Instructions on how to install DD-WRT
Are you frustrated by software limitations on your router? Go ahead and replace that software with DD-WRT software provided by Linux. Maybe you want to use your old router as a second access point for your home network or to make a Wi-Fi bridge or maybe you want more precise control over your bandwidth usage, so you can prioritize. bandwidth for gaming sessions or perhaps you simply hate the firmware that comes with your router and want something with more features.
Instructions on how to install DD-WRT
- Install DD-WRT on the router
- Make sure the router is compatible with DD-WRT
- Knowledge is the key to success
- Start installation
- Install DD-WRT from the router's administration page
- Install DD-WRT (X86) on PC
- Restrictions of the X86 version
- Prepare hardware
- Ready for installation
- Verify the hard drive requirements
- Transfer images using physdiskwrite
- Start with DD-WRT X86
Install DD-WRT on the router
Whatever you want your router to do, DD-WRT can do most of that. DD-WRT installation can be complicated, but the most common method involves using the Upgrade Firmware feature , which is included in the router's default firmware.

That means, there is no common way to install DD-WRT. Different routers require different firmware versions and steps. We cannot include all this in an article. Instead, today's article will outline how to set up operations in the simplest cases, and explain where to find the correct information if you encounter more advanced situations. Let's start now!
Make sure the router is compatible with DD-WRT
The first thing you need to do is make sure your router is compatible. Go to the DD-WRT database, then enter the correct model number of the router you are using. This database will tell you if your router belongs to one of the following 4 groups:
- Supported ( Supported ), which means you can install DD-WRT. This is indicated by a green letter Yes.
- A work in progress , which means you cannot install DD-WRT right now, but developers are looking for ways to make it work. This is indicated by a yellow Wip.
- Possible in theory, but no one is working on it (Probably in theory, but no one works with it), meaning you can't install DD-WRT. This is indicated by a red No.
- Không thể cài đặt , vì tên phần tử hardware (Cannot install due to hardware limitations), means that you cannot install DD-WRT. This is indicated by gray 'Not possible'.
Your router is not supported if it is not listed here, but you can also try searching on the DD-WRT wiki page, or simply search your Google router model followed by DD-WRT cluster. Note the correct router model. Typically, a different letter or number in the model name can also represent two completely different types of routers.
Back to the database. This article will install DD-WRT on an old Linksys e1000 v2.1. Below is the sample database results:

As you can see, the router in the example is supported. But that is not enough. To install DD-WRT, you need to learn about any specific steps the router may require and you also need to be absolutely sure that you have found the firmware compatible with your router. Let's move on to the next part!
Knowledge is the key to success
It is important that you read as much as possible before downloading the firmware. The router database usually contains obsolete information, non-standard firmware, or otherwise does not give you complete information. It is always necessary to learn more information.

From the database page for the router, click the link to the wiki. Read the instructions there, if available. If it links to an article on the forum, reading through that article is also very good. See if anyone has trouble installing the firmware, and reading suggestions from other readers to solve the problem. If possible, you should also find which firmware users have successfully installed recently. Forum topics on the forum will often provide active downloads (confirmed by other users). You will want to know about this information before continuing.
This may sound confusing, but it can't be helped, so take the time to read as much as possible. In many cases, you will discover the firmware that you can download and flash simply, but the process also depends on different types of routers. If your device falls into a special case, you need to know and learn the full additional steps before continuing.
To make it easier to understand, go back to the Linksys e1000 v2.1 router, an old router. Firmware is provided by the router database for Linksys e1000 v2, similar but not identical to model v2.1. It may sound like no difference, but installing the wrong firmware may damage the router.
Once you are sure that you have found the correct firmware for your router and you understand the steps needed to install, continue and download. Do not download anything until you are sure.
Start installation
If your router is currently in use, the next part will be quite dangerous. You need to unplug all devices plugged into your router, including power.

Now, reset the router to factory settings. The way to do this will be different on each router, so you should consult the official documentation before continuing. However, normally, the steps to do will be to unplug your device and hold the Reset button on the back of the router for 30 seconds.
Install DD-WRT from the router's administration page
IMPORTANT : The following instructions assume that you only need to flash the firmware using the router's default upgrade tool. Again, please research the information carefully, otherwise you may damage your router device.
Once your router has been reset, plug it back into the power and connect it from the computer you used to download the firmware before. You can connect directly with an Ethernet cable or via Wi-Fi. Also, remember that you previously reset your router to the original settings, so the network name has also changed to default. Refer to your router manual if you are not sure what it is.
Now you need to connect to the router's administration page, in most cases, you just need to enter 192.168.1.1 in the address bar of the browser, then enter the default username and password. Refer to the documentation for the router you are using if the IP does not work, or if you are not sure what the username and password are. Also, take a look at the list of user names and default password of Quantrimang for routers:
- List the default password of the Linksys router
- List the default password of Cisco routers and switches
- List the default password of NETGEAR router
- List the default password of D-Link router
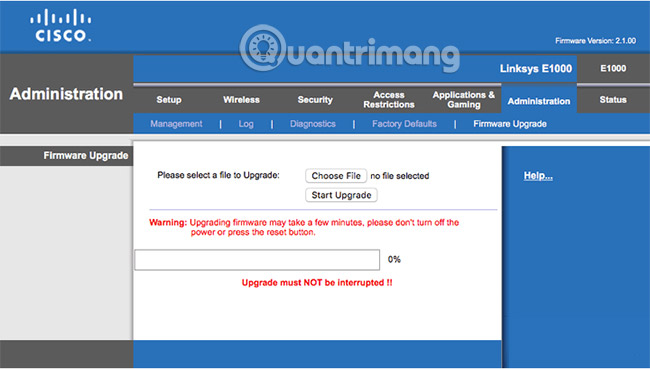
Now we will come with a very interesting part. Find the Firmware Upgrade section of the router - usually found in the Administration section or a similar section - then click the Browse button or Choose file. Select the firmware you downloaded earlier, then continue to upgrade the firmware. Again, do this only if you confirm this is the appropriate process after thoroughly investigating the relevant documents.
Patience is essential at this time. Firmware will be uploaded to your router, then the router will restart. Do not unplug or turn off, until all lights turn on (it may take a long time). Unplugging too early may damage your router, so please wait patiently.
Finally, you will be able to connect to your router at 192.168.1.1 and log in to the DD-WRT for the first time, assuming you are connected via cable. If you are connected wirelessly, you will see a Wi-Fi network with the title dd-wrt. Connect to it, then go to 192.168.1.1 to configure the router.
If you see the DD-WRT login screen, you need to do what Google calls a 30/30/30 hard reset to ensure absolutely nothing in your router. To learn more about how to do this, please refer to the article: Explain the rule 30-30-30 when resetting the router.

Connect again from your computer, then go to 192.168.1.1 to start configuring the router. If everything goes well, you can start exploring all sorts of new options! The DD-WRT Wiki provides instructions for achieving everything from bridged Wi-Fi networks to using QoS to prioritize specific traffic. Be sure to check through everything! Good luck!
Install DD-WRT (X86) on PC
Network administration - Usually when introducing DD-WRT and other software alternatives for wireless routers, we often introduce software upgrades for routers.Although this is a special case, DD-WRT has an X86 version that can be installed on PC computers.
This is a great thing if you don't have a compatible router and don't want to track it to find the right model and version number.Plus, it allows you to overcome the usual 16MB of RAM and a slow CPU in customer-level routers.
In this tutorial, we will show you how to build and set up a DD-WRT machine on your PC.
Restrictions of the X86 version
It should be noted that;If you want to use it for free, you will only have one wired router - but you can add other access points.Wi-Fi support is only available in the registered version by purchasing the Professional Activation for € 20.00 ($ 28.36).
You also do not get the following features for the X86 version of DD-WRT:
- USB Support .For example, you cannot connect to USB drives or printers to share them on the network.
- Journaling Flash File System (jffs) .Allows saving files directly on the router, such as for NoCatSplash hotspot restricted portal pages and other custom configurations.
- Itsy Package Management System (Ipkg) .The feature allows you to add features from OpenWRT not included in DD-WRT.
Prepare hardware
First, make sure you have a compatible X86, i386 or newer computer.You only need 16MB or a bit more RAM.However, at least two network cards (Ethernet), one for Internet and other network cards for LAN are required.
Do not forget a separate hard drive.It must be used separately to avoid being reformatted or repartitioned.
Although screens and keyboards are not required, they can be very useful if you have problems, then you can access the console.
Ready for installation
We will use a Windows program to upload the DD-WRT image to an empty hard drive.So you need to remove the hard drive from the DD-WRT machine and temporarily plug it into the working computer.
On the working computer, you need to download the transmission utility, physdiskwrite and the X86 version of DD-WRT.At the time of this writing, the current release is v24 Service Pack 1. If you use it for free, you can download dd-wrt_public_vga.image or dd-wrt_full_vga.image in case of registration.
Verify the hard drive requirements
When uploading the image to the hard drive, the utility will reference the computer's hard drive using the disk number.So you have to make sure you have the right disc - not a daily use disk - to verify these drive requirements.
You can open the Computer Management program to see the Disk Management utility in Windows:
In Windows Vista, click Control Panel > System and Maintenance > Administrative Tools > Computer Management .
Disk numbers (Disk0, Disk1, Disk2, .) will be displayed on the chart of drives and partitions.
Transfer images using physdiskwrite
When ready, here's how to install DD-WRT X86 on your hard drive from the working computer:
1. Launch Command Prompt.If you're using Vista, click the Start button, type cmd in the search box, right-click the cmd icon and select Run as administrator . In XP, click Start > Run , type cmd and press Enter.
2. Navigate to the directory, where the physdiskwrite and image utilities are located.It can be easier by browsing to the location in Windows and copying the location from the address bar.Then in the Command Prompt, type cd and paste the path, then hit hit Enter.
3. Type physdiskwrite -u dd-wrt_public_vga.image and press Enter.Adjust the image file name if you are using a different file name.
4. Type the disk number of the newly installed hard disk.Note that this will delete everything that is in the drive and you will lose all the files on it.
5. Once done, shut down the computer and remove the hard drive that you just inserted into the computer and install it back to the DD-WRT computer.
Start with DD-WRT X86
After DD-WRT starts, the router will start working.You need to plug the WAN / Internet cable into the ether0 interface, usually an on-board Ethernet port.The remaining interfaces are for LAN / network.You can connect them to a computer or to a switch.
You can calculate the interface by referring to the console after plugging the cable into the interfaces.It will notify you of the status, including the interface number.
The default IP address of the router is 192.168.1.1.The DHCP server is enabled, just like with software versions, so users will automatically enter the IP address.To access the management interface on the web, type the router's IP address into the browser.To access the management interface on the computer, press Enter.The default username is root and the password is admin .