Instructions for creating ISO files on Linux
If you need to back up your files and folders, you can save them to an ISO file. On Windows, use AnyToISO. On Linux, follow the instructions below from TipsMake.
Instructions for creating ISO files on Linux
1. Create ISO file on Linux via Archive Manager
On Ubuntu or Gnome, use Archive Manager to create ISO files easily.
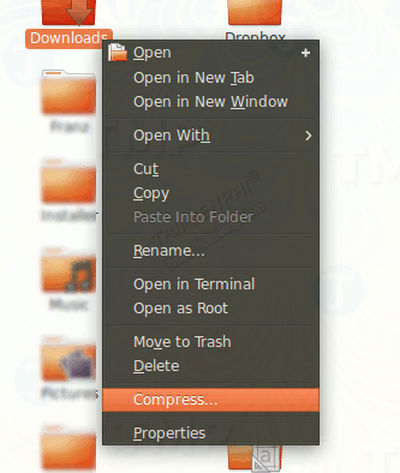
Step 1 : Open File Manager , select files and folders to backup. Right click, select "Compress".
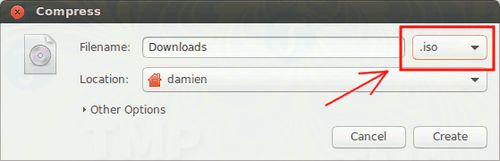
Step 2: Select .iso, then click "Create" to compress files and folders into ISO.
2. Via command line utility
dd is a useful command that you can use to create ISO files on Linux. All you need to do is specify the source and destination, and the command will do the work of creating the ISO file.
Use the basic command below:
dd if=source of=destination
For example, if you want to mount a CD-ROM drive to '/dev/hdc ', and you want to backup the files and folders in the drive to the file my-cd-backup.iso , you can use the command below:
dd if=/dev/hdc of=/home/username/my-cd-backup.iso
The source does not have to be the CD-ROM drive. It can be a partition on the same hard drive, an external drive, or a file path, although it does not work on folders.
You can also use the mkisofs command to create an ISO file. The advantage of mkisofs is that it gives users many options to customize how they want to create an ISO file.
Use the basic command below:
mkisofs -o destination-filename source
For example, use the following command to back up the Home directory:
mkisofs -o myHomeBackup.iso /home/username
You can tell mkisofs to enable the Rockridge extension by setting the -R option :
mkisofs -R -o myHomeBackup.iso /home/username
Joliet extensions are enabled with the -J flag :
mkisofs -J -o myHomeBackup.iso /home/username
You can also set the partition (-V option) for the ISO file. If you burn the ISO file to a CD, the partition name will be used as the CD drive letter.
mkisofs -V "Home Folder Backup" -o myHomeBackup.iso /home/username
You can also exclude some files from being added to the ISO file using the ' -m ' option. It supports asterisks (*) so you can use the command as below to exclude all hidden files (file names with a ' . ' in front) from being added to the ISO file:
mkisofs -m ".*" -o destination source
Check all mkisofs options with the command below:
mkisofs --help
Although not the best backup option, ISO files will be useful to you in some cases. Above TipsMake has just guided you how to create ISO files on Linux. Hope the above article will be useful to you. Wish you success.
 What is Clickhouse? Installation and Usage Guide on Ubuntu 20.04
What is Clickhouse? Installation and Usage Guide on Ubuntu 20.04 Autrace - Tool to check, count and monitor Linux processes
Autrace - Tool to check, count and monitor Linux processes What is SCP Command? How to use SCP Command in Linux
What is SCP Command? How to use SCP Command in Linux What is Sed? Learn about the Sed command in Linux
What is Sed? Learn about the Sed command in Linux What is Cloud Server Linux? Advantages and disadvantages of Cloud Server Linux
What is Cloud Server Linux? Advantages and disadvantages of Cloud Server Linux TrickBot Linux Variants Resurface Despite Removal
TrickBot Linux Variants Resurface Despite Removal