How to Enable and Use Script Execution Policy in Windows PowerShell
PowerShell, by default, allows you to run commands (cmdlets) through its console. To execute a script, you can create a notepad file with the script code, save it with the .ps1 file extension and execute it via the PowerShell console. You can also paste the script directly into the console for execution.
However, if this is your first time executing a script via PowerShell, you will get a "running script is disabled" error. By default, script execution on PowerShell is disabled as a security measure to prevent malicious scripts from running on the system. The following article will show you two ways to enable Script Execution Policy in Windows PowerShell.
How to check the current enforcement policy
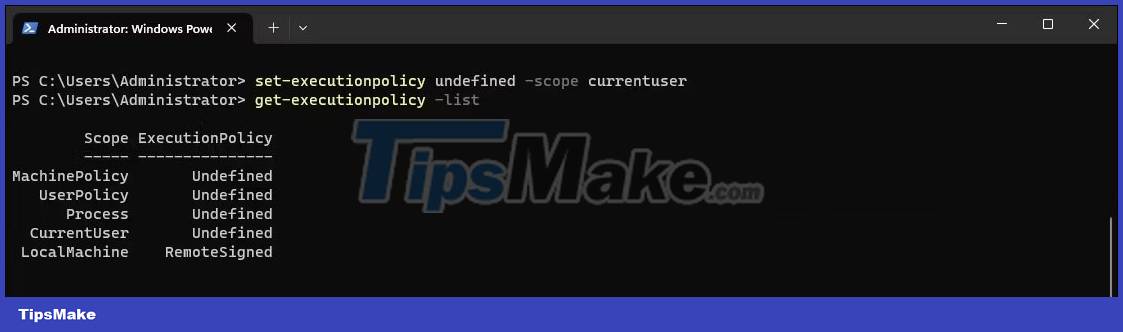
You can use a PowerShell cmdlet to get your current execution policy. Knowing the current enforcement policy is necessary to know if you need to change the policy.
To get the policy to execute for the current user:
1. Open Windows PowerShell with admin rights.
2. Type the following command into the PowerShell console and press Enter :
get-executionpolicy3. Since you encountered an error while executing the script, the returned result may show Restricted for your current execution policy.
4. If you need to see the enforcement policy for all supported scopes:
get-executionpolicy -listYou will need to change the execution policy to RemoteSigned to run the script locally without errors. You can change the execution policy from the Settings and PowerShell apps.
How to enable PowerShell execution policy using the Settings app
You can change and set the PowerShell execution policy to RemoteSigned using the Settings app. All you have to do is adjust the PowerShell settings in the developer section to change the execution policy to enable PowerShell script execution.
To change the execution policy using Settings:
1. Press Win + I to open Settings.
2. Open the Privacy & Security tab in the left pane.
3. Next, click For developers .
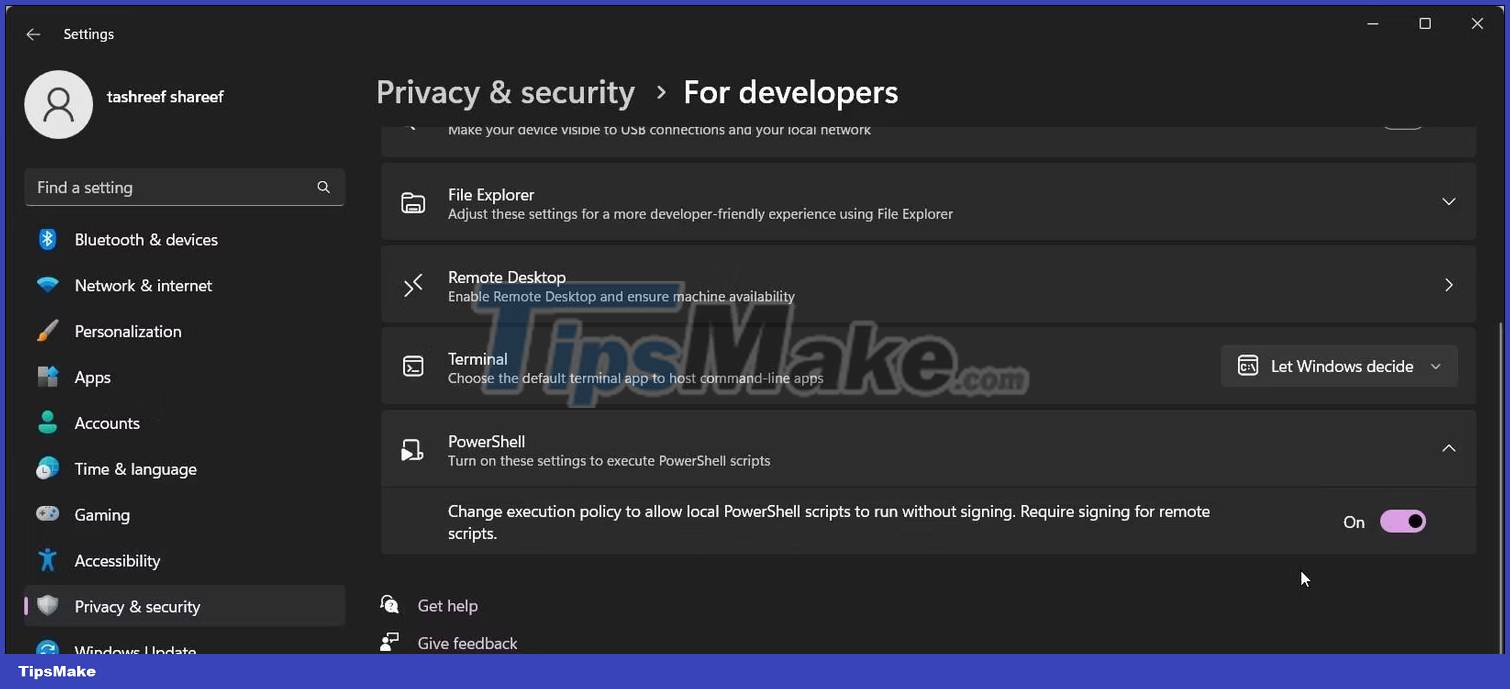
4. Click to expand the PowerShell section.
5. Turn on the Change the execution policy to allow local PowerShell scripts to run without signing - Require signing for remote scripts switch .
6. Once done, open PowerShell, type get executionpolicy and press Enter. Execution Policy for the current user is set to RemoteSigned.
7. If you need to disable the enforcement policy, turn on the PowerShell switch and set it to Off .
How to allow scripts to run in PowerShell using PowerShell
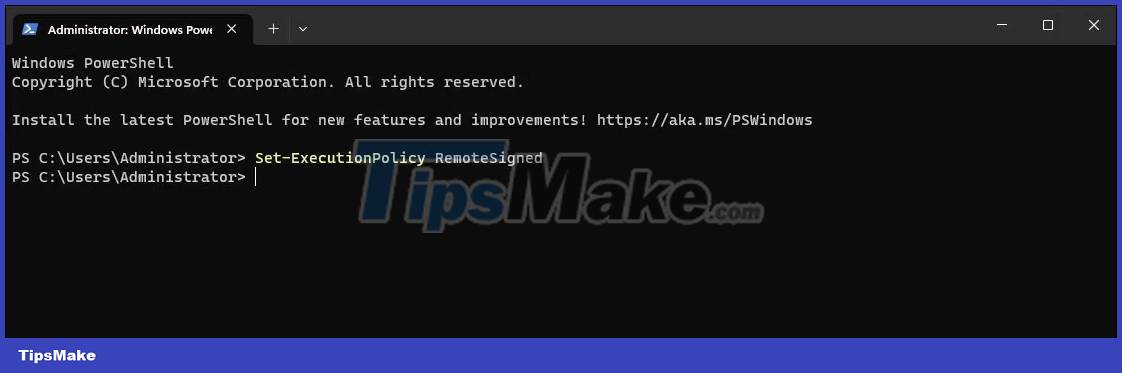
You can use the PowerShell cmdlet to set the execution policy to RemoteSigned. The command-line interface makes it easy to change enforcement policies on the fly without using the Settings app.
Also, the Settings app can only enable or disable the RemoteSigned enforcement policy. While PowerShell also allows you to set other policies and scopes.
To change the execution policy using PowerShell:
1. Open PowerShell with admin rights.
2. In the PowerShell window, type the following command and press Enter :
Set-ExecutionPolicy RemoteSigned3. If prompted, press A to confirm action. This will set the RemoteSigned enforcement policy for all users. If you only want to set the execution policy for Current User , use the Scope parameter followed by the username.
4. For example, to set the RemoteSigned execution policy for CurrentUser , use the following command:
Set-ExecutionPolicy RemoteSgined -Scope CurrentUser5. Replace CurrentUser in the above command with another user (Scope) according to your requirements.
How to delete Script Execution Policy with PowerShell
If you want to disable script execution, set the execution policy to Undefined using the Set_ExecutionPolicy cmdlet. This is the default state and prevents PowerShell from executing any scripts.
To disable script execution using PowerShell:
1. Open PowerShell with admin rights.
2. Next, type the following command and press Enter to disable script execution for all users:
Set-ExecutionPolicy undefined3. The above command will set the default execution policy (undefined) for all users. If you want to disable script execution for a specific range, use the following command:
Set-ExecutionPolicy undefined -Scope CurrentUser4. The above command will disable script execution for CurrentUser .
You should read it
- ★ Execution Plans - Execution plan in MS SQL Server
- ★ How to convert PowerShell script file (.ps1) to .exe by IExpress on Windows 10
- ★ How to use Local Group Policy Editor to tweak your computer
- ★ Mount Network Drive on Windows Client using Group Policy
- ★ Managing Windows networks using Script - Part 13: The script returns all values