What is DNS and DNS Lookup?
When surfing the web you will often encounter 3 DNS words, then questions like Google DNS is how, DNS anti-domain poison is like, DNS help to Facebook, the site is blocked, beyond the firewall? Even when looking for ways to speed up the network, you get a solution to change DNS.
So what is DNS in essence? What role does it play and why should you care about it? Besides DNS there are many additional concepts, one of which is DNS Lookup. And in this article we'll learn about both DNS and DNS Lookup as well as how DNS works and a small part of DNS is D (Domain).
LEARN ABOUT DNS, DNS LOOKUP
- 1. What is DNS?
- 2. How does DNS work?
- Example 01:
- 3. What is Domain (in DNS)?
- 4. DNS Lookup working mechanism
- Example 02:
1. What is DNS?
DNS is a Domain Name System, abbreviated for Domain Name Servers, that translates Internet domain names and hostnames to IP addresses (helping servers and network devices understand) and vice versa. On the Internet, DNS automatically converts domains we type into the address bar on a web browser into an IP address.
- Learn about DNS Hijacking
2. How does DNS work?
Before we start, it is good to know the basics of how DNS works. When you enter the URL of a web address like quantrimang.com , this URL needs to be compiled into a numerical IP address so that web servers and Internet routers can understand. For example, if you enter the address quantrimang.com it will be compiled by the DNS server to the address 65.182.110.189.
We all know that the number of websites today on the Internet is unlimited. And every website can have multiple sub-domains, and it's impossible to remember the corresponding IP addresses of those websites. This is a major reason for us to use the domain name - Domain instead of entering the website's IP address into the browser (in the technology world, we use the alias term to refer to the domain).
Out there, there are many systems that are working at full capacity to resolve domain names via IP addresses and transfer data back to users, which is DNS. When you enter quantrimang.com in the address bar on the browser, all content, photos, text . on TipsMake.com website will be displayed for us. And that is the operation of DNS - Domain Name System .
Thereby, you can imagine that the working mechanism of DNS is to distribute, transmit information and data containing information that matches the domain name to the corresponding IP address of the website.
As mentioned above, domains and sub-domains are also known under alias names. Server systems, servers store information about addresses and different aliases are called Name Servers. And there are 2 main server types that serve the Domain Name System:
- Root Server : contains information about TLD (part of the domain).
- Another server processes key information about domain, sub-domain.
To make it easier to understand, we will go through a specific example.
Example 01:
In the case of abc.xyz.com , the Root Server will contain information about xyz as a tail form (* .com), besides that some Name Servers will contain data about xyz.com . Since you manage and store abc.xyz.com , this address may be on this or another Name Server . And if you add a sub-domain to abc.xyz.com , this new address may be the same or different from the data on the Name Server (depending on the server you are hosting). This ambiguous "relationship" is easier to understand through the diagram below:
- xyz contains com.
- abc is in xyz.com.
If you add a sub-domain qwe to abc.xyz.com:
- qwe will belong to abc.xyz.com
To set the address to qwe, the Domain Name System Service system will have to resolve some of the following:
- .com
- .xyz.com
- .abc.xyz.com
- .qwe.abc.xyz.com
And this is just a very small case where the Domain Name System Service does not use any cache (perhaps we will discuss caching in later articles). The chart above shows that the last address will be qwe.abc.xyz.com, DNS will have to review the entire DNS database up to 4 times . This will become more complicated when different parts of the URL are different on each Name Server system. But with the Internet speed today, in the slowest case, the resolution of the IP address and the content display of the website only takes a few seconds. Please rest assured!
Refer to: 10 solutions for troubleshooting DNS Resolution
3. What is Domain (in DNS)?
This is the domain name of a website. For example:
- quantrimang.com
- download.com.vn
- meta.vn
- gamevui.com
All these domain names are the Domain of the respective website. Theoretically, the general structure of a domain will be:
- http:///www.domainname.tld
Where http is the connection protocol, www or no www is the World Wide Web , domainname is the domain name (of course !!!) and ltd is the top-level domain . The tails include:
- * .com ( commercial organizations - commercial organizations , companies .)
- * .org ( non-profit organizations , works for the community, scientific research .)
- * .net ( commercial - similar to 1)
- * .gov ( government - governmental organizations)
- * .edu ( educational - educational purpose)
- * .mil ( military - military)
- * .int ( international - international)
And with the increasing demand of users, there are now many more domain names (by geography) such as:
- * .asia (Asia)
- * .us (US)
- * .in (India)
- * .ca (Canada)
- .
And the types of TLD belong to the genre, for example:
- * .tv (sharing, streaming video)
- * .me (individual)

What is DNS?
Previously, if we wanted to access a website, we had to enter the full www.domainname.com . But later, the hosting service providers have allowed direct transfer www.domainname.com to domainname.com . This can be considered as a big development, to help users save time, and help the website's SEO capability is also better (in the opinion of many people). When conducting a domain purchase, we are required to choose the domain name, the tail (part tld), and the price is also different depending on the domain name, domain name.
Let me explain a little more about this domain. For example, the access URL to TipsMake.com website is:
- https://quantrimang.com
- Or https://quantrimang.com
Here, quantrimang is part of the top-level domain ( * .com ), and many domains will have additional subdomains included. For example:
- www.forum.quantrimang.com
You can understand here: the forum is a sub-domain of quantrimang . Actual photos for you to easily imagine:

4. DNS Lookup working mechanism
Through the above part of the article, you've probably figured out what part of DNS, how DNS works . And the process of finding the IP address of any URL, any path on the Internet is called DNS Lookup. . Let's continue with the next example.
Example 02:
Imagine, in a system there is a computer, a laptop. And every 1 computer has a separate IP address, in case there is an additional 11th computer with information, the database has the alias name of the other 10 computers, as well as the corresponding IP address. Users can access any computer via IP address, account name. More specific:
- Computer A wants to use the printer connected at computer B, then machine A will have to check the database on the 11th computer to know the IP address of computer B, then the printer is connected at machine B. After acquiring such information, machine A will transfer the print job to the printer at computer B.
In that case, the following actions have taken place:
- Machine A connects to the 11th computer.
- Machine A communicates to computer B.
- Machine A makes a connection to the printer - connecting to computer B.
Imagine how similar DNS Lookup works. Here, when you click and access: https://quantrimang.com , your router device, modem . will "contact" with the DNS service to conduct the corresponding DNS resolution. The DNS service will continue to communicate with the Root Server and request the IP address of the server that contains the * .com, which will be sent back to the DNS service. This DNS service will continue to look in the Name Server containing all domain * .com addresses and ask: "Hey, is quantrimang.com here?" After obtaining the corresponding IP address of quantrimang.com, the DNS service will return the IP address to the computer, which is when the content, photos, text on TipsMake.com website are displayed on the browser. And in the process, the DNS service sent at least two requests to retrieve the domain's IP address. The diagram of the above operating process will look like the following:
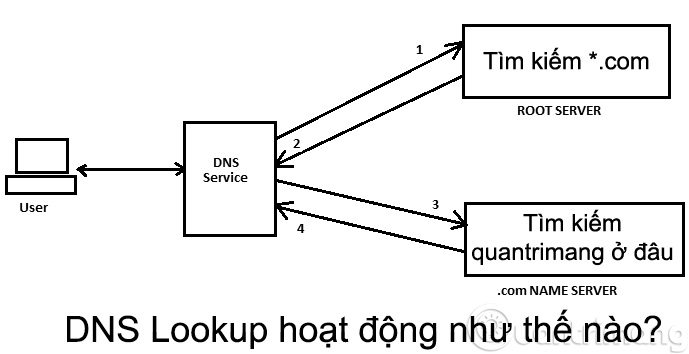
Suppose that, in the above case, instead of replacing https://quantrimang.com with http://forum.quantrimang.com , the DNS service system will have to add a request to find the sub-domain forum section. Hopefully, through the above theory and model, you understand the mechanism of DNS Lookup .
Good luck!