Remote workstation security in Windows Server 2008 R2
In this article we will discuss some of the security mechanisms included in RDS and how to use Group Policy and configuration settings.
Remote Desktop Services (RDS) in Windows Server 2008 R2 has many new features compared to the previous Terminal Services. With new features (one of them already in Windows Server 2008) such as RemoteApp, RD Gateway and RD Virtualization Host, this Windows Server role now allows you the flexibility to deploy your own applications. retail or workstations complete via RDS or VDI solutions - in many cases without Citrix systems or other third-party add-ons.
However, in terms of security, these additional complications turn into new forms of security. So in this article, I will show you the security mechanisms within RDS, which will show you how to use configuration settings and Group Policy for better security, besides the real way. Best security for a RDS deployment.
New in R2
If you come to RDS from Windows Server 2008 Terminal Services, you will not see as many changes as you upgraded from Windows Server 2003. WS 2008 adds a lot of major improvements to Terminal Services, including TS Web Access. for connecting web browsers, TS Gateway to users connected via the Internet, RemoteApp for distributing single applications to users via Remote Desktop Protocol (RDP) and Session Broker are included in the load balancing feature.
WS 2008 R2 has added many interesting points:
- Remote Desktop Virtualization for VDI solution
- RDS Provider for PowerShell so that administrators can change the configuration and perform tasks at the command line and through the script.
- Remote Desktop IP Virtualization, allows assigning IP addresses for connections based on session or program.
- A new RDP version and Remote Desktop Connection (RDC) client, v. 7.0
- Fair Share CPU scheduling allows dynamic allocation of processing time between sessions based on the number of active sessions.
- Windows Installer compatibility allows easy installation of programs that require configuration on the user.
- True multiple monitor supports up to 16 screens, so programs work like they do when running on the client.
There are also improvements in audio / video as well as support for Windows Aero in the RD session (although it should be noted that the Desktop Composition, which allows Aero, is not supported in a multi-screen session).
Security mechanisms and effects
Obviously, potential security issues depend on how you implement RDS. If you have a more complex setup, for users who connect via the Internet or through a web browser, you will have more security issues than if there is only one simple deployment where the user Only connect via RDC client via LAN.
RDC includes a number of security mechanisms that can help you create safer RD connections.
Network level authentication (NLA)
For best security, you should request Network Level Authentication (NLA) for all connections. NLA requires users to be authenticated against the RD Session Host server before creating a session. This helps to protect remote computers from malicious users and malicious code. To use NLA, the client must use an operating system that supports the Credential Security Support Provider (CredSSP) protocol, meaning Windows XP SP3 or higher operating system version, and running the RDC client 6.0 or higher than.
NLA is configured on the RD Session Host server via Administrative Tools | Remote Desktop Services | Desktop Session Host Configuration. To configure a connection to use NLA, follow these steps:
- Right-click Connection
- Select Properties
- Click the General tab
- Check the box to 'Allow connections only from computers running Remote Desktop with Network Level Authentication' as shown in Figure 1.
- Click OK .

Figure 1
Transport Layer Security (TLS)
A RDS session can use one of three security layers to protect the communication between the client and the RDS Session Host server:
- RDP security layer - This layer uses original RDP encryption and is the least secure class. The RD Session Host server is not authenticated.
- Negotiate - TLS 1.0 (SSL) encryption will be used if the client supports it. Otherwise the session will return to RDP security.
- SSL - TLS 1.0 encryption will be used to authenticate the server and encrypt the data sent between the client and the Session Host server. This is the safest option.
For best security performance, you can request SSL / TLS encryption. To get there, you need a digital certificate, which is a certificate that can be issued by a CA or signed by itself.
In addition to selecting the security class, you can select the encryption layer for the connection. The options you can choose here are:
- Low - Use 56 bit encryption for data sent from client to server. Do not encrypt data sent from the server to the client.
- Client Compatible - This is the default option. It encrypts data sent in both directions between the client and the server with the maximum key length the client can support.
- High - This option encrypts data sent in both directions between the client and server with 128-bit encryption.
- FIPS Compliant - This option encrypts data in both directions between the client and the server with FIPS 140-1 encoded.
It should be noted that if you choose High or FIPS Compliant, clients that do not support these levels will not be able to connect.
Here's how to configure server authentication and encryption settings:
- On the RD Session Host, open the Remote Desktop Session Host Configuration and the Properties dialog box of the connection as described above.
- On the General tab, select the appropriate security class and encryption level from the drop-down boxes, as shown in Figure 2.
- Click OK .
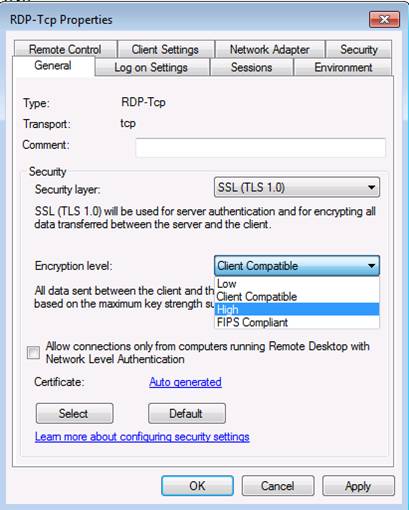
Figure 2
You can also use Group Policy to control these authentication and encryption settings, along with other aspects of RDS.
Group Policy
There are several Group Policy settings for RDS in Windows Server 2008 R2. These settings are located under Computer ConfigurationPoliciesAdministrative TemplatesWindows ComponentsRemote Desktop Services in the Group Policy Management Console for your domain, as shown in Figure 3.

Figure 3
As you can see, there are many policies to register, RDS clients and RD Session Host. Security related policies for the RD Session Host include:
- Server Authentication Certificate Template: Use this policy to specify the name of the certificate template to determine which certificate will automatically be selected to authenticate the RD Session Host server. If you enable this policy, only the certificates created with the specified template will be considered while selecting the certificate to authenticate the RD Session Host server.
- Set Client Connection Encryption Level: This policy is used to control whether a specific level of encryption is needed. When enabling this policy, all media must use a specific encryption level. The default option level is High.
- Always Prompt for Password upon Connection: You can use this policy to force RDS to always request user passwords when logging into an RD session, even if the password is entered in the RDC client. By default, users can log in automatically if the password is entered in the RDC client.
- Require Secure RPC Communication: Enabling this policy means that only requests that are authenticated and encrypted from the client are allowed. Communication with untrusted clients will not be allowed.
- Require Use of Specific Security Layer for Remote (RDP) Connections: If you enable this policy, all communications between the client and the Session Host server must use the security layer you specified here (RDP, Negotiate or SSL / TLS).
- Do Not Allow Local Administrators to Customize Permissions: This policy will disable administrative rights to customize security permissions in the RD Session Host Configuration tool, the purpose of which is to prevent administrators from changing User groups on the Permissions tab in the configuration tool.
- Require User Authentication for Remote Connections by using Network Level Authentication: With this policy, you can request NLA for all remote connections to the RD Session Host server. Only NLA-enabled clients can connect.
Note:
Here you can find out whether a client supports Network Level Authentication: Open the RDC client and click on the icon in the upper left corner, then select ' about '. If NLA is supported, you will see 'Network Level Authentication Supported'.
Other Group Policy settings worth checking are located under the RD Connection Client button. They include:
- Không cho phép mật khẩu để được lưu: Enabling this policy will disable the password check box in the RDC client dialog box. If a user opens an RDP file and saves their settings, previously saved passwords will be deleted. This forces users to enter the password every time they log in.
- Specify SHA1 thumbprints of certificates represented trusted . rdp publishers: With this policy, you can specify a list of fingerprints and when a certain fingerprint is valid for a pattern on the list, it will be considered trusted.
- Prompt for credentials on the client computer : This policy will prompt the user for certificates on the client instead of on the RD Session Host.
- Configure server authentication for client : With this policy, you can determine whether the client can establish a connection with the RD Session Host when the client cannot authenticate the RD Session Host server. The highest security setting is 'Do not connect if authentication fails'.
You can also use Group Policy to configure FIPS consent, but you won't find that policy here with other RDS security policies. Instead, it's located in Computer ConfigurationWindows SettingsSecurity SettingsLocal PoliciesSecurity Options. In the right pane, scroll down to the section: 'System Cryptography: use FIPS compliant algorithms for encryption, hashing and signing.' When you activate this policy, it will only support Triple DES (3DES) encryption algorithm for RDS communication.
RD Web Access
For clients who have not installed the RDC client software, users can access the published applications with them using a web browser. Users type Url into the browser to access the published RDS resources with them. RD Web Access Server is an isolated server with the RD Session Host. You define which RD Web Access servers can connect to the RD Session Host server.
The web interface is configured with SSL and users must be authenticated with their certificates. Authenticated users will only be able to view remote RemoteApp programs that their accounts have access to because the published programs will be cut off, using the access control list (ACL). .
Web Access Server uses X.509 certificate to provide encryption. By default, a self-signed certificate will be used. For better security, you should have a certificate from a certain CA or your company's PKI.
RD Gateway
RD Gateway (RDG) is used to provide access to RD resources to users over the Internet. The Gateway server is located at the edge and it will filter incoming RDS requests according to the Network Policy Server (NPS). NPS uses two policies: Connection Authorization Policy (CAP) policy to list which users can access RDG and Resource Authorization Policy (RAP) used to specify the device. Which CAP users can connect to via RDG.
Conclude
Remote Desktop Services in Windows Server 2008 R2 has indeed expanded a lot of functionality compared to its predecessor, Terminal Services - but it also has some new security issues that need to be mentioned. The best security implementations in configuring components in RDS deployments such as the RD Session Host, RD Web Access Server, RD Gateway and clients - and by using Group Policy to configure controls will help you maintain get a safe environment, while still giving you many other benefits.
You should read it
- ★ Deploying IPsec Server and Domain Isolation with Windows Server 2008 Group Policy - Part 2
- ★ Deploying IPsec Server and Domain Isolation with Windows Server 2008 Group Policy - Part 4
- ★ Application security with AppLocker
- ★ Install Remote Desktop Web Connection on Windows XP
- ★ Deploying IPsec Server and Domain Isolation with Windows Server 2008 Group Policy - Part 1