What is CIDR?
CIDR, short for Classless Inter Domain Routing, is an IP addressing scheme that improves IP address allocation. CIDR replaces the old system based on classes A, B and C. CIDR significantly extends the IPv4 "life span", as well as slowing the rise of routing tables.
In this article, you will discover how CIDR really works, as well as provide examples to better illustrate the concepts explained.
Incident with class-based IP address allocation
An inefficient method of allocating old IP addresses and depleting the availability of IPv4 addresses is faster than necessary. Full routing system includes classes A, B and C:
- Class A - Over 16 million host identifiers
- Class B - 65,535 identifies the host
- Class C - 254 host identifiers
The problem often occurs when an organization requires more than 254 servers. This case will no longer fall into Class C but instead will be Class B. This means that the organization will use Class B licenses even though they have less than 65,535 hosts. Therefore, if an organization only requires 2,500 hosts, they will waste about 63,000 hosts if they hold a Class B license. This will significantly reduce the availability of IPv4 addresses unnecessarily.
How does CIDR work?
CIDR is based on Variable Length Subnet Masking (VLSM). This allows CIDR to identify prefixes of arbitrary length, making it much more efficient than the old system. CIDR IP address consists of two sets of numbers. The network address is written as a prefix, as you would see in a normal IP address (for example, 192.255.255.255 ). The second part is the suffix indicating how many bits in the entire address (eg / 12 ). Put these two parts together, a CIDR IP address will look like this:
192.255.255.255/12 Network prefixes are also specified as part of the IP address. This varies depending on the number of bits required. Therefore, with the above example, we can say that the first 12 bits are the network part of the address, and the last 20 bits are for the host address.
Wikipedia's CIDR IPv4 block table below provides a clear overview of how different address formats output a different number of addresses. The format is also classified according to typical usage.
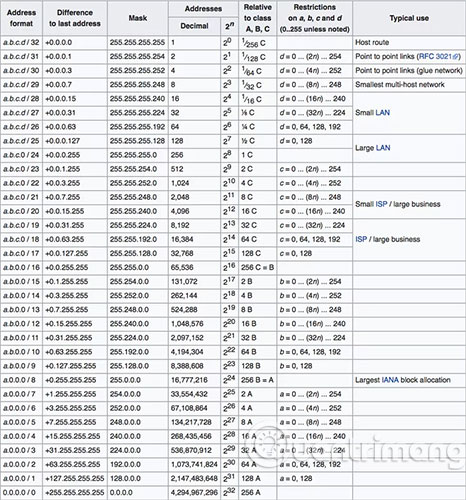
Example of CIDR
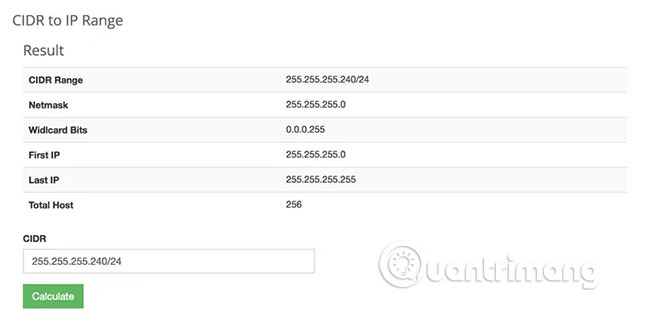
The article mentioned how the CIDR IP address looks. Now, let's look at a few examples to analyze their format. The CIDR Calculation tool is great if you want to easily determine the IP range that the CIDR address is equivalent to. Just enter the CIDR address into the tool and click the Calculate button . This will return information like First IP (first IP), Last IP (last IP), Number of Hosts (number of hosts), etc.
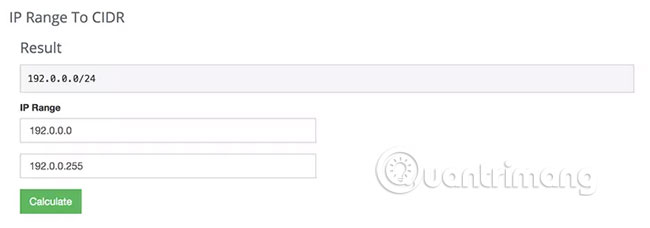
Similarly, you can also convert the IP range to CIDR. For example, suppose you want the CIDR notation for IP ranges between 192.0.0.0 and 192.0.0.255. You simply enter these two numbers into the IP Range tool to CIDR and let it return the corresponding CIDR address.
CIDR is a great way to improve the efficiency of IP address distribution. The important thing for IPv4 is that IP addresses are quickly exhausted. IPv6 is currently being deployed and although the IP address is no longer a problem, CIDR will continue to be used. Read the article about TipsMake.com 's IPv6 address to learn more about the differences that are available in the latest version of Internet Protocol.
 What is Segurazo Antivirus? How to remove Segurazo Antivirus
What is Segurazo Antivirus? How to remove Segurazo Antivirus What is syntax error?
What is syntax error? Learn about fileless malware Astaroth
Learn about fileless malware Astaroth What is DHCP error? How to overcome it?
What is DHCP error? How to overcome it? What is Fileless Malware?
What is Fileless Malware? What do you know about Windows NT?
What do you know about Windows NT?