Learn about Web applications
Web applications have become a form of existence everywhere in the world, as computers become personal tools for both work and entertainment activities of people. But due to high technical and natural complex factors, Web applications are often not known correctly and seriously misunderstood in busy, daily life. This article aims to provide the most basic information, the most common understanding of the functionality and security issues of Web applications.
Web Application (Web Application) or Website Widget
Remembering the past decades, the Web has become a cheap way for millions of businesses to implement communication, exchange, and transaction with prospective customers and partners.
Specifically, the Web provides a way for market developers to know who is visiting their website and start contacting them. That is to ask those who visit the website to register for a newsletter, fill out an application form when requesting content information about the product or provide preparation details for a visit to a specific website later.
Web is also a smart sales channel for thousands of organizations, businesses, large and small. With more than a billion Internet users today (source: Computer Industry Almanac 2006), US e-commerce uses about 102 billion dollars in 2006 for transactions (source: comScore Networks 2007).
All such data needs to be packaged, stored, processed and transmitted in a certain way, which can be used immediately or someday later. Web applications, in the area of registration, submission, query, login, sales and content management systems, are widget websites that allow to perform all the desired work.
Web is the basic factor that helps businesses enhance their online image in the world of the network, creating and maintaining many long-term profitable relationships with potential customers and existing customers.
No doubt Web applications have become available everywhere in the world. But due to high technical and natural complex factors, they are not known to many people, even seriously misunderstood in daily life.
Web application definition
From a technical perspective, the Web is defined as a highly programmable environment, enabling a multitude of customization on the direct deployment of a large number of applications to millions of users around the world. The two most important components of the website are currently flexible Web browsers and Web applications. Everyone can use the two components without paying any fees.
Web browsers are software applications that allow users to query data and interact with content on Web sites within the website.
Website today is far different from the graphic and static text of the nineteenth century or earlier period. Modern Web pages allow users to download personalized content according to their own settings and preferences. Moreover, they can also run scripts on the client, which can 'change' the Internet browser into an interface for applications such as email, interactive mapping software (Yahoo Mail, Google Maps).
Most importantly, a modern website that allows packaging, processing, storing and transmitting sensitive customer data (such as personal information, credit card numbers, social security information .) can be used. immediately or use periodically later. And, this is done through Web applications. It could be a webmail component, a login page, a support program and a product or activity request form, a content management system, a modern website development site, providing for Enterprise means necessary to communicate with prospective customers and existing customers. All of them are popular, close and vivid examples of Web applications.
From a functional perspective, Web applications are computer programs that allow website users to log in and query data in / out through the Internet on their favorite Web browser. The data will be sent to the user in the browser in the form of dynamic information (in a specific format, like with HTML, using CSS) from the Web application through a Web Server.
More technically explainable, Web applications that query the server contain content (mainly on the content storage database) and create dynamic Web documents to serve the client's request (it is the website user). Documents created in standard format support all browsers (such as HTML, XHTML). JavaScript is a client-side script that allows dynamic elements to be on each page (such as changing the image each time the user moves the mouse). Web browser is the key. It translates and runs all scripts and commands . when displaying web pages and required content. Wikipedia, the world's largest online encyclopedia, now defines the Web browser as a "client for all web applications."
Another significant improvement in the process of building and maintaining Web applications is that they can operate without regard to the operating system or browser running on client computers. Web applications are deployed anywhere with Internet access, at no cost, and most do not require installation for the end user.
The number of businesses that benefit from business through the Web is increasing. Therefore, the use of Web applications and other related technologies will continue to grow. Furthermore, when Intranet and Extranet networks are adopted, Web applications become a big 'hub' in any media infrastructure of organizations and businesses. Range and technical ability, high level are expanded.
How does it work?
The figure below illustrates in detail the three-tier Web application model. The first layer is usually a Web browser or user interface. The second floor is technology to create dynamic content such as Java servlets (JSP) or Active Server Pages (ASP). The third layer is the database containing content (such as news) and user data (such as username, password, social security code, credit card details).
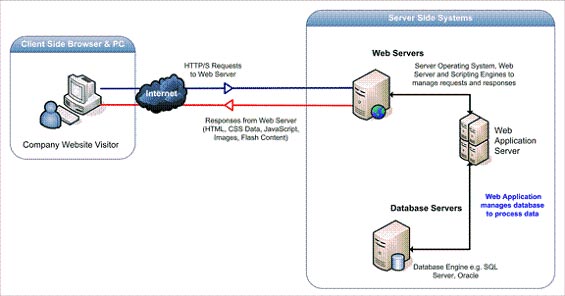
Figure 1
The operation begins with the request created from the user in the browser, sent over the Internet to the application Web server (Web application Server). Web application access server contains the database to perform the required task: update, query information that is in the database. The Web application then sends the information back to the user through the browser.
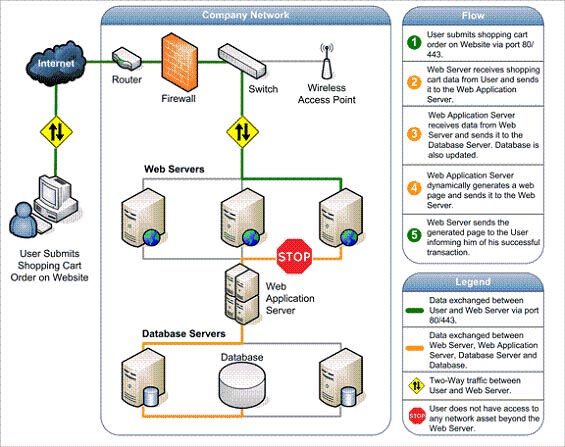
Figure 2
Web security issues
Although there are undeniably significant improvements in the current improvements, the security issues in Web applications are constantly increasing. Cause may stem from inappropriate code. Many serious weaknesses or vulnerabilities allow hackers to penetrate directly and access the database to extract sensitive data. Many databases contain valuable information (such as personal details, financial information) making them the target of most hackers. Although the attack on the business website is still taking place regularly, hackers now prefer to increase the ability to access sensitive data on the server containing the database because of the huge profits from the sales. data brought.
In the framework described above, you can see how easy it is for a hacker to quickly access information on the database with just a little bit of creativity. If they are more fortunate, they may encounter vulnerabilities resulting from negligence or user errors on Web applications.
As mentioned, the website depends on the database to distribute the required information to users. If the Web application is not secure (such as a vulnerability, has some kind of hacking technique), the entire database containing sensitive information is in serious danger.
Some hackers can insert malicious code into Web applications that have vulnerabilities to trick users and lead them to phishing websites. This technique, called Cross-site Scripting, can be used even if the Web Server itself and the database repository do not have any vulnerabilities.
A recent study shows that 75% of network attacks are done at the Web application level.

Figure 3
• Website and related Web applications must always be available 24/7 to provide services according to customer requirements, requests from employees, suppliers and many other related people.
• Firewall, SSL cannot protect Web application from all hacking activities, simply because accessing the website must be in public mode so anyone can visit the website. All modern database systems (such as Microsoft SQL Server, Oracle, MySQL) can be accessed via specific ports (such as port 80, 443). If desired, someone can connect directly to the database effectively when bypassing the security mechanism of the operating system. These ports are open to allow communication with legitimate network traffic, and thus also formulate a dangerous loophole.
• Web applications often access the last data such as customer databases, control valuable data, and therefore it is difficult to be absolutely secure. At this time, data access usually does not include script to allow packing and transferring data. If a hacker recognizes a weakness in a script, he can easily reopen traffic to another area and illegally share user details, even though sometimes not intentionally doing so.
• Most Web applications are self-created, so there are fewer qualification tests than similar software. Therefore custom applications are often more vulnerable to attack.
It can be said that Web application is a gateway of the database, especially customized applications. They are not developed with the best level of security because they do not have to go through regular security checks. In general, you need to answer the question: 'Which part of the website do we think is safe but open to attacks?' and 'What data do we bring into an application making it do something not to do?'.
It is the software's job of reviewing Web vulnerabilities.
You should read it
- ★ How to use Weebly to create a website on your phone
- ★ How to turn the website into an application on Linux?
- ★ How to convert a web application to a desktop application on Peppermint Linux
- ★ How to relax with sounds on Elpy Windows 10
- ★ You feel boring! These 15 websites will keep you busy right away