How to Check if Android Phone is Rooted
Use Root Checker

Open the Play Store app store on Android. Tap the Play Store app icon, a multicolored triangle on a white background.
Click the search bar at the top of the screen. The Android keyboard will appear.
Find the Root Checker app. Enter root checkerand click on Root Checker that appears in the drop-down menu.
The Root Checker application has a check mark icon over the pound sign (#).

Click INSTALL . This green button is in the upper right corner of the page. Root Checker will begin the installation.
You may need to tap ACCEPT if asked.

Open Root Checker. Tap OPEN in the Google Play Store, or tap the Root Checker icon in Android's App Drawer.

Click AGREE (agree) when asked. The option is in the pop-up window in the middle of the screen. This shows that you have agreed to the privacy statement that Root Checker displays in the pop-up window.

Tap GET STARTED . It's at the bottom of the screen. The Root Checker application will be reloaded.
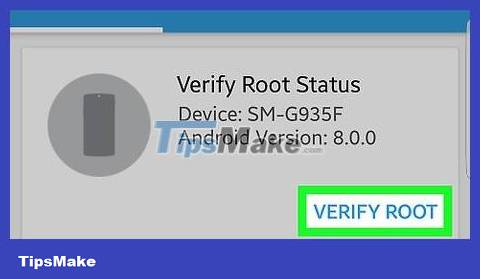
Tap VERIFY ROOT at the top of the screen. Root Checker will start checking to see if the Android device has been rooted.
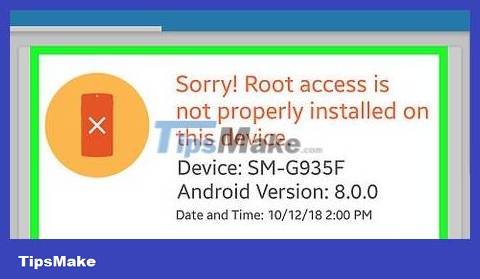
See the results appear. If you see the message "Congratulations! Root access is properly installed on this device" (Congratulations! Root access is properly installed on this device) appear at the top of the screen, your Android device is rooted.
If instead the message "Sorry! Root access is not properly installed on this device" appears at the top of the screen, the Android device is not properly installed on this device. be rooted.
Use the Terminal emulator program

First try looking for signs that your device is rooted. In most cases, rooted Android devices—especially older models—will have an app called "SuperUser" or similar installed in the App Drawer. If you see such an application in the App Drawer, this Android device is rooted and you do not need to proceed with the method below.

Open Play Store. Tap the multicolored triangle Play Store icon on a white background or briefcase.
Find the Terminal Emulator application. Tap the search bar at the top of the screen (you may need to tap Apps or similar first), then type terminal emulator for androidin and tap the "Search" or "Enter" button.
Install apps. Select the Terminal Emulator for Android app with the green Android icon on a blue background, then tap INSTALL (or similar) and then tap ACCEPT when it appears. The application will be downloaded and installed on the Android device.
Open Terminal Emulator. Tap OPEN in Play Store (if available); or tap the Terminal Emulator app icon in Android's App Drawer.

Enter the command "super user". On the main Terminal window, type suin and then press the "Search" or "Enter" button on your Android keyboard.
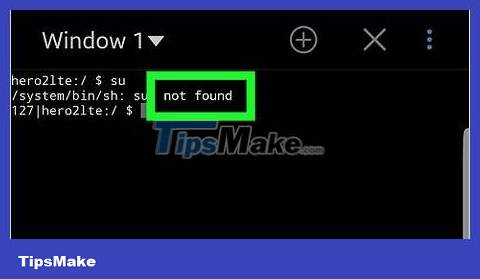
View response results. If you see the command line symbol change from $ to # , your Android device is rooted; Similarly, if you are asked for permission to execute commands as a super user (or something like that), it means your Android device is rooted.
If you get "su: command not found" or another error message, it means your Android device doesn't have root access (for example, it's not rooted).