Learn about local area networks - LAN: Ethernet - Part II
What is Ethernet?
Ethernet is a local area network developed and developed by Xerox, Intel and Digital equipment. Ethernet is the most popular network for small networks today. EthernetLAN is built according to the 7-layer standard in the network structure of ISO, Ethernet data transmission network allows multiple network types of computers including mini computers.
Ethernet has the following key specifications:
Ethernet uses a logical bus network structure that all nodes on the network are connected to equally. Each data packet sent to the receiving place is based on the address specified in the package. Ethernet uses CSMA / CD (Carrier Sense method of Multiple Accesswith Collision Detection) to handle simultaneous access to the network. The factors that limit network size are mainly the density of traffic on the network.
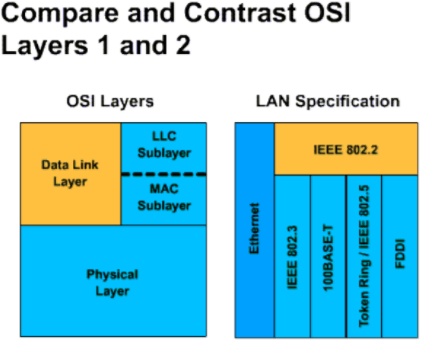
Ethernet network types
- 10Base2: Also called thin Ethernet because it uses thin coaxial cable. The maximum length of the network segment is 185m.
- 10Base5: Also called thick Ethernet because it uses thick coaxial cable. The maximum length of the segment is 500m.
- 10BaseF: Using fiber optic cable.
- 10BaseT: Use UTP cable. 10BaseT is commonly used in star-shaped structures and has a limit of one segment of 100m.
Network TOKEN RING
Another major LAN technology currently in use is Token Ring. The principle of the Token Ring network is defined in the IEEE 802.5 standard. The Token Ring network can run at 4Mbps or 16Mbps. Access method used in Token Ring network is called Token passing. Token passing is a defined access method in which conflicts are prevented by only one station at a time that can be transmitted. This is done by passing a special signal bundle called a token (token) that rotates from one station to another. A station can only send data bundles when it receives a code that is not busy.

Next: Local area network - LAN: Devices - Part III
Previous part: Local area network - LAN (Part I)
See more:
- Distinguish 10 types of popular computer cables
- Basic information about network equipment