What is Journaling File System?
Each operating system uses its own file system to store data. Windows uses NTFS, macOS uses APFS, and most Linux distributions use Ext4. Although these file systems are fundamentally different, one feature that exists in all of these file systems is journaling.
Let's find out more about journaling file system through the following article.
What is journaling?
Imagine every file on your computer is a unique library catalog, including magazines, newspapers or documents. Each new document added to a catalog changes its information slightly. Instead of searching the entire library to find an item, you just have to check the relevant category.
Journaling in computer file systems works very similar. Its purpose is to keep track of uncommitted changes to the file system. Even after a crash or unexpected shutdown, you can still access the latest file version with a lower probability of failure.
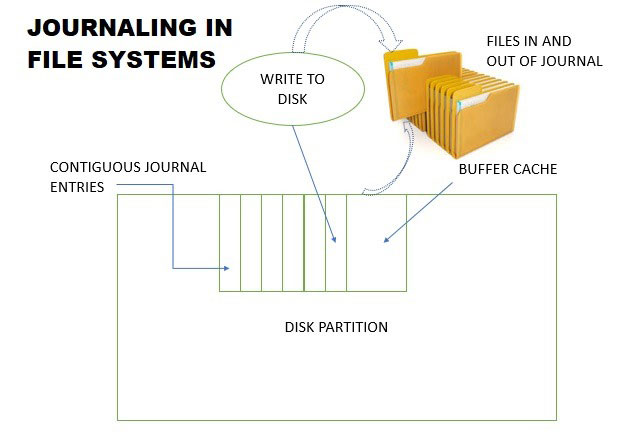
The term 'journal' comes from the similarity to a diary. Any changes you record in the log will be archived by date and time. In a similar way, journaling allows all updates to a file to be stored in an adjacent section of the drive.
These updates do not need to be physically adjacent. Actually, the recorded items are scattered on the drive. But instead of accessing them randomly, they are available in a log-like sequence, thousands of times faster.
The definitions
Depending on the operating system, there are different types of journaling that the article will discuss below. But first, we need to understand some terms.
- Tebibyte (TiB): We all know what a gigabyte is. 1 tebibyte (TiB) = 1024 gigabytes. TiB is one of the default units to represent great values in file storage. Additionally, 1 TiB = 1,09951 terabytes (TB).
- Pebibyte (PiB): 1 pebibyte (PiB) is equivalent to 1024 TiB or about 1 million gigabytes. This is really a great value.
- Cluster : Data cluster is the smallest unit of disk space that can be used to store a file. It can range from 512 bytes for a sector to 64KB for 128 sectors.
1. NTFS
New Technology File System (NTFS) is Microsoft's default journaling system for Windows and Windows Server. It uses log files and checkpoint information to restore the stable values of the file system after reboot.
NTFS supports large volumes of data. For 4KB cluster capacity, it can hold 16TiB data. For 64KB cluster capacity (maximum), NTFS can hold 256TiB data with 256TiB as the maximum file size.
Today, NTFS fixes any errors in online files through what is called 'Self-healing NTFS'. Windows 10 users may still remember the downtime experience caused by Chkdsk. In the latest NTFS Self-healing update, the problem has been resolved online and no downtime occurred.
2. Ext
The Extended File System (Ext) is a journaling system for Linux. It was inspired by the Unix File System (UFS) and has gone through 3 versions since its appearance in the early 90s.
- ext2 was originally used in Debian and Red Hat Linux. Ext2 is still used in flash media such as SD cards and USB. It can hold 2 to 32TiB data with a maximum cluster size of 8KB.
- ext3 is used with Linux, BSD and ReactOS. The capacity limits are similar to ext2.
- ext4 is the latest version of Ext, it is used by BSD, PowerPC and most current Linux distributions. Capacity limit is 1024PiB or about 1 million TiB. The largest cluster size is 64KB.
3. APFS
Apple File System (APFS) is used with macOS High Sierra, iOS 10.3 or above and some other systems. It supports up to 8000PiB, about 8 times larger than Ext4.

The main capabilities of APFS include creating snapshots, like a copy of the system at a specific point. Like NTFS, it uses checksum to ensure data integrity and protect against system failure, using an approach called 'copy on writer'. Besides, APFS uses whole drive encryption.
Journaling in file systems is a basic protection against system failures and sudden shutdowns. By recording changes quickly, users can ensure that all changes to the files are recorded and are not lost when the power is turned off or the computer crashes.
You should read it
- ★ How to fix corrupted Windows NTFS file system with Ubuntu
- ★ IOS 10.3 update will help free up memory capacity for iPhone / iPad
- ★ What is NTFS? What is FAT32? Compare NTFS and FAT32
- ★ Disable NTFS file compression to speed up Windows computers
- ★ How to enable or disable NTFS file encryption in Windows