How to fix 'No Space Left on Device' error on Linux
There are many ways to fix " No Space Left on Device " error on Linux, of course you can use tools in the desktop environment. However, the fastest solution is to use the command line utility according to the detailed instructions below.
How to fix "No Space Left on Device" error on Linux
Check if your Linux computer has free space using du and df
First check to see if your device's hard drive has free space. Although using tools in a desktop environment is the ideal solution, the fastest solution is to use commands.
To use the commands to fix the No space left on device error, you need to access Terminal on Linux, which is an indispensable tool on Linux for users to manage this operating system.
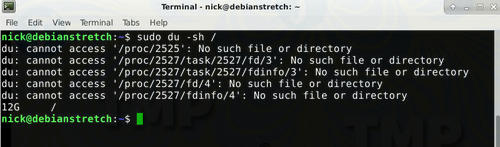
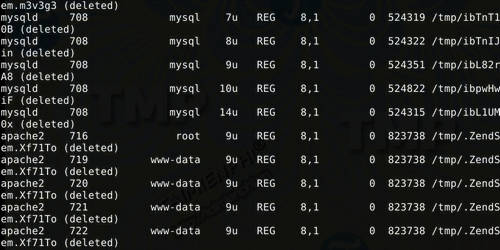
Start with the du command . Point to the base directory on the hard drive that reports the error. In this tutorial TipsMake assumes it is the root partition.
sudo du -sh /

The checking process will take some time. Next is to use the df command .
sudo df -h
Add the root partition and the mounted file systems in it. For example, if '/home' is a separate hard drive, you add this drive to read the root partition.
du will display free space. Otherwise the command may point to a deleted file that is being used by some process.
Of course the main concern here is whether the results these commands return indicate whether there is free space left on the hard drive. If so, there is clearly something wrong with the system.
Cause of "No Space Left on Device" error on Linux
There are several main causes of "No Space Left on Device" error on Linux. If the results returned by the du and df commands are different, here are some causes of the error and solutions to fix the error:
- Process uses deleted files:
Sometimes a file is deleted but the process still uses that deleted file. Linux does not release free space from deleted files while the process is still using the deleted file. All you need to do is find that process and restart it.
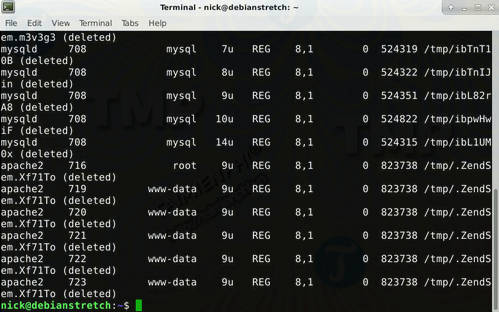
Find processes using deleted files:
sudo lsof / | grep deleted
The above command will list the failed processes, then you just need to restart these processes and you're done.
sudo systemctl restart service_name
- Not enough Inodes:

On file systems there is a set of metadata called "inodes". Inodes' task is to track file information. Many file systems consist of multiple inodes, so it is possible for files to be allocated to inodes without being allocated to the file system.
Use df command to check:
sudo df -i /
Compare the inodes used with the total number of inodes. If the inodes are used less, you will have to delete some unused or obsolete files to delete the inodes.
- Bad Block (error blocks):
The last common cause can be Bad Blocks (corrupted blocks) in the file system. The file system is corrupted and the hard drive is dead. Your operating system will consider the blocks to be usable, unless the blocks are marked otherwise. The best way to find and mark blocks is to use the fsck command followed by the -cc flag.
One thing to note is that fsck cannot be used on the same filesystem you are testing. In this case you can use a CD drive.
sudo fsck -vcck /dev/sda2
Obviously the above command will replace the hard drive location with the drive you want to check. The inspection process will take a long time.
Above, TipsMake has just shown you how to fix the "No Space Left on Device" error on Linux. Besides, you can take some measures to scan for viruses and rootkits on Linux to avoid malicious programs appearing and causing errors on Linux. Hope the above methods will help you fix the error. If you have any questions that need answering, please leave your comments in the comments section below the article.
Additionally, if you are experiencing No Route to Host error when connecting to a server on Linux, see how to fix No Route to Host connection error here
 Install and use 7 ZIP on Ubuntu Linux
Install and use 7 ZIP on Ubuntu Linux How to mount and mount storage devices on Linux Terminal
How to mount and mount storage devices on Linux Terminal What makes Astra Linux stand out?
What makes Astra Linux stand out? How to integrate Thunderbird into Tor browser on Linux
How to integrate Thunderbird into Tor browser on Linux How to install AVG Antivirus on Ubuntu
How to install AVG Antivirus on Ubuntu 10 popular software new Ubuntu users must know
10 popular software new Ubuntu users must know