determine Determine as accurately as possible!