Restore laptop performance
Upgrading RAM, taking advantage of the old hard drive as an external storage device, choosing the right power management mode will help your laptop work better.
Additional RAM
Over time, laptops will become old and slow, this is when you need to consider upgrading your hardware, bringing new power to the machine. Attaching more RAM is the fastest solution to increase system performance at the lowest cost.
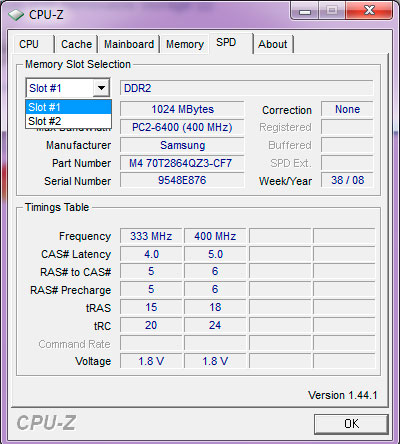
Cpu-z helps quickly identify the type, amount of RAM and number of slots in use.
First, you need to determine the type, amount of RAM and the number of slots you are using with Cricial's Cpu-z or System Scanner . In addition to providing important parameters of BMC, CPU, graphics card and memory (RAM), Cpu-z also helps identify the type, amount of RAM and number of slots in use. After selecting the correct type of RAM, turn off the power, turn on the laptop, remove the battery before attaching more RAM. The RAM mounting position on the bottom usually has a RAM icon or an M symbol (short for Memory).
It should be noted that most laptops only have 1 or 2 DIMM slots and there is no spare slot for upgrades. In case both slots are used up, you must remove 1 (or both) to mount the new RAM with larger capacity; For example, you have to remove 2 RAM 512MB to install 2 1GB RAM (or 1 2GB stick) if you want to increase the RAM capacity to 2GB. To remove the old RAM, push the metal latch on the 2 ends of the slot until the RAM pops out and gently pull it straight out. Put the new RAM in the same direction, same angle as the old RAM, then press down slightly until it hears the 'split' or the 2-pin slot latch that holds the RAM. In turn attach the cover, reinsert the battery and start the computer to check the results.
Take advantage of the old hard drive
Upgrading your laptop hard drive in addition to expanding storage space also significantly improves data access speed. However, what will you do with the old hard drive? The external hard drive box (HDD Box) will turn the old hard drive into an external storage device, enhancing the ability to store, backup or share data. Similar to other storage devices, external hard drives connect to computers via USB ports. It should be noted that you need to check the hard drive using standard IDE or SATA interface to select the corresponding hard drive box.
Set up power management
Some readers choose to fold the laptop when having to leave the computer in a short time. The problem is that when you go back, the computer often falls into a blank screen with no mouse or keyboard (the only way to fix it is to press and hold the Power button until the computer is turned off). Power saving modes like Standby , Sleep , Hibernate only work well if there is a compatibility between hardware, hardware (driver), ACPI (Advanced Configuration and Power Interface) power management with the system onions.
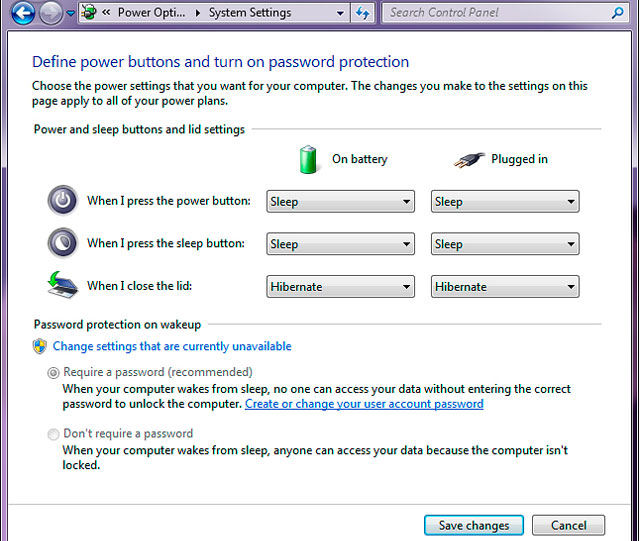
Hibernate has a higher level of reliability, making personal data not lost when an error occurs.
For most laptops, folding the lid is synonymous with the " sleep mode". In this mode, the hard drive and the screen will stop working but all information, operating status still exists in memory and only requires the minimum source to maintain. The computer only takes a few seconds to 'wake up'. In contrast, Hibernate will back up the current state of the computer to the hard drive and turn off the computer completely (similarly when selecting Shut down the system). So when returning to work, the system takes time to read and restore the state from the file on the hard drive. In time, Windows boots up faster in Sleep mode and much slower in Hibernate mode. However, Hibernate has a higher level of reliability, data changes in the previous session will not be lost when an error occurs (or when the computer runs out of battery).
To switch to Hibernate instead of the default Sleep mode: Click Start . Control Panel . Power Options . Click the Choose what closing the lid does item on the left frame and select Hibernate for the When I close the lid section .