The function takes whole parts in Excel - Specific examples

Excel has 2 functions that involve taking integer parts: QUOTIENT , INT . There are many people who have a confusion between these two functions, only when you understand the nature of each one can you use them most accurately. In this article TipsMake.vn will clarify more about those two functions.
1. What is the integer part? Related issues.
Integers are numbers that include positive integers (1, 2, 3, .), negative integers (−1, −2, −3, .) and 0.
A rational number is a real number that can be expressed as a fraction (quotient) a / b, where a and b are integers with b other than zero. The rational number can be a finite number of decimal places or a decimal number. Cyclic infinite stool.

An irrational number is a real number that is not a rational number, meaning it cannot be expressed as a / b ratio (where a and b are integers).

All real numbers (including rational and irrational) can be written as:
x = n + z
where: n is an integer
0 ≤ z ≤ 1
The integer is the largest integer that does not exceed it. The symbol of the integer is [x], where x is a real number.
The decimal fraction of real numbers is determined by subtracting the whole numbers from that real number. The notation for the decimal part is {x}, where x is a real number.
Many people understand that the integer part is the number before the comma and the decimal part is the number after the comma , but this is only true when you are considering that a positive real number is wrong with a negative real number. For example, we have:
9.4 is a positive real number, where 9 is an integer and 4 is a decimal.
But with -9.4, the part before the comma -9 is not the whole part because -9> -9.4
In this case -9.4 = -10 + 0.6 with -10 is the integer part of -9.4
2. The function takes an integer part in Excel
Let's look at an example of the following table:
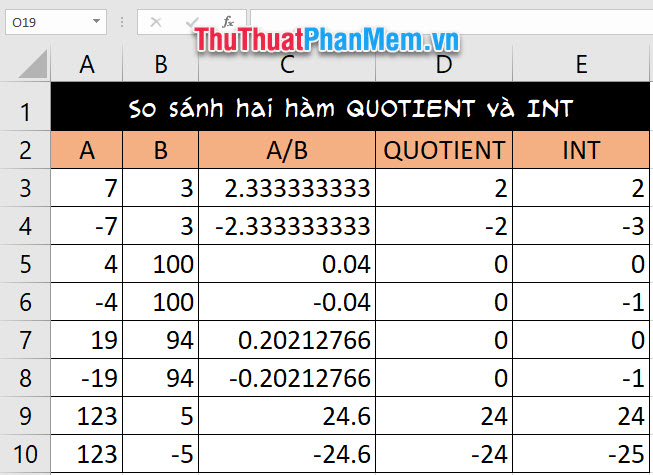
Where we have a and b are integers with b other than zero. We have the effect of a and b are rational numbers or here we need to consider is the numbers with both integers and decimals.
The 'take integer' result of QUOTIENT and INT will produce the same result if it is positive number and different if it is negative number.
Based on the integer part theory, we can see that the INT function is exactly the integer function and the QUOTIENT function is just the function that takes the number of digits before the comma.
2.1. How to use the integer get function
The integer integer fetch function has the formula:
= INT (number to be taken)
In which the number to take integer can be a specific number or a cell address.
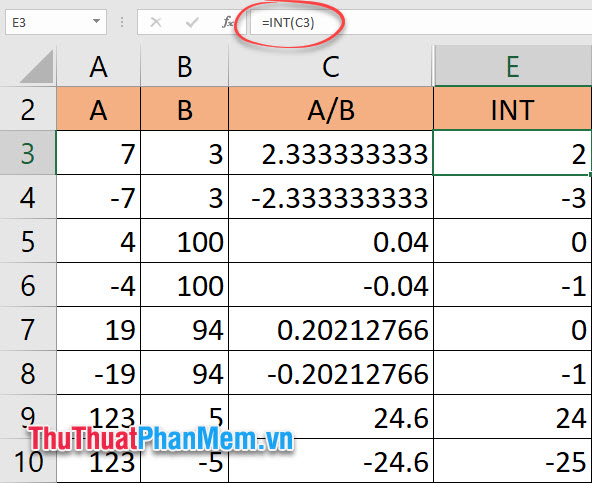
Note: The INT function only accepts numeric data (and only a number), so when entering data for INT with two or more numbers, you need to insert the calculations, for example:
= INT (7/3)
2.2. How to use the function to get the part before the comma QUOTIENT
The QUOTIENT function has the formula:
= QUOTIENT (dividend, divisor)
In which the divisor must always be non-zero.
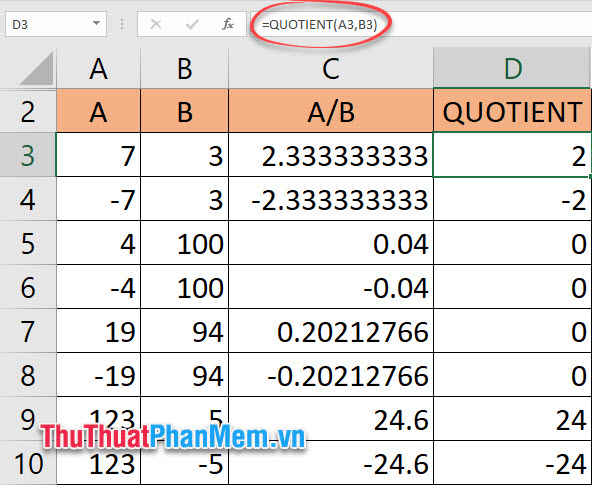
Unlike INT function, QUOTIENT function does not need to be calculated separately because it is already a division itself.
3. Practical examples
Thuthuatphanmem.vn Company allows employees to go on business trips on different occasions. The finance department needs to calculate the number of weeks and days spent at the hotel to pay the staff.
Data are given as hotel arrival and departure dates together with price list for room types.
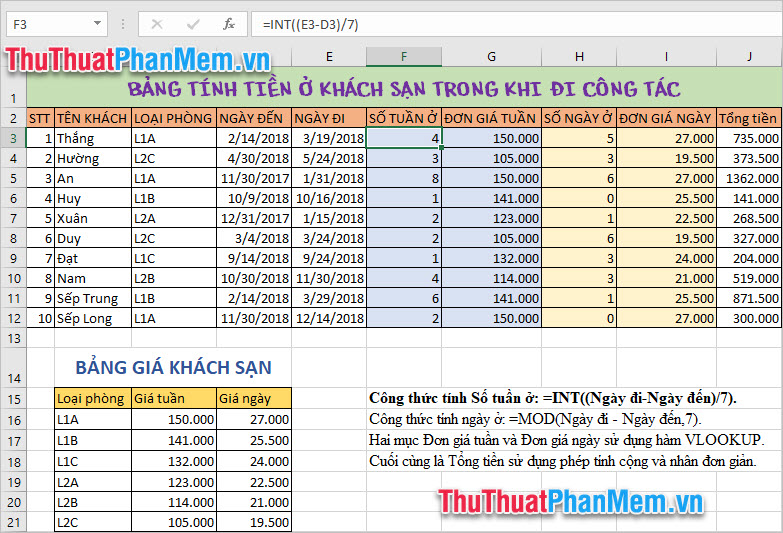
In the Number of weeks in, we can use the INT function to calculate.
The diagram here is to calculate the number of days then spend 7 to calculate the number of weeks. But the days in the hotel are not all week round because we can stay odd days so we only get the whole result.
Therefore, the calculation function is given as:
= INT ((Departure - Arrival) / 7))
The article about taking functions in Excel is here now, thank you for following the article of TipsMake.vn . Wish you can do it successfully!
You should read it
- ★ DCount function in Excel - How to use the DCount function and examples using the DCount function
- ★ INDIRECT function in Excel - How to use INDIRECT function and examples using INDIRECT function
- ★ Offset function in Excel - Usage and examples
- ★ IRR function in Excel - Usage and examples
- ★ Function Address - The function returns the address of a cell in Excel (usage, examples, examples)