Learn about local area network - LAN (Part I)
What is LAN?
Local Area Network (LAN) is a high-speed communication system designed to connect computers and other data processing devices to work together in a small geographic area like one. floor of the building, or in a building . Some LANs can connect together in a work area. LANs become popular because it allows users (users) to share important resources such as color printers, CD-ROM drives, application software and other necessary information. Before developing LAN technology the computers are independent of each other, limited by the number of utility programs, after connecting to the network it is clear that their efficiency is multiplied. To take advantage of all the advantages of LAN, people have connected separate LANs to the wide area network (WAN).
Topology of LAN
The network topology is a spatial geometrical structure that is essentially a layout of the network as well as a way to connect them. Commonly, there are three types of structures: Star Topology, Ring Topology and Linear Bus Topology. In addition to the three types of configurations above, there are some other variants of these three types such as tree network, star-ring network, mixed network, etc.
Star topology
Star-shaped networks include a center and information nodes. Information nodes are terminal stations, computers and other network devices. The center of the network coordinates all activities in the network with the basic functions:
- Identify pairs of addresses to send and receive permission to occupy information lines and communicate with each other.
- Allow monitoring and mishandling in the process of information exchange.
- Notify the status of the network .

Advantages of a star network:
- Operating on a parallel connection principle, if there is a broken device in an information node, the network will still function normally.
- Simple network structure and stable control algorithms.
- The network can be expanded or shrunk according to user requirements.
Disadvantages of star-shaped networks:
- Network scalability completely depends on the capabilities of the center. When the center has a problem, the whole network stops working.
- The network requires independent connection of each device separately at information nodes to the center. The distance from the machine to the center is very limited (100m).
In general, the form network allows connecting computers to a centralized unit (HUB) with twisted cable, this solution allows to directly connect the computer to the HUB without going through the BUS axis, avoiding the causing factors Network stall. Recently, along with the development of switching hubs, this model has become increasingly popular and accounts for the majority of newly installed networks.
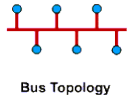
Linear network (Bus Topology)
According to the road corridor layout as shown, the server (host) as well as all other computers (workstations) or nodes (nodes) are connected together on a main cable line to convey signal. All nodes use this same main cable. The two ends of the cable are covered by a device called a terminator. Signals and packets when moving up or down in cables carry the address of the destination. This type of network uses the least cable, easy to install. However, there are also disadvantages that there will be traffic congestion when moving data with large traffic and when there is a failure in some section it is difficult to detect, a stop on the line to repair will stop the whole system.
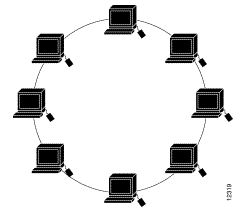
Ring Topology (Ring Topology)
This network, arranged in a circular form, is designed to be a closed loop, the signal running around in a certain direction. The buttons that communicate each other at a time are only one button. The transmitted data must be accompanied by the specific address of each receiving station. The ring network has the advantage of being able to extend far away, the total line needed is less than the two. The downside is that the line is not closed, if it is disconnected somewhere, the whole system is also stopped.
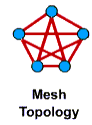
Mesh topology - Mesh topology
The slender structure is used in high-importance networks that cannot be deactivated, such as in nuclear power plants or security and defense networks. In this type of network, each computer is connected to the rest of the computers. This is also the structure of the Internet.
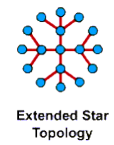
Star network expanded
This network configuration combines star-shaped networks by connecting HUBs or Switches. The advantage of this network configuration is that it can extend the distance as well as the size of the star network.
Hierachical topology - Hierachical topology
This network is similar to an extended star network, but instead of connecting switches / hubs together, the system connects to a computer that performs network traffic monitoring.
See next section: Local area network - LAN: Ethernet - Part II
Explore more:
- How to find the IP address of another computer on the LAN
- Use static IP address in network
- What is VLAN? How to configure a VLAN on Cisco Switch?