Learn basic functions of network devices
TipsMake.com - In the following article, we will explore and refer to the characteristics and uses of some familiar network devices such as switches, hubs, routers . Main functions of switches, routers or What is hub? Do you really need a router with only 1 computer? In the field of information technology, in particular, this is a very large network, but if you understand the nature and exact capacity of each device, we can easily set up and deploy the system. The network is extremely simple and still ensures maximum performance and cost savings.
Describe requirements via network diagram:
Instead of starting with a series of specialized concepts about networking, we can absolutely 'go' in the implementation. The following is the simplest example in the process of setting up and configuring the network: 1 computer connects up to 1 modem directly with the direct signal from the ISP via telephone, ADSL or fiber:
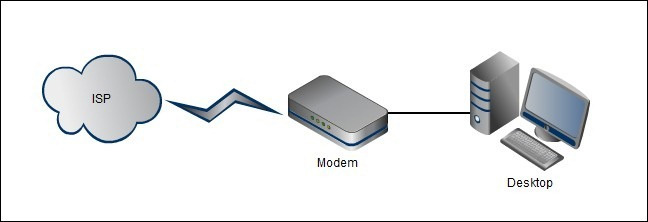
Technically, the above model is not much more complicated than the system as below, but the configuration and setup stages are not simple. Users cannot connect directly to the Internet with Wi-Fi enabled devices (eg smartphones, tablets .) and they will suffer from using a router to connect a computer and a provider. Internet service provider - ISP . In the chart below, we have two main components: wireless router and laptop connected to Internet via Wifi standard:
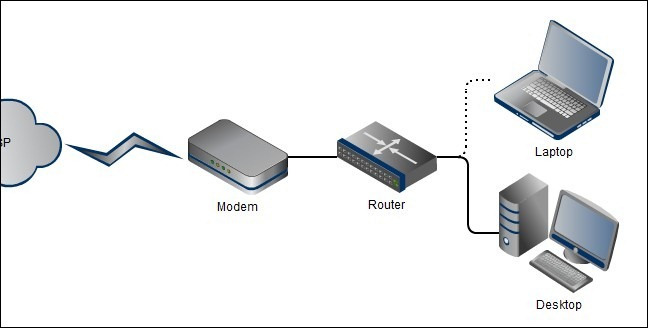
So when should we use the router? Only for personal use, low cost, usually most router models have integrated Firewall function. On the other hand, home router is a quite complete and close combination of functions: routers , firewalls and switches . But first, let's check the main function of the router.
Basically, a normal router will take on the task of connecting two different models and networks: inside and outside the house. Some main functions:
- IP Sharing : service provider - ISP will assign you a fixed IP address or not depending on the selected product package. If you use Desktop computers, laptops, media boxes, iPads . then obviously an IP address is not enough to meet the demand. The router device takes care of the sharing process, manages different connections and ensures that data packets will be delivered to the right place. Without this feature, there is no option for desktop and laptop users to access the Internet at the same time, or perform other tasks.
- Network Address Translation (NAT): also related to the IP Sharing feature, NAT has the ability to edit the information in the package header when they go through the router to navigate them to the corresponding device. Or simply, you can imagine that NAT undertakes the task of the receptionist inside the router system, knowing exactly the packets - where the package needs to go.
- Dynamic Host Configuration : If DHCP is not available, users will have to manually configure and assign hosts to the network. This also means that whenever a new computer joins the system, the administrator will have to assign the IP address to that machine manually. DHCP will take care of that job for you, and is completely automated. Therefore, when you plug any new device into the network, the system will provide the appropriate IP address for that device without the user having to manipulate anything.
- Firewall : In essence, the router already has the functions of the firewall, including automatically preventing inappropriate data when they go through the router. For example, if a user submits a request to download music to Pandora , the router will respond with 'message': 'We're expecting you, come on in ', and that information will go straight to the device. corresponds accordingly. On the other hand, if some strange signal flow from any source appears, the router will immediately reject these requests.
In addition to some of the above functions, home router devices can also act as a switch device - taking on the main task related to stability in communication and communication between multiple computers in same network. Without this function, each individual computer can connect to the Internet through the router but cannot communicate with each other.
Most router devices have 4 Ethernet ports, allowing users to connect 4 different separate devices with the switch function. If you want to increase your demand, replace it with another router with more ports or choose a dedicated switch . Note that you should only upgrade if you really need it. For example, if there is only 1 computer, 1 printer, and other devices operating via Wifi , there is no need to switch to using an 8-port or more router. Next, let's take a look at the network model with a fixed switch:

Although the 4-port limit on most home router devices has met the demand for users, our number and usage requirements have increased significantly over the past 10 years. In fact, this is not uncommon as more and more digital devices are available, such as game consoles, media centers, servers, printers . to connect and operate in the LAN . And with such a model, it is understandable for individual users to use 8 or 16 port switches.
Back in the past, many people chose and used hubs because they were much cheaper than switches. Technically, hubs do not have the function to manage or monitor system input or output signals, but simply to divide data, as opposed to the switch mechanism. Simply put, because hubs don't have a data management mechanism that only performs partitioning, so if the overall performance of the system is impaired using a hub. The share of hub users has also declined significantly over the past decade, even some manufacturers no longer offer this product on the market, notably Netgear.
With the above mentioned points, we can see that the switch is very suitable for personal use with a completely reasonable cost. If you want to use more, you can combine with one or two other switches, disconnect all other devices from the router and plug in the switch, then connect the switch and router together. Keep in mind that the switch does not have a route-signal feature, so it cannot be replaced for router devices.
Decode line speed signal:

After understanding the basics of the principle and operation mechanism of the network, in the next part of the article we will move to the transmission speed section. Currently, the 2 most used connection protocols are: wired and wireless.
Ethernet connection is built according to 10BASE standard, the original Ethernet protocol (up to this time of about 30 years) usually operates at a maximum speed of 10 Mbit / s . Later, the Fast Ethernet standard was first published in 1995 and the limit was pushed to 100 Mbit / s. In 1998, Gigabit Ethernet was officially launched but has not attracted the attention of the customer market until recent years (the maximum speed can reach 1000 Mbit / s ). Symbols like 10/100 or 10/100/1000 you can easily recognize on network devices are the Ethernet standard that the device supports.
If you want to transfer multiple data files with large capacity or HD video via local network, you should upgrade to Gigabit standard, and if you only browse the Internet and work normally, then choose 10/100 standard.
Some Wifi standards:

Operation speed of Wifi standard is divided by characters, not numbers. And these characters relate to the version of the IEEE 802.11 standard, and specify the parameters of the Wifi protocol.
- 802.11b : is the first version that is accepted and widely used by consumers. Devices that support 802.11b operate at a maximum speed of 11 Mbit / s , but mainly depend on the signal strength and quality of the device, the actual number can fluctuate in the range of 1 - 5 Mbit / s . However, devices using 802.11b will be hampered by some types of small computer monitors, Bluetooth, cordless phones and 2.4GHz band devices .
- 802.11g : is considered the next generation with many improvements in technology and performance, the maximum speed is pushed up to 54 Mbit / s (in fact, about 22 Mbit / s in the field). with obstacles and signal strength. Some of the obstacles that 802.11g devices use are similar to those of 802.11b.
- 802.11n: this is an upgrade and improvement that can be considered the most significant for Wifi standard, as well as devices supporting Multiple Input Multiple Output - MIMO to operate on both bands: 2.4GHz and 5GHz . In theory, the maximum speed of 802.11n can be up to 300 Mbit / s , but if excluding unfavorable cases, obstacles . then only about 100 - 150 Mbit / s.
Similar to Ethernet , Wifi speed is limited by the weakest links in the direct network. If you use the 802.11n standard router, the netbook only supports Wifi 802.11g , you only get the maximum speed of 802.11g . Besides the basic speed limits, there is another reason for us to 'remove' outdated Wifi 802.11b standards. Users must use the same encryption mechanism on all devices in the system, and the encryption mode applied on 802.11b devices is quite weak, easy to be compromised (eg WEP). Just like Ethernet , upgrading the system, supporting devices to the highest level of operation (here is 802.11n ) is very suitable for work and entertainment requirements that often have to transfer large files or HD video.