HD DVD compared with Blu-ray
Following the DVD format was quite old, born in 1994, Blu-ray and HD DVD are the two brightest faces. However, this transition is not easy, but a direct confrontation between the two technologies. The article does not dissect the market of anyone who has lost it, but gives you a detailed view of the "weapons" that Blu-ray and HD DVD are carrying in them.
Source
 Blu-ray can also be called Blu-ray Disc (BD), which is a format developed by Blu-ray Disc Association (BDA), which is co-founded by disc manufacturers, electronic devices and computers. Main members include Apple, Dell, Hitachi, HP, JVC, LG, Mitsubishi, Panasonic, Pioneer, Philips, Samsung, Sharp, Sony, TDK and Thomson. Unlike current DVD technology based on red laser for data read / write, Blu-ray uses blue-violet laser. Therefore BDA incorporates Blue (Blue) and Ray (ray) to name this technology but removes the "e" character. BDA stylized "e" as the main logo for this brand.
Blu-ray can also be called Blu-ray Disc (BD), which is a format developed by Blu-ray Disc Association (BDA), which is co-founded by disc manufacturers, electronic devices and computers. Main members include Apple, Dell, Hitachi, HP, JVC, LG, Mitsubishi, Panasonic, Pioneer, Philips, Samsung, Sharp, Sony, TDK and Thomson. Unlike current DVD technology based on red laser for data read / write, Blu-ray uses blue-violet laser. Therefore BDA incorporates Blue (Blue) and Ray (ray) to name this technology but removes the "e" character. BDA stylized "e" as the main logo for this brand.
HD DVD's father is the DVD Forum, led by Toshiba, NEC, Sanyo and recently backed by Microsoft and Intel. DVD Forum has "sponsored" DVD format - (not DVD +), so there was a battle between 2 groups: DVD Forum and DVD + RW Alliances. In November 2003, the DVD Forum decided that HD DVD would be the successor to today's DVD. At that time, HD DVD was named Advanced Optical Disc (AOD).
General shape and technology
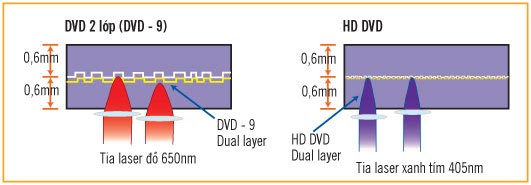
HD DVD, Blu-ray and CD / DVD discs are the same shape, 12cm in diameter. Like CD and DVD, Blu-ray and HD DVD also have a smaller version with a diameter of 8cm. The only physical difference is that the thickness of HD DVD is 0.6mm (equal to DVD), while the BD is 0.5mm.
BD has the following popular formats : read-only BD-ROM, for storing movies, games and software; BD-R recorded once; and BD-RE record (BDA can record 10,000 times). Currently, Blu-ray only has dual-layer disc technology and maximum capacity of 50GB for 2-layer discs. According to BDA, the group is working to raise the capacity of 100GB for 4-layer discs and 200GB 6-layers in the future. Currently, TDK has a 4-layer and 6-layer disk prototype. And with a 50GB disc can store up to 9 hours of HD video and 23 hours of standard video.

Red laser.
Green laser for thicker density
HD DVD is similar, there are 3 formats: HD DVD-ROM read-only, HD DVD-R recorded once and HD DVD-RW recorded. Currently, HD DVD discs also have 2 types: 1 layer of 15GB and 2 layers of 30GB. Particularly for HD DVD-RW format, the data slot width is smaller, 0.34µm compared to 0.4µm of the other two formats, HD DVD-ROM and HD DVD-R, so it has a slightly larger capacity: 20GB single layer and 32GB 2 layers (under development).
In terms of class, HD DVD's capacity is smaller than Blu-ray. While one layer of Blu-ray has a capacity of 25GB, HD DVD only reaches 15GB. According to DVD Forum, by the end of the summer this year will launch a 3-layer HD DVD disc with a capacity of up to 45GB. It is possible that film studios will consider this capacity issue, but in the eight hottest titles recently released by Warner Bros and Universal, no movie has the capacity to exceed the storage capacity of a disc. HD DVD 2 layer uses VC-1 and MPEG-4 AVC encryption. Specifically, the movie "The Last Samurai" 27.3GB, "The Phantom of the Opera" 24.8GB, "The Bourne Identity" 22.7GB, "Serenity" 19.6GB, "Doom" 16.5GB .
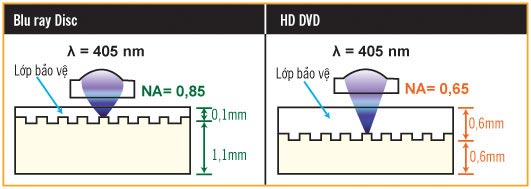
Both formats use blue lasers to read / write discs, but there is a different approach in each format. The advantage of a blue laser is that it has a short wavelength (405 nm) compared to the wavelength of red laser (650nm for DVD and 780nm for CD), so the laser will be much more accurate and can stack data on the disk surface more tightly. , so you can store more capacity on the same disk area. Thanks to this blue laser and some other new mechanisms, it is possible to achieve very high data density.
The "eye" in Blu-ray readers / writers is dual lens, there are two laser emitters and BD discs with a thinner coating to avoid bad optical effects, so the laser can record data. Good material and thicker density. Thanks to dual lens, Blu-ray players can be backward compatible with old DVD and CD formats. Many major manufacturers promise to offer a backward-compatible Blu-ray reader / writer with regular DVDs and CDs, and Blu-ray players will also be able to raise DVD image signals to 1080i or 1080p levels for quality. Current DVD is better than regular DVD. By reducing the wavelength, increasing the NA light diffusion index (see "NA index" in the article) is higher (0.85, compared to the DVD of 0.6 and HD DVD is 0.65) and is The width of the track is smaller (0.32µm compared to 0.40µm of HD DVD), so the BD is more storageable than HD DVD.
HD DVD is based on AOD (Advanced Optical Disc) technology. The advantage of HD DVD is the method of producing DVD almost like that of DVD, so the product cost is lower than Blu-ray and therefore the price is much cheaper than the rival. Another advantage for disk manufacturers is that they only need to edit the current disc production system, which can produce HD DVD, while to produce Blu-ray, it must buy a new production line. Thanks to Blu-ray's "single eye" instead of "dual", the HD DVD players will be more compact. The "eye" of the HD DVD player can play both red and blue lasers, so it can be compatible with the old DVD standard and the hybrid disc containing both the movie version, HD DVD and DVD on the same disc.
The general mechanism of Blu-ray and HD DVD reading / writing is no different than the standard CD and DVD: use a laser reader to read the disc tracks by reclaiming the reflected ray. A sensor near the "eye" will receive that signal and decode it.
Data processing
BD HD DVD Parameter Convert bit NRZI NRZI Modify 17PP ETM Correct error LDC = RS (248,216,33)BIS = RS (62,30,33) PI = RS (182,172,11)
PO = RS (208,192,17)
HD DVD uses a modulation mechanism called ETM (Eight to Twelve Modulation), borrowed from CD and DVD: each byte of data is changed to 18 bits, to satisfy the code RLL (1.10) (meaning bit "1) "must be separated into" 0 "bit at least 1 and at most 10). All of these conversion templates will be saved to the ETM table.
In contrast, Blu-ray uses a new modulation mechanism called 17PP (RLL (1.7) with parity conservation rules (modulated bits must be even, or even odd with the original data bit). at http://www.blu-raydisc.com/assets/downloadablefile/BD-ROMwhitepaper20051123clean22-13264.pdf.
When the data track is smaller, it is much more difficult to fix the scratched disk because the amount of data will be more compromised. Therefore, both of these green formats provide a new error correction mechanism. HD DVD chooses the simplest solution: all data containers (frame, sector, ECC block) and error correction algorithms (PI / PO) are borrowed from DVD. The only difference is that an ECC block of HD DVD corresponds to the two ECC blocks of DVD linked together. For example, an ECC block consists of 20 parity PI columns and 16 PO parity rows with a total capacity of 64kB. As a result, the groove area contains more error correction data than DVDs, up to 7.1mm.
Blu-ray uses other error correction mechanisms, based on Reed-Solomon code, named LDC (Long Distance Code) and BIS (Burst Indication Subcode) and also "occupies" the length of the error correction almost as much as HD DVD. , about more than 7mm.
Speed
1x speed of Blu-ray standard corresponds to 36mbps. BD-ROM movies require a minimum of 54mbps, so the speed of the BD-ROM disk will reach 2x (72mbps). And the ability of this speed will be even higher thanks to the NA index because the larger the NA, the less Blu-ray requires less power and slows down the recording speed while still maintaining the read / write speed. If the speed of the optical disc was previously limited to the speed of recording, then Blu-ray, the only factor that affected the speed was the speed of the burner. If the drive speed is 10,000 rpm (rpm), the write speed can be up to 12x at the outer edge of the disc is feasible (about 400mbps).
The HD DVD's 1x speed is 36.55mbps, slightly higher than Blu-ray, but this is already the maximum speed of HD DVD.
In this respect, Blu-ray is superior to HD DVD thanks to the combination of NA index and wavelength. These two specifications relate to the data density. At 36mbps bandwidth, Blu-ray discs need much less disk rotation speed than HD DVD discs. Therefore, with a maximum speed of 10,000 rpm, Blu-ray discs reach 12x speed while HD DVD discs only reach 9x. So to keep up with Blu-ray's bandwidth, HD DVD must raise the drive's rotation speed.
 Compared to the current DVD, the Blu-ray format has five times faster speed while the rotation speed is only twice as fast.
Compared to the current DVD, the Blu-ray format has five times faster speed while the rotation speed is only twice as fast.
Surface coating technology of Blu-ray
The highlight of Blu-ray compared to other competitors is the coating technology. Because Blu-ray burning technology records data much closer to the disc and coating surface than the DVD and HD DVD, only 0.1mm thick (compared to DVD and HD DVD is 0.6mm) so the discs The first Blu-ray is quite susceptible to damage due to foreign forces such as dirt or scratches and still has to be sold with a protective case.
Finally, in January 2004, BDA found a solution with scratch-resistant polymer coating technology for Blu-ray. This coating developed by TDK under the name "Durabis" (refer to www.durabis.com), which can resist dust, scratches and fingerprints. You just need to use a towel on the surface of the disc. In the past, you took the CD and DVD wipes like this, causing damage to the disc, as did HD DVD. TDK also used this Durabis coating technology on its Scratchproof DVD line. Recently, TDK also launched the new Durabis Durabis2 technology version, which, according to the company, can withstand sandpaper and steel fibers, and the next technology is implanted "privileged" on Blu-ray.
DIFFERENCE BETWEEN 3 FORMATS
Specifications
DVD
Blu-ray
HD-DVD
Capacity
4.7GB (l class)
8.5GB (2 classes)
25GB - 8cm 8GB disk (class)
50GB - 8cm 15.6GB disc (2 layers)
15GB - 8cm disk 4.7GB (l class)
30GB (2 layers) - 8cm 9.4GB disc (2 layers)
45GB (3 classes, late summer 2006)
Wavelength
650nm (red laser)
405nm (blue laser)
405nm (blue laser)
Numerical aperture (NA)
0.60
0.85
0.65
Disc diameter
Thickness
12cm, 8cm
1.2mm
12cm, 8cm (for cameras)
1.2mm
12cm
1.2mm
Protection class
Coatings
0.6mm
Is not
0.1mm
Have
0.6mm
Is not
Energy reading
3-5 mW
0.35mW
0.50mW
Data slot width
0.74µm
0.32µm
0.40µm (HD DVD-RW 0.34µm)
Speed reading data
Video / audio read speed
11.08Mbps (1x)
10,08Mbps (<1x)
36Mbps (1x)
54Mbps (1.5x)
36.55Mbps (1x)
36.55Mbps (1x)
Video resolution (maximum)
Video bit rate (maximum)
720 × 480/720 × 576 (480i / 576i)
9.8Mbps
1920 × 1080 (1080p)
40Mbps
1920 × 1080 (1080p)
28Mbps
Video encoder
MPEG-2
-
-
MPEG-2
MPEG-4 AVC
SMPTE VC-1
MPEG-2
MPEG-4 AVC
SMPTE VC-1
Audio encoder
Linear PCM
Dolby Digital
DTS Digital Surround
-
-
-
Linear PCM
Dolby Digital
Dolby Digital Plus
Dolby TrueHD
DTS Digital Surround
DTS-HD
Linear PCM
Dolby Digital
Dolby Digital Plus
Dolby TrueHD
DTS Digital Surround
DTS-HD
Interactive
DVD-Video
BD-J
iHD
Copy management mechanism
40-bit CSS
128-bit AACS
128-bit AACS
Video and audio encoding
Both Blu-ray and HD DVD support video and audio encoding standards. Both support 3 video encoding standards: MPEG-2; MPEG-4 AVC (H.254) and SMPTE VC-1 is based on Microsoft's Windows Media Video (WMV) technology.
HD readers will have to support the above 3 video encoding standards and the studios will choose which encoding to use for the movie. MPEG-2 encoding "consumes" the most disk space, for example, a single-layer BD-ROM can only store about 2 hours of HD movies, but the following 2 encodings can store up to 4 hours of HD on one layer. .
In the immediate future to support backward compatibility, Sony's BD-R and BD-RE discs will use MPEG-2 encoding; In order to record digital television videos, BD's minimum speed is 1x 36mbps quite appropriate compared to HD video that requires a minimum speed of up to 1.5x. Meanwhile, HD DVD from Warner Bros and Universal uses codec VC-1 or MPEG-4 AVC. However, HD DVD players currently only support 1080i (videos that are already 1080p) compared to Blu-ray that supports 1080p.
Both formats also support the following audio standards :
Linear PCM (LPCM) - supports 8 uncompressed audio channels.
Dolby Digital - for 5.1 audio.
Dolby Digital Plus (DD +) - extension of Dolby Digital, for audio 7.1.
Dolby TrueHD - is the extended standard of MLP Lossless, 8 audio channels.
DTS Digital Surround - often used for DVD, has 5 audio channels.
DTS-HD - extension of DTS, increasing the sampling rate (bitrate) and supporting 8 audio channels.
Digital rights management (DRM) and copy protection mechanisms
Blu-ray uses AACS copy protection technology (see also "AACS security management mechanism" in the article), with DRM features called BD + using dynamic conversion mechanisms. When an encryption is "cracked", the manufacturer will update the encryption mechanism and put a new encryption mechanism on every disc released later, just in case like the DVD is when hackers break the hack. It is possible that the entire product line is unlocked, and according to HP's proposal, BDA also uses the Mandatory Managed Copy system to allow users to securely export video from disc to file in a specified format. before.
BDA also agreed to apply watermarking technology to the disk (see "Digital copyright protection solution", ID: A0507_116). Under the other name "ROM-Mark", this technology will be available on read-only devices and will prevent large-scale copying without authorization.
Commercial HD DVD discs will also use Advanced Access Content System License Administrator (AACS) technology combined with "Audio Watermark Protection" technology. Every HD DVD reader has a sensor that can "hear the" layer of watermark in the audio part of the movie. An illegal copying disc will not be able to copy this audio watermark layer and when the sensor of the reader cannot read this watermark, it will not be played. The audio track of this watermark is based on the voice and music voice wavelengths in the usual form and is converted into code. These variants cannot be heard by human ears, but HD DVD players or audio editing software are easily identifiable. Therefore, this solution eliminates film discs originating from stealing or recording with microphones. Theater watermarks will differ from home entertainment watermarks and HD DVD readers will check if the disc is legitimate.
Manufacturers also plan to monitor HD DVD readers over the network, watching the reader as a digital cable box. Anyone who wants to unlock the reader, or project a disc that has been cracked, or an incorrect disk of the area code will disable the reader.
HIGH-DEFINITION MULTIMEDIA INTERFACE - HDMI
A point-to-score communication for transmitting audio and visual signals.This interface includes only a single line, used for home theater and consumer electronics devices.Appeared in 2002 by the HDMI association, this interface is similar to DVI video output but HDMI also has a voice path, and the HDMI jack is also more compact than DVI.HDMI and DVI have the same security and digital rights management mechanism as HDCP (High-bandwidth Digital Content Protection).
Also 19 feet but HDMI (left) is more compact than DVI.
Also HDMI / DVI input, but DVI must have additional input for audio.
HDMI has bandwidth up to 165 megapixels (618MB / s) so this communication easily transmits the highest definition digital TV. HDMI also supports up to 8 audio channels encoded at 24-bit / 192kHz.
Both HDMI and DVI are based on the same TMDS connection technology of Silicon Image, so HDMI is backward compatible with DVI. HDMI-DVI and DVI-HDMI converters and cables allow video signals to be exchanged between HDMI and DVI devices. Since DVI is just a line, the line must have its own cable.
HDMI has just passed HDMI 1.3, which offers many new features.Most notable is the mini-HDMI connection for HDMI output on the graphics card.Because the graphics card has very little space, the mini-HDMI is very suitable.In addition, the bandwidth is raised from 618MB / s to 1.27GB / s and supports color depths of up to 30bit, 36bit and 48bit RGB compared to the previous standard that only supports 24bit colors.Thanks to the larger bandwidth, HDMI is able to upgrade the new audio format: Dolby TrueHD and DTS-HD Master Audio and the new audio / video Lip Sync sync feature.See more at www.HDMI.org.

 Also 19 pins but HDMI (left) is more compact than DVIAlso HDMI / DVI input but separately DVI must have additional lines for audio.
Also 19 pins but HDMI (left) is more compact than DVIAlso HDMI / DVI input but separately DVI must have additional lines for audio.
Area code management
One concern is the regional limits offered by manufacturers and studios to help optimize their business and counter piracy, also known as the Regional Playback Control (RPC) setting. This mechanism limits users to using products in a certain geographic area. Unlike DVD divided into 8 area code areas, Blu-ray will only have 3 areas (see table). The notable point in BDA's new division is Japan, Taiwan and South Korea (without China) with the same region 1 code with the US. According to some initial comments, this will help reduce the problem of "unlocking" the area code that the previous generation of DVD suffered.
Area code
Area 1America, territories of the US, Japan, South Korea and Taiwan
2Europe and Africa
3Asia (except Japan, Korea and Taiwan) and countries and islands in the Pacific Ocean
As for HD DVD, the DVD Forum is still negotiating with Hollywood studios about partitioning, they haven't "decided" to follow the old partitioning method like DVDs or creating new partition tables, just like good Blu-ray. is not. In the short term, some of the first HD DVD products do not have partition management features. But HD DVD will definitely have partition management in the near future. As for China, the DVD Forum made a draft to establish a separate security standard for this country.
Compatibility issues
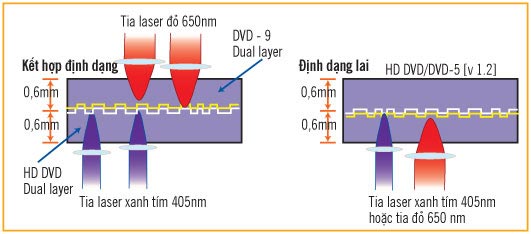
Currently, both formats are backward compatible with the "world" CD / DVD using red laser quite well. NEC has a reader for all 3 formats: HD DVD, DVD and CD. Philips also has a drive that can read / write CD, DVD and Blu-ray. Another trend is that a number of disc makers have released multi-layer hybrids. JVC is a support group for Blu-ray format, has launched 3-layer disc technology in hybrid BD / DVD discs, combining both BD and DVD formats. If the commercialization process is successful, this hybrid disc format will be compatible with both regular DVD players and high definition BD heads. Cinram DVD-9 / HD DVD is also developed by Cinram, the first layer is DVD-9 with 8.4GB capacity and the second layer is HD DVD 15GB. Memory-Tech and Toshiba are also developing hybrid DVD-5 / HD DVD discs with the first 4.7GB layer and the second 15GB class.
In particular, Samsung has announced that it is researching products that support both Blu-ray and HD DVD formats planned to be released later this year or early next year. Samsung now has a Blu-ray reader but said it will not develop HD DVD players but only to compatible readers for both standards.
Another problem related to AACS protection feature. Blu-ray players only output HD content via HDMI and DVI-D connections, meaning older HDTV TVs may not have these two (see HDMI section in this article). For computers that want to display Blu-ray, both the screen and the video card must be HDCP compatible. Currently, although there are a few monitors that support HDCP, no graphics card supports this standard yet. Even the latest graphics cards from ATI and NVIDIA are HDCP Ready labeled but are not yet fully compatible.
NA INDEX
Numerical Aperture (NA) is an optical index that specifies the allowed angle of projection of that ray.This index differs between different types of optical rays due to different NA calculations.
The nature of the laser when transmitted, the size of the beam will "hatch" gradually but at a small angle. At this time, the laser is not cylindrical but has a pyramid shape. Therefore, the edge of the laser at the expanded area is no longer "sharp" compared to the area when the beam is formed. Therefore, the light will be further reduced as the laser axis approaches.
NA is calculated by the formula: NA = n sin θ
In which, θ is an indicator of the light diffusion of the laser.With this laser indicator is calculated by:
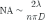
In which, λ is the wavelength of light and D is the diameter of the light ray at the smallest point as the source point.You should also note that a laser coming from a small point may "hatch" very quickly, while the laser has a large starting diameter, the smaller "hatch".
Interactive interface
In addition to the video and audio storage area, Blu-ray and HD DVD have a separate interactive layer for you to include graphics, menus and other special features; For example, it is possible to view the system menu of a translucent window system without stopping the movie like in a normal DVD player.
BDA collaborates with Sun to make Java applications an interactive interface for Blu-ray discs. In addition to the usual interoperability like on DVD, Blu-ray also has network features for content producers that support many new features such as downloading extensions, updating content via the web and watching broadcast. live special events.
Unlike Blu-ray, HD DVD uses the iHD interactive format developed by Microsoft and Toshiba. This is an open standard that film studios are willing to support, especially Disney. Microsoft's upcoming Windows Vista operating system will also support iHD. iHD allows data formats in XML and ECMAScript (standardized Javascript).
AACS SECURITY MANAGEMENT MECHANISM
AACS (Advanced Access Content System) is the digital copyright management standard for optical disc formats, especially for DVDs and optical disc generation using green laser technology.This management mechanism development team includes well-known companies such as Disney, Intel, Microsoft, Matsushita, Warner Brothers, IBM, Toshiba, and Sony.The past of AACS is not very glorious.AACS has a mechanism similar to the CSS (Content Scrambling System) and has been broken by hackers as soon as it was launched.A famous player nicknamed DVD Jon once surpassed the original CSS security encryption predicting that AACS will also be penetrated around the end of this year or early 2007.
AACS takes advantage of encryption to manage, content will be encrypted under one or more title keys using AES encryption (Advanced Encryption System). These title keys are created by combining a key named media key with several other factors, including the optical disc ID number (like the disk serial number) and a cryptocgraphic hash code. called usage rules. Each reader when produced will be provided with a set of multiple encryption keys so that suppliers can "revoke" the reader. So when "unlocked", the licensing of AACS simply does not reuse the keys that are "broken" for new content products.
However, currently the AACS copy management mechanism for Blu-ray and HD DVD is still incomplete, especially important technical details.This is currently a barrier for manufacturers to not provide standard security mechanisms.You can refer to this AACS security mechanism at the official websitehttp://www.aacsla.com/.
Conclude
It is clear that Blu-ray is superior to HD DVD in some ways, the most obvious being the capacity. However, in terms of market factors, HD DVD excels in price because disc manufacturers can take advantage of existing production lines. Whatever format is "crowned", both of these formats open up new possibilities for promising new movies and archives.
Le Duy
Reference :
www.cdfreaks.com
www.avsforum.com
www.blu-ray.com
www.hddvdprg.com
www.cdrinfo.com