How to install Java Runtime in Ubuntu
Java is not installed by default in Ubuntu, but is required to run Java applications, such as Minecraft, on the computer. This article will show you how to install Java Runtime in Ubuntu.
What is Java Runtime?
Java is an 'interpreted' language, meaning that the code is not compiled into an executable ready file. To run Java applications, you need to have an interpreter, called Runtime. This runtime translates program code in real time to instruct the computer to understand and enable the program to run.
Java test
To check that you have installed Java, use:
java -versionThe output will tell you whether you have Java on your computer and if not, which versions are available to install. Save as you may need them later.
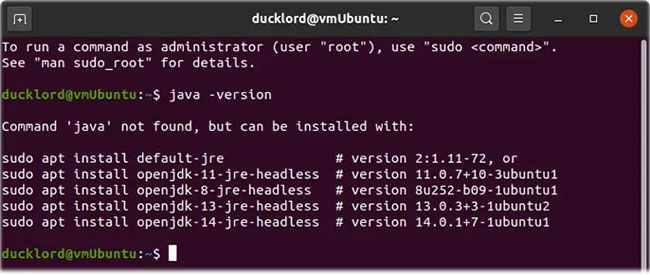 The result of the command indicates that Java is not installed
The result of the command indicates that Java is not installed Install the default version
Among all available versions of Java, one is considered the default version for the distribution. It may not be the latest version, but it is usually the stable, secure and generally the best version for almost any purpose.
To install it, use:
sudo apt install default-jreAfter some time and installing some additional dependencies, Java will be installed on the computer.
Use the command java -versionagain to check which version has been installed.
 Use the java -version command again to check which version has been installed
Use the java -version command again to check which version has been installed However, unfortunately, some programs created for a particular version of Java may have trouble using different versions. Thankfully, there is a solution to such problems.
JRE and JDK
To run Java code, you need Java Runtime. However, in rare cases, some additional extras may be needed. They can be found in the full Java Development Kit.
To install it, enter the following command in Terminal:
sudo apt install default-jdkInstall (and switch to) the older version
If what you have tried still fails, install an older version of Java just like you did with the default Runtime. For example, to install the oldest version available at this time for Ubuntu 20.04, the article used:
sudo apt install openjdk-8-jreYou do not have to uninstall the installed Java version. Multiple versions can coexist in parallel. However, only one of them works at a time. But even if you installed an earlier version, that would not solve the problem of not being able to run the jar file automatically. You must first switch to the older version. To do that, use the command:
sudo update-alternatives --config JavaA numbered list for the available versions will appear in the Terminal. An asterisk before the part number that marks the active version. Press Enteron the keyboard to keep the active version or select the number corresponding to another version and then press Enterto switch.
 Select the number corresponding to another version and press Enter to convert
Select the number corresponding to another version and press Enter to convert Install Oracle Java
Stubborn programs may refuse to work with any open Java version and require an Oracle version. Unfortunately, installing Oracle Java is a bit more complicated. You must first download it manually from the official Oracle Java page.
Save the file somewhere, activate a terminal and move to the same directory. Get dpkg in the downloaded file with the command:
sudo dpkg -i DOWNLOADED_JDK_FILENAMEUse the update-alternativesprevious command to install JDK with:
sudo update-alternatives --install /usr/bin/java java /usr/lib/jvm/jdk-14.0.1/bin/java 1 sudo update-alternatives --install /usr/bin/javac javac /usr/lib/jvm/jdk-14.0.1/bin/javac 1Remember to update the example paths with the version of Java you will install. Also note that you can switch between 'open' Java versions and Oracle's Java versions.