Use Snort to detect some of the current popular attacks on Web applications
The solution to use Snort to detect some of the most common types of attacks on Web applications
1. Introduction
According to statistics from leading security company Acunetix, recently the number of attacks on web applications has increased rapidly (75% of the attacks are done in the application layer. web) [See 1]. In which two attack techniques commonly used by hackers are cross-site scripting and sql injection [See 2] and the following figure:
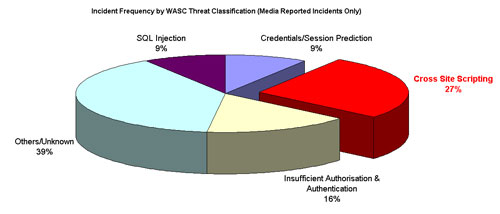
Source: acunetix.com
Cross-site scripting (also known as xss) is done by hackers by embedding script tags into a url (uniform resource locator) and trying to trick users into clicking on these links. Then this malicious code will be executed on the victim's computer. The technique of implementing these types of attacks is not complicated and mainly hackers take advantage of the trust between the user and the server (because the url seems to come from a reliable source) along with the lack of authority. Look carefully at the server I / O data to refuse to serve those maliciously inserted urls. SQL Injection involves a technique of inserting keywords, SQL language commands (the language used to query and manipulate a relational database) into the input data of web applications. to control the execution of SQL statements on the server.
This article describes a technique for detecting SQL injection and cross-site scripting attacks using Snort. Part one of the article will introduce snort. Part 2 of this article will describe how to write rules for snort against these two types of attacks.
2. So what is snort?
Snort is a type of IDS (Instruction Detection System). In short, IDS is a system installed on your network (or computer) and its task is to monitor incoming and outgoing packets for your system. If an attack is detected by Snort, it can react in different ways depending on the configuration you set, such as it can send a warning message to the administrator or remove the package. believe when detecting abnormalities in those packets.
However, snort also has weaknesses. It is similar to virus scanners, snort can only fight attacks effectively if it knows the signature of those attacks. Based on this point, high-profile hackers can adjust attacks to change the signature of that attack. Since then these attacks can "bypass" the supervision of snort.
So it can be seen that, to snort effectively, one of the important factors to pay attention to is the writing rules for snort. When snort works, it reads the rules, monitors the flow of data through the system and responds if there is any data stream that matches its rule set. More specifically, the rule set can be created to monitor scanning attempts, footprinting, or other methods that hackers use to find ways to hijack the system. This rule set can be created by the user or the user who can access the home page of snort is: http://www.snort.org to retrieve it.
Now let's see a law written for snort and find out how snort understands them.
alert icmp! $ HOME_NET any -> $ HOME_NET any (msg: "IDS152 - PING BSD";
content: "| 08 09 0a 0b 0c 0d 0e 0f 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 |"; itype: 8;
depth: 32;)
The first part of the law describes the rule's action as an alert, protocol (ICMP) and source, destination IP address and port information. This section is called the 'rule header'. Here, $ HOME_NET is just a variable representing your network and it can be declared as follows: var HOME_NET 192.168.1.1/24
The rest of the rule, known as the 'rule option', contains an alert message and information will be used by snort to check whether the rule matches the packet. To better understand, we will see the details of the following ping command:
March 23, 2009: 46: 41.866911 192.168.1.10 -> 192.168.1.1 ICMP TTL: 50 TOS: 0x0 ID: 2403
ID: 8474 Seq: 256 ECHO
36 12 7B 39 1B C6 0B 00 08 09 0A 0B 0C 0D 0E 0F 6. {9 ..
10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 1A 1B 1C 1D 1E 1F ...
20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 2A 2B 2C 2D 2E 2F! "# $% & '() * +, -. /
30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 01234567
When snort monitoring packets through our network. Our rule requires snort to verify that all ICMP packets do not have to originate from our network ' ! $ HOME_NET ' and to our network ' -> HOME_NET '. The parameter depth in the rule is set to 32, meaning that snort will look in the first 32 bytes of the packet to search for content in the ' content ' field. If the content of the 'content' field in the law matches the contents of the packet (in this case from byte 9 to byte 24), snort will generate a message that will be logged again. . The content of the log message is: " IDS152 - PINGBSD ". The 'itype' field indicates the type of an ICMP packet, in this case 8 ie an ICMP packet with an echo request type.
3. Conclusion
In part one of this article, two popular types of attacks were introduced into the web application class: cross-site scripting and sql injection. This section also briefly introduces snort, one of the most used IDS to date and how to understand how laws work.
Part 2 of this article will describe how to design laws to combat these types of attacks.
References :
1. http://www.acunetix.com/websitesecurity/webapp-security.htm
2. http://www.acunetix.com/websitesecurity/cross-site-scripting.htm
3. http://www.securityfocus.com
-------------------------------------------------- -----
Nguyen Tang Hung
Network security department - Athena Network Management & Security Training Center.
Address: 2 Bis Dinh Tien Hoang, DaKao, District 1, Ho Chi Minh City :: Phone: 8244041
Website: www.athena.edu.vn
You should read it
- ★ The 4 most popular network attacks towards older people in 2018
- ★ Controlling Internet access - Part 4: TMG Network and Network Rule
- ★ How to Set Up an Independent IDS/IPS Lab Enviroment (Using Snort, Pytbull, Eclipse and Tomcat)
- ★ IDS for Web application attacks
- ★ Learn about Man-in-the-Middle attacks - ARP Cache spoofing