What is Mbps?
Megabits per second (Mbps) is a measure of network bandwidth and throughput. Each megabit is 1 million bits.
Mbps belongs to a family of metrics used to measure power and data transfer rates. Units less than Mbps are kilobits per second (Kbps), with the kilo prefix representing 1000 bits per second and greater than Mbps being gigabits per second (Gbps), with the giga prefix only 1 billion bits per second. Using these figures, 1000Mbps is equivalent to 1Gbps.
A megabit is one million binary or 1,000,000 pulses (bits).
How is Mbps different from MBps?
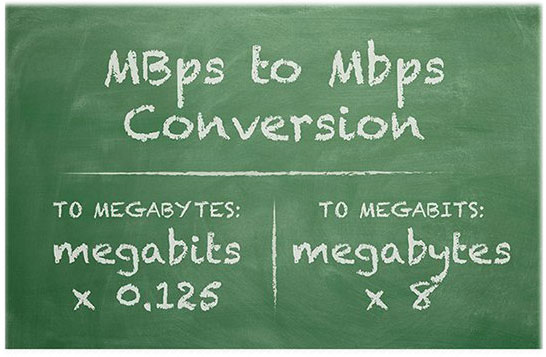
Although they share the same abbreviations, Mbps and MBps have different meanings. MBps stands for megabytes per second, with the suffix byte referring to a unit of measurement for file size. In contrast, Mbps represents the capacity in bits of the network connection.
1 bit does not have the same capacity as 1 byte, so Mbps and MBps are not interchangeable. Each byte contains 8 bits. The following formulas can be used to convert each metric:
Calculate download time
It should be noted that adding more Mbps bandwidth does not guarantee faster transmission, including upload and download speeds. Bandwidth is a measurement of network capacity - meaning the maximum amount of data can be transmitted in a second. Factors like congestion and latency can reduce connection speed. Internet service providers and network devices often advertise certain Mbps, which suggests a theoretical maximum, but is difficult to achieve at all times outside the laboratory.
It is possible to estimate download time using the formulas provided above. For example, to download a 100MB audio file via a 100Mbps Internet connection, the following calculations help determine the approximate download time of this audio file:
- Convert megabytes in file size (100MB) to megabits: 100 × 8 = 800 megabits
- Divide that sum by the connection speed (100Mbps): 800: 100 = 8 seconds
How are Mbps network connections classified?
The most common Mbps speeds provided by Internet service providers are:
- 8Mbps
- 16Mbps
- 32Mbps
- 50Mbps
- 100Mbps
For network equipment providers, devices such as switches are often advertised as "10 / 100Mbps", meaning their ports can support 10 and 100Mbps Ethernet connections.
You should read it
- ★ Smart light model can transfer internet data through light at speeds up to 250Mbps
- ★ The program helps users to check DDoS malware
- ★ Korean mobile Internet speed is 10 times faster than Vietnam
- ★ Qualcomm released three new Snapdragon processors for mid-range phones
- ★ Medical discovery: 'Drinking clean water increases the risk of asthma'