Knowledge of TCP / IP network protocols
TCP / IP or Transmission Control Protocol / Internet Protocol is a set of communication protocols used to connect network devices on the Internet. TCP / IP can be used as an information exchange protocol in a private network (intranet or extranet).
The entire Internet protocol suite - a set of rules and procedures - is often called TCP / IP, although there are other protocols in the suite.
TCP / IP specifies how data is exchanged over the Internet by providing end-to-end communication with the aim of determining how it is divided into packets, addressed, shipped, routed and received. destination. TCP / IP does not require much management and it is designed to make the network more reliable with automatic recovery capabilities.
There are two main network protocols in the network protocol suite for specific functions. TCP determines how applications create communication channels in the network. In addition, it also manages how items are broken down into packets before being transferred over the Internet and assembled in the correct order at the destination address.
IP determines how to assign addresses and route each packet to ensure it arrives at the right place. Each gateway on the network checks this IP address to determine where to forward the message.
Learn about TCP / IP network protocols
- History of TCP / IP protocol
- How does TCP / IP protocol work?
- TCP / IP layers
- Advantages of TCP / IP
History of TCP / IP protocol
The Defense Advanced Research Projects Agency (DARPA), the US Department of Defense's research arm, created the TCP / IP model in the 1970s for use in ARPANET, a wide area network available before the Internet. TCP / IP was originally designed for Unix operating systems and is integrated into all operating systems after it. The TCP / IP model and related protocols are maintained by the Internet Engineering Task Force.
How does TCP / IP protocol work?
TCP / IP uses the client / server communication model, in which the user or device (client) is provided by another computer (server) with a service (like sending a website) in the network. .
In general, the TCP / IP protocol suite is classified as non-state, meaning that each client request is considered new because it is not related to the previous request. The absence of this state frees up network lines, so they can be used continuously.
However, the transport layer has a state. It transmits a single message and its connection remains the same until it receives all the packets in the message and concentrates at the destination.
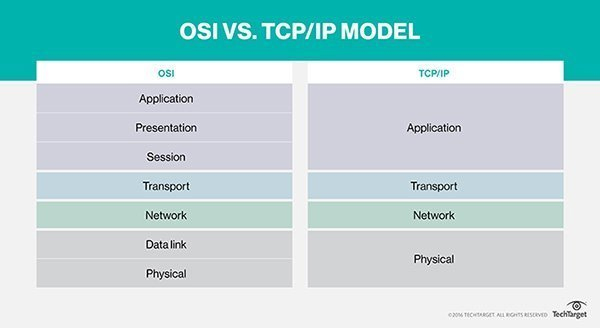
The TCP / IP model is slightly different from the seven-layer OSI (Open Systems Interconnection) model designed after it, which determines how applications communicate within a network.
TCP / IP layers
TCP / IP is divided into four layers, each consisting of specific protocols.
- Application layer provides applications with standardized data exchange. Its protocols include Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP), File Transfer Protocol (FTP), POP3 Protocol, Simple Message Transfer Protocol (Simple Mail Transfer Protocol - SMTP). ) and Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP).
- The transport layer is responsible for maintaining end-to-end communications throughout the network. TCP handles communication between servers and provides flow control, multiplexing and reliability. Transport protocols include TCP protocol and User Datagram Protocol (UDP), sometimes used instead of TCP for special purposes.
- The network layer , also known as the Internet layer, is responsible for handling packets and connecting independent networks to transport data packets across network boundaries. Network layer protocols include IP and ICMP (Internet Control Message Protocol), which are used to report errors.
- The physical layer consists of protocols that only work on one link - the network component connects nodes or servers on the network. The protocols in this layer include Ethernet for local area network (LAN) and Address Resolution Protocol (Address Resolution Protocol - ARP).
Advantages of TCP / IP
TCP / IP does not belong to and is under the control of any company, so this network protocol suite can be easily modified. It is compatible with all operating systems, so it can communicate with other systems. In addition, it is compatible with all types of computer hardware and networks.
TCP / IP is highly scalable and as a routing protocol, it can determine the most efficient path through the network.
See more:
- Things you should know about HTTP / 2 protocol
- The difference between TCP and UDP protocols
- How to protect high-risk network ports?