How to Install Wireshark on Debian 11
Wireshark can be used as a simple network troubleshooting tool, as well as for security analysis and software development.
Installing Wireshark on Debian 11 is easy. Follow this step-by-step guide to install Wireshark on Debian 11.
Condition
To follow this guide to install Wireshark on Debian 11, you need:
- Connect to the Internet (to download and install packages)
- An account with sudo privileges to install and remove packages.
Update source list
Wireshark depends on a number of open source libraries. Make sure they are updated before installing the program. Debian 11 keeps all its packages up to date through regular updates, so do the update first.
sudo apt update -y
During the installation process, you will be asked to allow non-superusers to collect data from network interfaces. Select Yes to continue.
Installing Wireshark on Debian 11
Once updated, you can proceed to download and install Wireshark.
Wireshark is distributed as a .deb file. This means there is no need to download anything manually. Instead, it can only be installed through apt, like any other program on Debian 11.
sudo apt install wireshark -y
During the installation process, you will be asked to allow non-superusers to collect data from network interfaces. Select Yes to continue.

Check out Wireshark
Now, after installing Wireshark, let's quickly experiment.
First, start the program by typing sudo wireshark. This will open Wireshark in its own window.
sudo wireshark
You can also open Wireshark from the desktop environment's menu system.

Wireshark has a graphical user interface (GUI) to capture packets, as shown below. You will see a list of available network interfaces that Wireshark understands. If you want to monitor the interface where the web browser is receiving the Internet connection (e.g. wlan0), select the interface and click the Start button.

However, you can also use it from the terminal by typing tshark followed by the command to capture some traffic. Tshark is a command line program for monitoring network traffic. Along with TShark, it is part of the Wireshark suite. Just like the GUI equivalent, it can capture packages and then display descriptions in a terminal window or save them to a file in binary format.
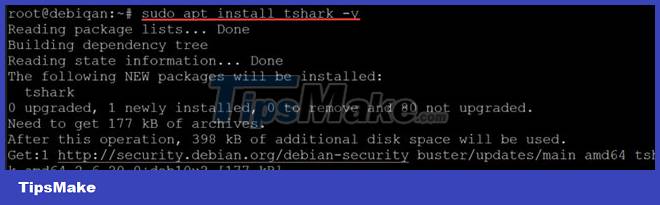
You can install tshark by entering the following command in a terminal window:
sudo apt install tshark -y
Run the tshark –help command below to see the different options tshark offers.

Run the tshark -D command below to check if the network interfaces are recognized by tshark.
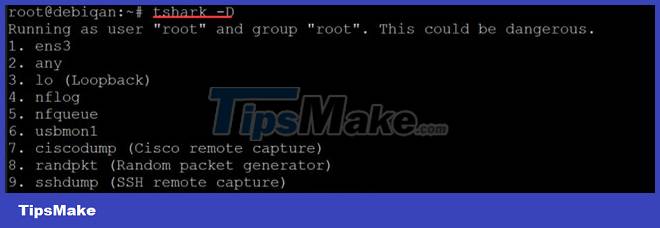
You will get a list of network interfaces like below. Note that some network interfaces may be in the "disabled" state. Not all network interfaces are active by default. You will have to find the active interfaces. In this demo, it's interface ens3 and lo.
You can tell which interface is active by typing ifconfig in the terminal.
ifconfig

Once you have identified the desired interface, run the following command to start capturing packets:
tshark -i
Where is the name of the desired interface.
tshark -i ens3
When you are done with data collection, press Ctrl + C in the command line window. This will stop the capture and close tshark. You will see the captured data displayed in the command line window below.
