What is VLSM?
Variable Length Subnet Masking - VLSM - is a technique that allows network administrators to divide IP address space into different sized subnets.
What is Variable Length Subnet Mask (VLSM)?
Variable Length Subnet Masking (VLSM) is equivalent to dividing subnet (subnet). That means that VLSM allows network engineers to divide an IP address space into a system of different sized subnets, helping to create subnets with very different host numbers, without distracting. Charge large amounts of IP addresses.
To further simplify, VLSM is to divide the IP address into subnets (at multiple levels) and allocate it according to individual needs on the network. VLSM can also be called an unclassified IP address. The classification of IP addresses according to the general rule has been proven to waste IP addresses.
How VLSM works
Before you learn about VLSM, you must be very familiar with the IP address structure.
A subnet mask determines the size of the subnet (the number of host addresses in the subnet).Fixed-Length Subnet Masking (FLSM) creates subnets of the same size. But in some cases, the subnet will have too many or few hosts. FLSM results in a number of subnets having multiple 'orphaned' addresses, while many subnets own too many unsuitable hosts. When VLSM is enabled, a large subnet can be divided into a smaller set of subnets, which can be used to handle smaller host groups.

The best way is that you should learn how to divide IP addresses through examples.
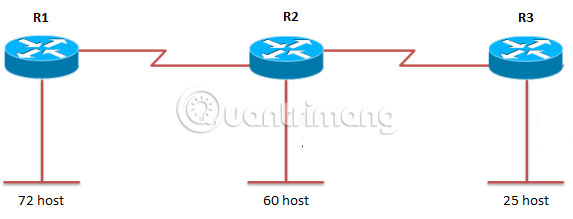
For example, consider a traditional Class C address space like 192.168.1.0 and an organization that has 4 computer groups: Data Center with 75 hosts; contact center with 50 hosts; The floors operate with 25 hosts and the operating layer with 20 hosts.
According to the fixed division method, dividing the 255 host addresses available into 4 subnets will only support 62 hosts on each subnet, not enough to meet the needs of the data center, but the excess is needed for the floors. operating and operating. Using VLSM, space is first divided into 2 parts, with each subnet can handle 126 hosts.
A subnet includes a data center. The other subnet is divided into two, providing two subnets for the subnet, with 62 hosts. One includes a contact center, the other is split in half, creating two smaller subnets with 30 hosts, to cover the needs of the operating and operating floors.
To use VLSM, network administrators must use routing protocols to support it, such as Routing Information Protocol v2 (RIPv2), Open Shortest Path First (OSPF), and Intermediate System-to-Intermediate System (IS-IS ), Enhanced Interior Gateway Routing Protocol (EIGRP) and Border Gateway Protocol (BGP).
Summary of Variable Length Subnet Mask deployment:
- Subnetting allows you to allocate addresses effectively by taking a large domain and dividing it into smaller pieces for easier management.
- VLSM allows you to allocate IP addresses more effectively by adding multiple layers based on the hierarchy.
- The benefits of route summarization (the method of minimizing the number of routing tables in the IP network) include smaller routing tables and the ability to isolate topology changes.
VLSM has a similar concept and purpose with the Classless Inter Domain Routing (CIDR), allowing a single Internet domain to have an address space that does not match the traditional address classes. The initial VLSM is defined in IETF RFC 1812.
 What is the Password Spray?
What is the Password Spray? What is CIDR?
What is CIDR? What is Segurazo Antivirus? How to remove Segurazo Antivirus
What is Segurazo Antivirus? How to remove Segurazo Antivirus What is syntax error?
What is syntax error? Learn about fileless malware Astaroth
Learn about fileless malware Astaroth What is DHCP error? How to overcome it?
What is DHCP error? How to overcome it?