Exchange Server 2007's spam filtering feature does not need the Exchange Server 2007 Edge Server
Markus Klein
In this article, I will show you the spam filtering features of Exchange Server 2007 that do not use the Exchange Server 2007 Edge Server Role.
Introduce
Many Exchange Server administrators know how to use features from Exchange Server 2003, which are not available by default if they do not use the Exchange Server 2007 Edge Server Role as a notification server. in DMZ. This feature is only available by default in that role, but can be enabled on Exchange Server 2007 while running on the Hub Transport Role. In this article, we will show you how to enable and configure this feature.
Enable AntiSpamAgent feature
Adding this feature and your Hub Transport servers is a completely simple process. First, launch the Exchange Management Shell. In the Scripts folder created earlier, you will see a PowerShell script to install Anti-spam agents. After running this command, you need to restart your transport service and restart the Exchange Management Console management interface. The script we need to run is called install-AntiSpamAgents.ps1 .
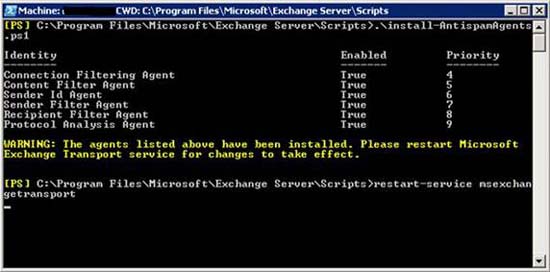
Figure 1: Enable AntiSpamAgent feature
After restarting the Exchange Transport Service, we have a new tab in the Exchange Management Console as shown in the following image:

Figure 2: Anti-Spam tab in the Exchange Management Console
Note:
We will examine more closely each of these anti-spam features:
- Content Filtering
- IP Allow List
- Allow List Providers IP
- IP Block List
- IP Block List Providers
- Recipient Filtering
- Sender Filtering
- Sender ID
- Sender Reputation
Internal content filtering (Content Filtering)
The Content Filter agents work with spam reliability rating (SCL for short). This rating is one of the numbers 0 - 9 for each message; A high SCL level means it is more like spam. You can configure this agent according to the message rating as follows:
- Delete notifications
- Refuse to notify
- Isolation of notifications
You can also customize this filter yourself and configure exceptions if you want.
Allowable IP List (IP Allow List)
With this feature you can configure certain IP addresses that are allowed to connect to your Exchange server. So if you have a dedicated mail forwarding server in your DMZ, you can add its IP addresses so that your server will not accept connections from other servers.
List of providers with IP permission
In general, you cannot configure your own IP-enabled lists without encountering any errors that can lead to problems receiving emails from your customers or other business partners. Therefore, you should contact a public IP that allows listing providers that work with you. This means that you will have better quality in this service and besides that is higher business value.
IP list is locked
This feature allows you to configure IP addresses so that these addresses are not allowed to connect to the server. In contrast to the allowed IP list, this feature provides a black list, not a white list.
List of providers with IP locked
This feature is similar to the blacklist of providers. Their task is to publish lists from servers or IP addresses that are currently spam.
Recipient Filtering (Recipient Filtering)
If you need to block emails to internal users or domains, this feature is one of the things needed to do that. You can configure this feature and then add the appropriate addresses or SMTP domains to your blacklist. Another interesting feature is that it allows you to set up a profile that will only allow you to accept emails from recipients on your global address list.
Sender filtering (Sender Filtering)
If you need to block certain domains or external email addresses, you will have to use this feature. With this feature, you can configure a blacklist of addresses of senders and domains that you will accept.
Sender ID (Sender ID)
Sender ID agent relies on the header of the simple mail transfer protocol multiplied - RECEIVED Simple Mail Transfer Protocol (SMTP) and a query for the domain name system (DNS) service of the system being sent to determine the action takes place on a notification sent. This feature is quite new and based on the needs of a specific DNS setting.
Sender ID is intended to combat the personalization of senders and domains (or problems can be called spoofing). A spoofed email is an email message whose address has been changed to appear as if it was sent from another sender. These spoofed mail often contain the FROM in the header of the message to confirm originating from a dedicated organization.
The Sender ID evaluation process will generate a Sender ID status for each notification. The Sender ID status will be used to evaluate the SCL rating for that message. This status may receive one of the following settings:
- Pass - IP addresses that are in an allowable set
- Neutral - Published Sender ID data is not specified
- Soft fail - The IP address may be in an unauthorized set
- Fail - IP address in file is not allowed
- None - No published data in DNS
- TempError - A temporary error has occurred, such as a DNS server currently unavailable
- PermError - Unrecoverable error appears, such as a record format error.
Sender ID's status will be added to the email metadata section and then transferred to the MAPI attribute. The Junk E-mail filter in Microsoft Office Outlook will use the MAPI attribute during the SCL value creation process.
You can configure this feature to perform the following actions:
- Stamp the status
- Reject
- Delete
Reputation of the sender
The sender's reputation is one of the new anti-spam features in Exchange Server 2007 that is intended to block notifications based on many features.
The sender's reputation level calculation is based on the following information:
- HELO / EHLO analysis
- Reverse DNS lookup
- Analysis of SCL
- Sender open proxy test
The sender's reputation will be in each of these statistics and give an SRL for each sender. SRL is a number between 0 and 9. You can configure what to do with the message in one of the following ways:
- Refuse
- Delete and store
- Accept and mark the sent sender
Conclude
As you can see after reading this introduction, Exchange Server 2007 provides a lot of features to increase spam protection on Exchange Server. If you do not use a dedicated Exchange Edge Server, you can add this feature to Exchange Server 2007 Hub Transport as described in the article. If you define a configuration for your specific server design, then you will have to add third-party software to meet your business needs.
If in case you need to have more than the functions described above, we recommend using Microsoft ForeFront Security for Exchange Server servers.