How to Fix Corrupted USB in Linux
Everyone has a flash drive. They're wonderful little things that make moving data around a breeze. But sometimes flash drives can get corrupted or stop working altogether. Luckily, if you're using Linux, you have access to a variety of tools that can help you troubleshoot the problem. This guide uses Ubuntu , but everything should apply to most modern Linux distributions. Here's how to fix a corrupted USB drive in Linux.
This article prioritizes data safety. You'll first learn how to back up the contents of your flash drive, then perform various fixes to the problem at hand. That way, if your troubleshooting efforts make things worse, you can still restore a snapshot of the current state of your flash drive.
Create a compressed full backup image
In Linux, there are many tools to backup any storage device. However, the tried and tested method is based on dd and gzip.
Before you jump into backup mode, you should check to see if the drive is actually broken. A simple first step is to plug the USB into a different USB port or even a different computer. Sometimes the problem isn't the drive itself — it could be something as simple as a loose connection or an unstable port.
Now, to back up your flash drive, first connect your USB to your computer. Launch your favorite terminal (or press CTRL + Alt + T ). Then, locate your flash drive using the following command:
ls /dev/disk/by-id 
Alternatively, you can identify your flash drive by running lsblk or sudo fdisk -l to find the device name (e.g. /dev/sdb , not the partition like /dev/sdb1 ).
Next, back up the flash drive to a GZIP compressed image file in a single command, using:
sudo dd if=/dev/disk/by-id/YOUR_FLASH_DRIVE status=progress | gzip -c > /home/USERNAME/backups/BACKUP_NAME.img.gz 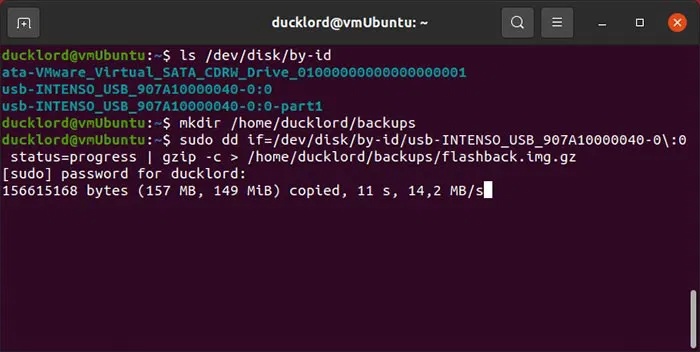
Also make sure that '/home/USERNAME/backups/' exists (create it with mkdir -p /home/USERNAME/backups ). Also, the if= parameter specifies the flash drive and gzip compresses the output.
To restore the backup, you will need to reverse the order of the two commands and specify your flash drive as the output device. The full command will look like this:
sudo gzip -cd /home/USERNAME/backups/BACKUP_NAME.img.gz | sudo dd of=/dev/disk/by-id/YOUR_FLASH_DRIVE status=progressNote : This will overwrite the entire flash drive, erasing all data. Double check the device name to avoid data loss.
Repair corrupted file systems with FSCK
Once you've backed up the contents of your flash drive, it's time to try to repair it. To do that, you can turn to fsck. This is great for removing corrupted file blocks, as most (if not all) corruption and unreadability issues stem from issues like this.
For this command, you will need to specify a partition instead of a full drive. You will find the partition with the same name as your device by executing:
ls /dev/disk/by-id/usb*Then run fsck on that drive with the command:
sudo fsck -v -y /dev/disk/by-id/YOUR_FLASH_DRIVE-PARTITION-TO-CHECK 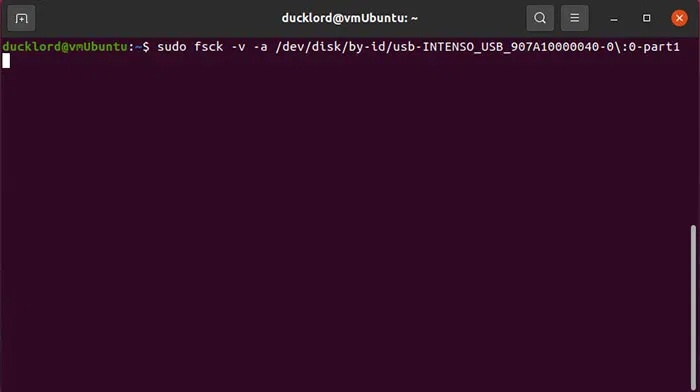
In this command:
- sudo fsck runs the repair tool with admin rights
- -v tells the tool to display detailed information about the process.
- -y tells the tool to automatically try to fix any errors it finds.
- /dev/disk… is the partition that will be checked for errors.
Format USB drive using Fdisk/MKFS from Terminal
If fsck fails to repair the device's file system, you can try formatting it to use it as if it were new.
The first step is to delete any existing filesystem structures and recreate them from scratch. You can use fdisk for this purpose. Run it with sudo on your device with:
sudo fdisk /dev/disk/by-id/YOUR_FLASH_DRIVE 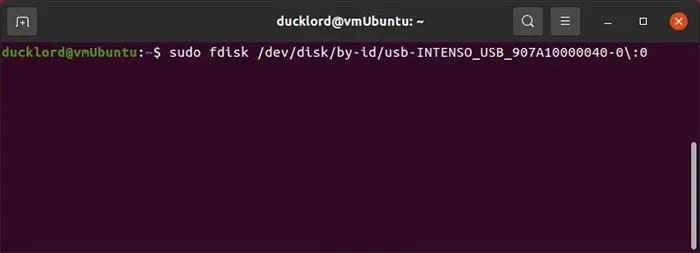
Press o and then Enter to create a new DOS partition table on it so your USB drive can read it everywhere. If you just want to use it on your modern computer and operating system, you can replace o with g to create a new GPT partition table.
Press n then Enter to create a new partition, then press p to make it a primary partition. If you use e instead of p , it will be created as an extended partition, but there is no point in doing so unless you plan on having more than 3 partitions on the drive. Then just press Enter when asked for the partition number, first sector, and last sector, to accept the defaults and let the partition span the entire USB drive.
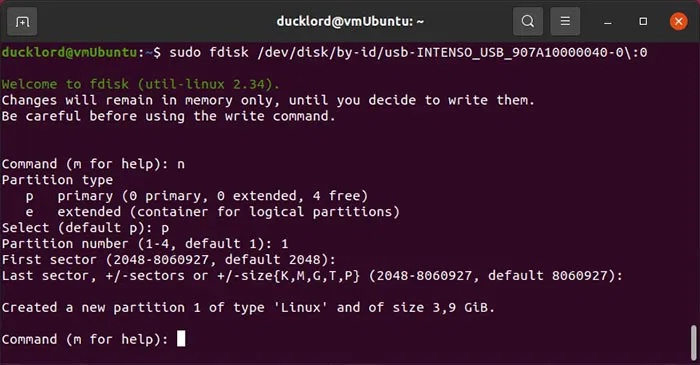
Press p and then Enter to test the new storage structure on the USB drive. Then, press w and then Enter to write the changes to the USB drive and exit fdisk.
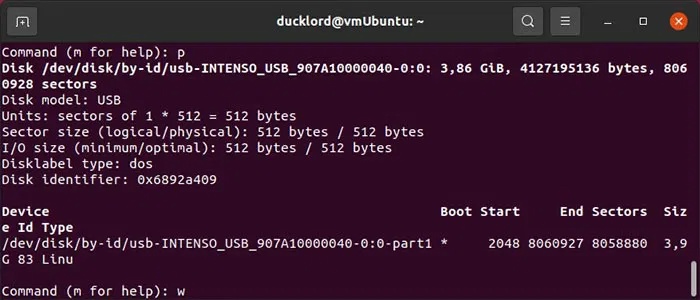
Format the new partition with a file system
Your partition will not be formatted and, since it does not have a file system, it will not be usable. You can create a file system using one of the mkfs tools that come with every modern Linux distribution. To format the partition to FAT32, which is usable on most devices, use:
sudo mkfs.fat -F 32 /dev/disk/by-id/YOUR_FLASH_DRIVE-PARTITION 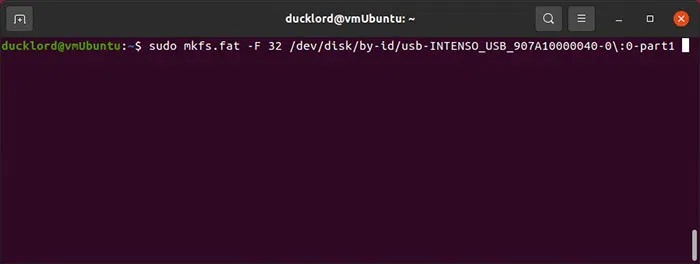
To format a partition with NTFS, for use with modern versions of Windows, or with EXT4, for use with Linux only, use:
sudo mkfs.ntfs /dev/disk/by-id/YOUR_FLASH_DRIVE-PARTITIONor
sudo mkfs.ext4 /dev/disk/by-id/YOUR_FLASH_DRIVE-PARTITION 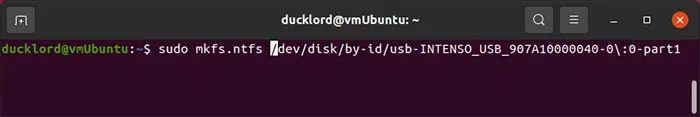
EXT4 is optimized for Linux but is not natively supported by Windows or macOS without additional software.
After formatting, you can plug in the USB and confirm that the drive is working. Just use lsblk again to check that the partition has a file system and is mountable.
Check and repair USB using Disks via GUI
If you don't like typing commands, you can switch to the Disks tool to check and format your USB. Disks comes pre-installed on Ubuntu.
Go to the applications menu and search for Disks . Launch the application when you find it.
Select your USB drive from the list on the left and click the gear icon. Then, select Repair Filesystem and follow the wizard's steps to repair the file system.
In this case, for example, it's not a hardware problem, but a corrupted file system. While the problem can't be repaired, you can reformat the USB drive and continue using it. To do that with Disks and the USB selected, click the gear icon again and select Format Partition .
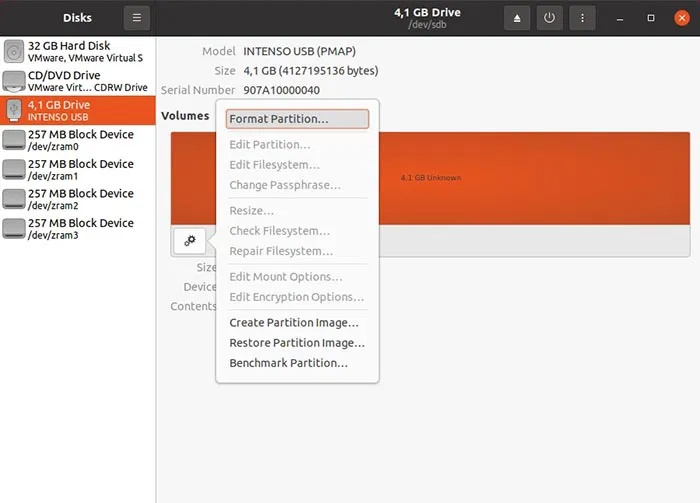
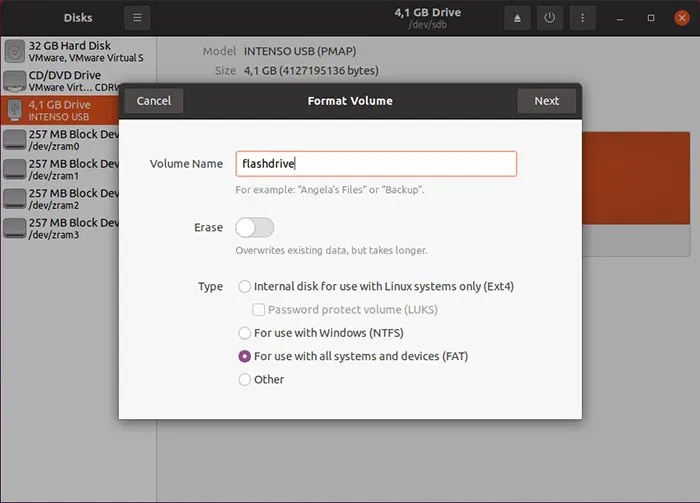
Enter a name for the USB drive in the Volume Name field and choose from the three most common file systems for that drive:
- Ext4 for use with Linux
- NTFS for use with modern versions of Windows
- FAT for use with both, as well as other types of devices (from smartphones to game consoles)
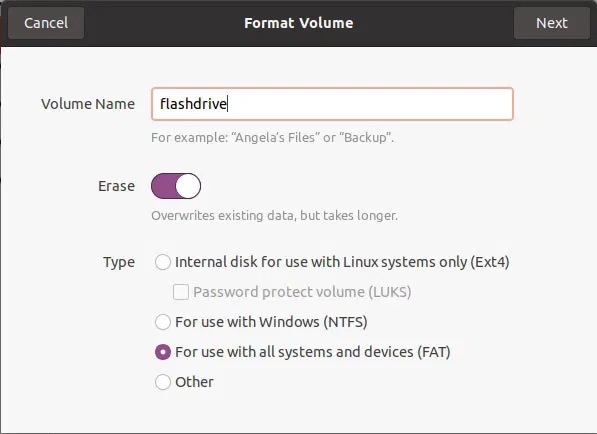
Pay attention to the Erase option . Leave this option disabled for a quick format. Swipe it to On for a full format, completely erasing the contents of the device. When dealing with damaged devices that may also have some bad blocks, it is better to use the full erase option.
Good luck!
See more articles below:
- Protect your Google account with a USB "security key"
- Summary of some ways to fix USB Device Not Recognized error on Windows 7, 8 and 10
- Want to know if your computer supports USB 3.0, read this article
You should read it
- ★ 6 ways to fix the error of not recognizing SSD drive in Windows 10
- ★ Instructions for fixing errors 'not recognized as an internal or external command' when using CMD in Windows
- ★ How to fix VPN error 619
- ★ Instructions on how to fix 53 error when restoring on iPhone
- ★ Fix error 3014 while restoring iPhone