Selecting a monitor for a computer
Computer monitor (Monitor) is a part that displays processing results of a computer in the form of text, images,. A computer screen is an external device (peripheral device) and connected to the processing unit of the computer (chassis) by a data cable through the communication port of the graphics device. For the casual user the screen is not important but in some professional use cases a high quality display is required.
The parameters to pay attention to the computer screen
Common types of computer monitors
 CRT and LCD computer monitors
CRT and LCD computer monitors
CRT Monitor (CRT Monitor)
- CRT (Cathode Ray Tube) screen is a traditional type of screen that uses image bulbs with a large, heavy design and consumes a lot of power.
- This type of screen was used for older computers in the past, and is no longer on the market today.
LCD Monitor (LCD Monitor)
- LCD (Liquid Crystal Display) is a type of flat screen (Flat Panel) using liquid crystal technology with a slim, light design and low power consumption.
- Early LCD screens were mainly used for notebook computers.
TFT LCD Monitor (TFT LCD Monitor)
- TFT LCD (Thin-Film-Transistor LCD) is an improvement of LCD monitors, using thin transistor (Thin-Film-Transistor) technology to improve image quality and contrast.
IPS LCD Monitor (IPS LCD Monitor)
- IPS (In-plane switching) screen is a technology for LCD screens, liquid crystal layers are arranged horizontally (In Plane) parallel instead of perpendicular to the two polarized glass panels above and below. This change helps to improve the color as well as the viewing angle of the screen better
LED Display (LED LCD Monitor)
- LED LCD (Light Emitting Diode LCD) screen is also an improvement of LCD screen, using LED technology to light up the screen background. The advantage of LED backlighting is that it saves energy even better, the best on the market, in fact. LED screens also provide better quality colors, clarity, faster refresh rates, clearer black and white ranges and provide better contrast with true colors,. so it shows more vivid and real picture.
- LED screens are thinner than LCD screens because the LEDs are located around the edge of the screen, which is the technology used for most computer monitors today.
OLED Monitor (OLED Monitor)
- OLED (Organic Light Emitting Diode) display is a new display technology that is brighter, more efficient, thinner and has better refresh rate and higher contrast than LCD screens.
- OLED displays provide the best picture quality ever and are used in smartphones and tablets and high-end computer monitors.
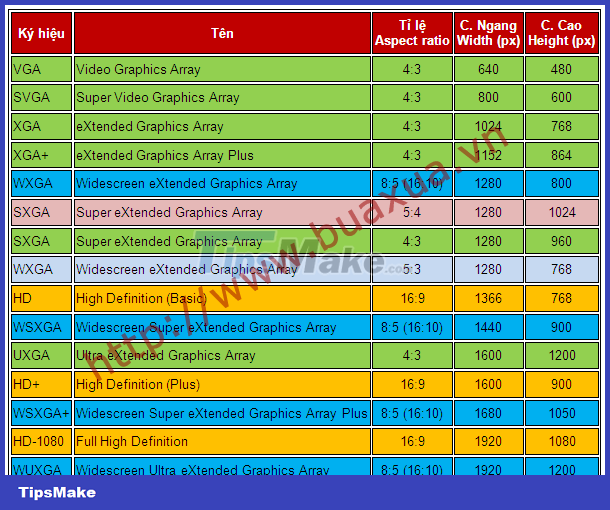
Size of the computer screen (Screen size, Display size)
- The screen size or display size (View Size, Viewable) is the size of the area where the image is displayed. The size of the screen is usually calculated according to the diagonal of the screen, i.e. the distance between two opposite screen corners, in Inche units (1 Inche = 2.54cm). This parameter determines the size of the screen and does not cause confusion when the aspect ratio changes.
- The size of the monitor is usually provided by the monitor manufacturer. The screen has many different sizes, the standard sizes of the screen are 13", 14", 15", 17", 19", 21", 23",.
- LCD monitors have a larger display size than CRT monitors of the same size.
Normally, the size of the screen is calculated as the display size, but some screens will also calculate the size of the panel (Panel size), you need to note this parameter.
Aspect ratio of the computer screen
 Scale of computer screen
Scale of computer screen
- The aspect ratio of the screen is the ratio of its height to its width, denoted by two numbers separated by a colon (x:y). Typical screen ratios are 4:3, 16:9, and 16:10.
- A 4:3 aspect ratio screen is called a square screen. This type of display is used for older computers.
- Wide screen type (Wide) has the aspect ratio of 16: 9 and 16:10. Most computer monitors today have an aspect ratio of 16:9.
- Some computer monitors have a larger width called Ultra-wide with an aspect ratio of 21: 9.
Display resolution
- The display resolution or display mode of a computer monitor is the number of distinct pixels (Pixel, Dot) in each size that can be displayed. It can be an ambiguous term, especially when display resolution is controlled by various factors in a CRT or liquid crystal display (LCD) monitor.
- Resolution is usually stated as the width times the height in pixels (px). For example, a screen with a resolution of 1024 × 768px means that it is 1024 pixels wide and 768 pixels high and is read as "one-of-a-kind four, seven six eight".
The screen resolution specifications given by the manufacturer are the optimal parameters for their monitors. In fact, users can change this resolution through the operating system and application programs, but the image may not be clear and not in the right ratio.
 Aspect ratio and resolution
Aspect ratio and resolution
Aspect ratio and resolution
Viewing Angle (Viewing Angle)
- The viewing angle of the screen is the maximum angle when the user can see the image on the screen without the quality of this image being unduly degraded. The viewing angle is measured in degrees horizontally and vertically of the screen.
- CRT monitors are visible from any angle while LCDs will be limited in viewing angles.
Contrast Ratio (Contrast Ratio)
- Monitor contrast is the ratio of the brightness of the brightest color (white) to the darkest color (black) that the monitor can display.
- Contrast ratios range from 200:1 to 1000:1 or higher for LED displays. The higher this ratio, the better because the color range of the screen will be wider and more realistic.
The contrast of the screen can be changed through the Contrast buttons on the screen or through the operating system and application programs.
Brightness of computer screen (Brightness, Luminance)
- This parameter will indicate the brightness of the LCD screen will display, usually in the range of 200cd/m 2 to 350cd/m 2 or higher.
- cd/m 2 is a measure of how bright the display is in bright lighting conditions. cd/m 2 stands for Candelas per square meter.
- The higher the brightness, the better, but most LCDs have enough brightness for whatever you need.
The brightness of the screen can be changed through the Brightness buttons on the screen or through the operating system and application programs.
Dot pitch
- Dot pitch is the distance between pixels of the same color on the screen, measured in millimeters.
- The smaller the distance between pixels, the sharper the image, the lower this parameter the better. Typical monitors have a Dot pitch between 0.28mm and 0.24mm and possibly lower.
Response time of the computer screen (Response time)
- Response time (or response time) is the time it takes for a pixel in the screen to go from active (white) to inactive (black) and back to active (white) again, units measured in milliseconds (ms). A lower number means a faster transition and therefore less "ghosting".
- Response time specifications of monitors are typically from 8ms to 4ms, high quality monitors have a response time of about 2ms to 1ms.
Refresh rate of the computer monitor (Refresh rate)
- Refresh rate is the number of times the image displayed on the screen is refreshed (changed) per second, the unit is Hertz (Hz). The maximum refresh rate is limited by the response time.
- The higher the refresh rate, the smoother the displayed image, and vice versa, if the refresh rate is too low, the image looks like it is flickering. The refresh rate of a typical monitor is 60hz. High-quality monitors have a refresh rate of up to 240hz.
The number of colors displayed by the computer screen (Colors Displayed)
- This parameter means how many colors the screen can display. However, you do not need to worry because now screens can display 16.7 million colors, enough to meet the needs of users.
Signal connection port of computer monitor
 Connection ports of computer monitors
Connection ports of computer monitors
VGA signal connection port (D-sub)
- VGA (Video Graphics Array) standard connector was born in 1987, used to transmit analog image signals (Analog) commonly found on CRT monitors and early LCDs.
DVI standard signal connection port
- DVI (Digital Visual Interface) standard connector was born in 1999, used to transmit digital image signals (Digital) commonly found on next-generation LCD screens.
- Where DVI-I (Integrade, combining digital and analog signals in the same connection); DVI-D (Digital only, digital only); DVI-A (Analog only, analog only).
- The DVI standard supports Full HD resolution.
Standard HDMI signal connection port
- The HDMI (High-Definition Multimedia Interface) standard connector was born in 2003, used to transmit 8-channel digital video and audio signals (Digital) often equipped on newer LCD screens.
- HDMI 1.x standard supports Full HD resolution and HDMI 2.0 standard supports 4K resolution.
DisplayPort standard signal connection port
- Displayport standard connector was born in 2007, used to transmit 8-channel digital video and audio signals (Digital) equipped on current LCD screens.
- Displayport 1.2a standard is similar to HDMI but newer versions can support 5K . resolution
Other features of the computer monitor
Matte screen or mirror screen (Glossy)
- Both are LCD screens, the only real difference between the two is the coating applied on the surface of the screen.
- The matte screen is coated with anti-glare, anti-glare (Anti-Glare). This type of screen displays a clear image in a well-lit environment and also feels like the color is slightly submerged in the surface of the screen, so when working for a long time with this screen, there is less fatigue and glare.
- Mirror screens display images with more vibrant, glossy colors and better contrast than matte screens. Colors on the mirror screen are bolder and blacks look deeper too. However, if it is exposed to direct light (when used outdoors or when there is a light shining on the screen), the mirror screen will reflect this light and cause glare for the user.
Other expansion ports
- Some screens have built-in receivers that allow you to watch TV, Video,. just like a TV.
- In addition, it can also integrate more Camera, speakers, audio jacks (microphone, Headphone), USB port, .
Screen rotation (Directional, Rotating)
- Allows to rotate the screen to change the height and width to suit the image display of the application program.
3D effect image display
- Support displaying images in the form of 3-dimensional space, viewers will have a sense of depth.
Touch screen
- The feature allows the user to command the computer control by touching the screen.
Accessories included with the computer monitor
- Accessories that come with the monitor usually include a power cord or an adapter (adaptor), a signal wire compatible with the connection port, a stand, a CD/DVD-ROM containing the monitor's driver program (Driver) of the monitor. .
Warranty of computer screen
-
Monitors are usually warranted from 24 to 36 months depending on the type and manufacturer.
How to choose a monitor for a computer?
- Based on the above parameters, you can choose the right computer monitor for your needs.
- If the same price is similar, then compare to choose which monitor has superior features.
- Choosing a large or small screen depends on your needs, but pay attention to image quality rather than size.
- Choosing a square or wide monitor depends on whether you need height or width, and be aware that some monitors allow 90 ° rotation . In addition, the followers of online games will be very surprised with the Ultra-Wide screen with 21: 9 aspect ratio, you will see "more" than the regular screen.
- The higher the resolution of the screen, the smaller the image displayed on the screen also means that the screen will display more. This can be a boon for opening multiple windows or running multiple applications at once, but can also be a pain for those with low vision.
- If you want to watch high-quality widescreen movies (High Definition), you should choose a screen with the symbol HD (High Definition). However, only Full HD (HD-1080) type with 16: 9 aspect ratio and 1920x1080px resolution can meet Full HD.
- Matte or mirror LCD screen, choose the right one for your working environment. However, you should note that the glass can be glued to the normal screen to be like a mirror screen.
- If you want to use monitors for cash registers, consider touch screens.
- Check your graphics device to make sure its signal ports and monitor are compatible. In case of force majeure, remember that there are always converters for these signal ports.
Whether the screen displays its full potential or not depends on the power of the graphics device.
Check the number of dead pixels on the LCD screen, these are the points that do not appear on the screen. Every screen has a certain percentage of dead pixels, the lower the number of dead pixels the better. Check these dead pixels by changing the color, black, white . on the screen and observe carefully, it will be detected. During the warranty period, you can get another screen replacement if your monitor has dead pixels.