How to make the script executable anywhere in Linux
When you create a Bash script and save it to a directory, you'll find that you can only execute the script while in that directory. Have you ever wondered how ls , imagemagick , apache and squid can be installed in different directories but still accessible everywhere? That's because their own paths have been added to the 'Path' variable. By adding multiple links to it, you can also make your script executable everywhere.
Add the path to Bash
You can adjust the Path according to 3 different levels. Bash is the first level. Everything we see here will affect Bash. Everything runs in there, but has no effect outside of Bash.
Suppose you have a collection of scripts in the directory you want to access from anywhere.
To do this, you can add their paths to '~ / .bashrc' . You can open the .bashrc file (it is located in the Home folder, but is hidden by default) in your favorite text editor, like gedit .
Go to the end of the file and add:
PATH="/path_of/the_folder_we/want_to_add_to:$PATH" For example, if you keep your executable scripts in the '/ home / myname / scripts' directory , the command would be:
export PATH="/home/myname/scripts:$PATH" 
To save the changes, save the file, exit the text editor, and enter this command in the terminal:
source ~/.bashrc 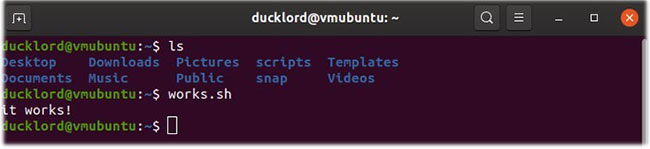
Then, move to many different directories and try to run scripts from there.
Add a link to the Profile
If you want the contents of the directory to be accessible from outside the Bash constraint, instead add it to the Profile variable.
Open the .profile file with your favorite text editor.
At the end of the file, enter:
export PATH="$PATH:$HOME/scripts" You must log out and log back in to apply changes.
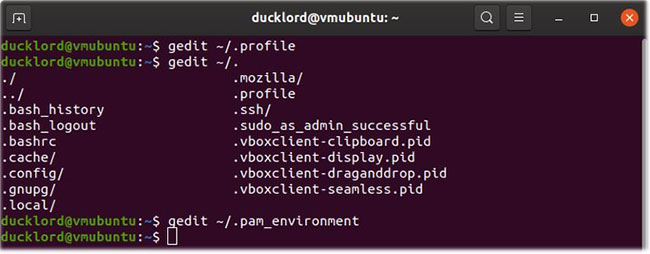
In Ubuntu and its derivative, you can edit the file '.pam environment' instead of '.profile' .
Open the file '.pam_environment' in the text editor. If the file does not exist, create it.
In the file, enter:
PATH DEFAULT=${PATH}:/home/@{PAM_USER}/scripts Note that instead of the path being completely hardcode and unlike in the profile file, here we will use a variable. This way, each user's '/ home / USER_NAME / scripts' directory will be added to the Path.
As with editing the .profile file, you must log out and log back in for the changes to take effect.
Add the path to the environment
An appropriate way to access the contents of a directory from multiple users, sharing the same computer, is to add it to an environment variable. Open a terminal and enter:
sudo nano /etc/environment The Path variable there contains a series of directories in quotation marks, separated by colons, similar to:
PATH="/usr/local/sbin:/usr/local/bin:/usr/sbin" To include your own directory in the list, right after the final path, before closing the quotes, enter a colon and the path to the directory. If your directory is '/ home / your_username / scripts' , it will look like this:
PATH="/usr/local/sbin:/usr/local/bin:/usr/sbin:/usr/bin:/sbin:/bin:/usr/games:/usr/local/games:/home/YOUR_USERNAME/scripts" Please log out and log back in to apply the changes.
With the above tips, you will be able to run your scripts from anywhere in Linux.