Deploying IPsec Server and Domain Isolation with Windows Server 2008 Group Policy - Part 1
Network Access Protection is a new technology available in Windows Server 2008, allowing you to control which computers are allowed to connect to other computers on your network. Network Access Protection (or NAP) allows you to set up 'health' policies on which network computers must have these factors before being allowed to access the network. Computers with all the necessary requirements for network access policies will be allowed to access the network. In other cases, the computer may not or you can configure policies to allow the computer to connect to the server to "suspend" it to allow the computer to settle and attempt to connect. connect back to the network after successful "negotiations".
There are many ways you can enforce a NAP policy. The easiest way is to use NAP with DHCP enforcement. However, this method is also the least secure method since users can manually configure the IP address on the computer and bypass the NAP DHCP enforcement policy. The safest method for implementing NAP is IPsec. When using IPsec NAP enforcement and agreeing with the NAP access policy, the computer will be issued with a health certificate to allow creating a secure IPsec connection with other computers on the 'virtual' NAP network. However, NAP with IPsec implementation is the most complicated configuration of the methods.
NAP itself is a fairly complex technology with hundreds of components. When using NAP with IPsec enforcement, you will find there are many parts and troubleshooting is much simpler. There is also a dependency on Group Policy, which increases the complexity of the solution, the cause of which is that you often need to fix problems with Group Policy when deploying NAP.
All the difficulties and challenges above do not discourage us, but the point we want to emphasize here is that when implementing this implementation you must know about its complex settings and configuration, from there. Be patient and test carefully during deployment. The more time you spend testing and understanding how the solution works, the more successful you will be in your deployment.
NAP with IPsec policy enforcement will be a very powerful method of deploying your NAP solution. You will have two solutions in one: the first solution is to have NAP network access control to allow you to block computers that do not meet the 'health' criteria connected to the network and Secondly, you will take advantage of isolating the IPsec domain so that it can prevent deceptive computers from connecting to your network. NAP with IPsec domain isolation will allow you to create a virtual network within the boundaries of your physical networks. Computers in the IPsec virtual private network can be on the same network segment or VLAN segment but are segmented virtually together by IPsec. Computers without IPsec 'health' certificates will not be able to communicate with 'healthy' computers in the network.
In this section we will introduce you from the beginning to the end of the NAP solution deployment process by implementing IPsec policy. The initial environment is very simple, as you can see in the picture below.

Figure 1
The computers that we are using on the network for example are:
WIN2008DC
This is a Windows Server 2008 Enterprise edition computer, which plays the msfirewall.org domain controller. There is only one server role installed on this computer, the Certificate Authority server role. We created on this computer a CA Enterprise Root. If you want to mirror this configuration, first take a domain controller role, then elevate it to a domain controller, install the CA role and select the Root CA option. If you want to mirror an enterprise CA configuration, name it CA msfirewall-WIN2008DC-CA .
WIN2008SRV1
This is a Windows Server 2008 Enterprise-based computer and is a member server in the msfirewall.org domain. There are no server roles configured on this machine. We will install the NPS server role on it and make it become a lower-level CA, but if you want to build this lab, install Windows Server 2008 on your computer and follow the instructions like them. I introduced in this series.
VISTASP1
This is a computer running Vista SP1. This computer is joined to the msfirewall.org domain. We used a default Vista installation and then installed SP1. If you already have a SP1 installation before then that is nothing to mention.
VISTASP1-2
This is a Vista-based computer, like VISTASP1 . This computer is installed in a workgroup called WORKGROUP. We will import this computer into a domain after testing NAP and IPsec policies.
The main steps we will take in this series include:
- Configure domain controllers
- Install and configure Network Policy Server, the Health Registration Authority and the Subordinate CA
- Configure NAP IPsec Enforcement Policy on the Network Policy Server
- Configure VISTASP1 and VISTASP1-2 for testing
- Test Health Certificate and Auto-remediation Configuration
- Verification enforces NAO policy on VISTASP1
- Configure and test IPsec policies.
Our goal in this series is to show you how to configure a solution and show that the solution worked.
Configure domain controllers
In this section, we will perform the following steps:
- Confirm the CA Enterprise Root configuration on the domain controller
- Create the NAP CLIENTS security group
- Create NAP Exempt security group
- Create and configure Certificate Template for the NAP Exempt Computers
- Make the Certificate Template available in Group Policy publishing.
- Distribute NAP Exemption Health Certificate through Group Policy Autoenrollment
Confirm the Root CA configuration
Verify that certificate requests do not require administrator approval. Perform the following steps on the domain controller computer, WIN2008DC:
1. Click Start , point to Administrative Tools, and then click Certification Authority
2. In the left pane of the interface, right-click CA , and then click Properties .
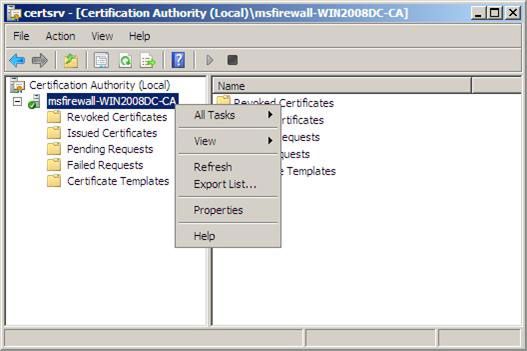
Figure 2
3. Click the Policy Module tab, and then click Properties
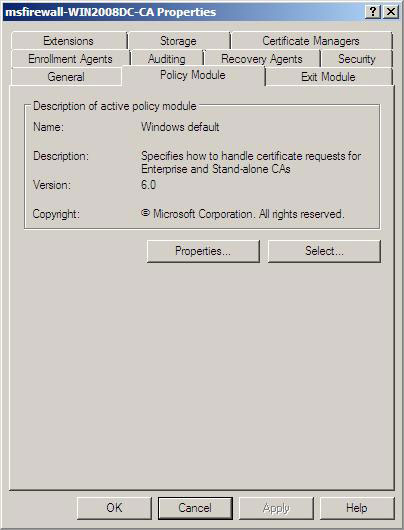
Figure 3
4. Verify that the option Follow the settings in the certificate template, if applicable. Otherwise, automatically issuing the certificate has been selected.
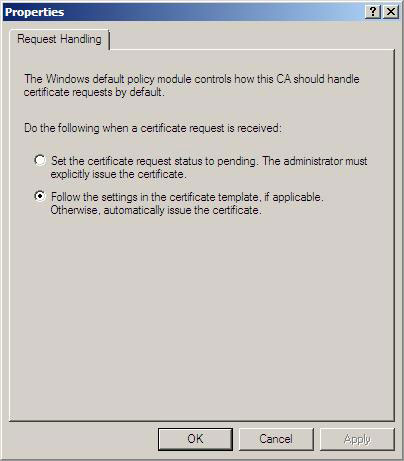
Figure 4
5. Click OK twice, and then close the Certification Authority console
Create the NAP CLIENTS group
Next, create a Group Policy security filter group. What we're going to do now is create a Group Policy Object to use the NAP policy machines that we'll use, then configure the GPO only for the members of the group. In this way, we do not need to create an OU for NAP clients. All we need to do is add NAP clients to the security group. VISTASP1 and VISTASP1-2 will be added to this group after we join the domain.
Perform the following steps on WIN2008DC computer:
1. In the left pane of the Active Directory Users and Computers interface , right-click msfirewall.org , point to New and then click Group .

Figure 5
2. In the New Object - Group dialog box, in Group name , type NAP Clients . In Group scope , select Global , and in Group type choose Security , and then click OK
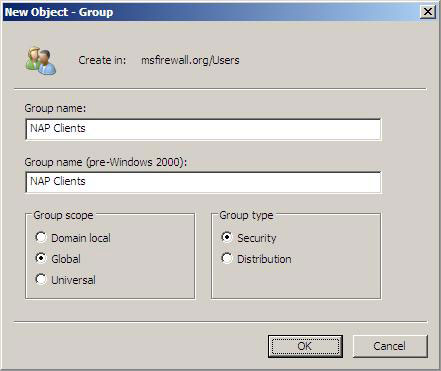
Figure 6
3. Leave the console to Active Active Users and Computers to open the procedure below.
Create NAP Exempt group
There will be machines on your network that need to communicate with members of the secure network, who cannot meet the necessary NAP security requirements. There are network infrastructure computers, such as domain controllers, DHCP servers and other components that need to communicate with secure network computers.
In our example, WIN2008SRV1 needs to connect to the members of the secure network to provide them with health certificates, which will be used to establish secure IPsec communication between members. in secure network. Therefore, we will place this computer as a separate group and then configure the health certificate to be automatically deployed to this computer. The health certificate will be deployed to this computer using automatic enrollment.
Perform the following steps on WIN2008DC computer:
1. In the Active Directory Users and Computers console, right-click msfirewall.org and point to New , then click Group .

Figure 7
2. In Group name , type IPsec NAP Exemption . In Group scope , select Global and in Group type choose Security , then click OK
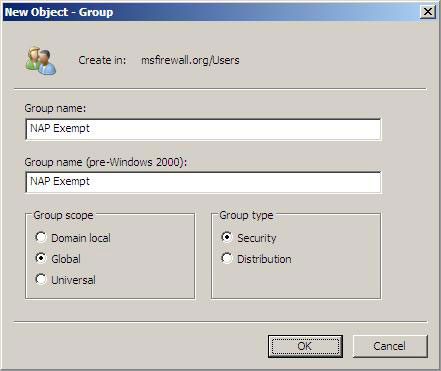
Figure 8
3. Leave the Active Directory Users and Computers console for the procedure below.
Figure 9
Create and configure certificate templates for NAP Exempt Computer
A certificate template must be created for computers that are granted NAP health exemptions. This certificate template will be configured with two application policies: client authentication and system health authentication. This certificate template will be configured with the System Health Authentication OID so that it can be used to communicate with NAP compliant computers in a secure network.
After creating the certificate template, we will publish the certificate template so that it becomes available to Active Directory for computers that are members of the NAP Exempt group. After publishing the certificate template for Active Directory, we will configure Group Policy so that the certificate is automatically assigned to members of the NAP Exempt group using the auto-enrollment feature (Autoenrollment).
Perform the following steps on WIN2008DC computer:
1. Click Start , click Run and type certtmpl.msc and then press ENTER
2. In the middle pane of Certificate Template Console , right-click Workstation Authentication , then click Duplicate Template . This template is used because it has been configured with the client application authentication policy.
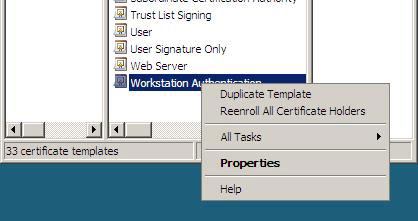
Figure 10
3. In the Duplicate Template dialog box, select the Windows 2003 Server , Enterprise Edition options and click OK .
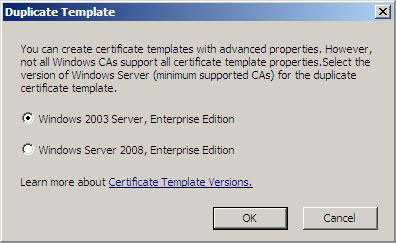
Figure 11
4. In the Display name Template , type System Health Authentication . Check the Publish certificate in Active Directory checkbox.
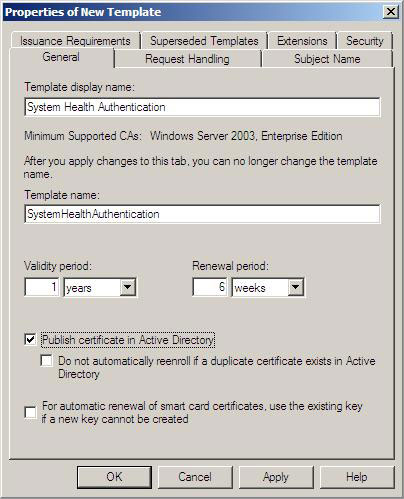
Figure 12
5. Click the Extensions tab, then click Application Policies . Then click the Edit button
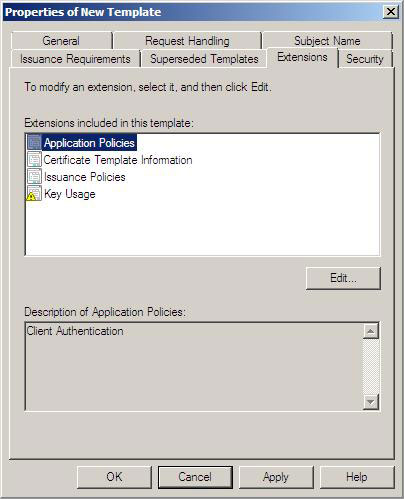
Figure 13
6. In the Edit Application Policies Extension dialog box, click Add .
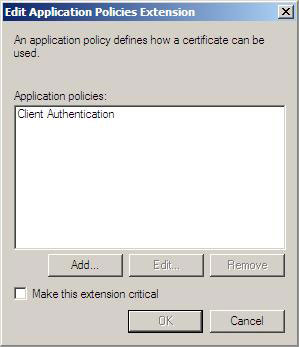
Figure 14
7. In the Add Application Policy dialog box, select the System Health Authentication policy and click OK .
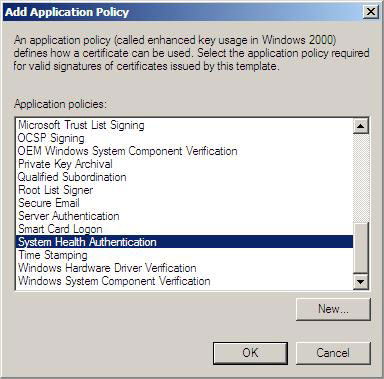
Figure 15
8. Click OK in the Edit Application Policy Extension dialog box
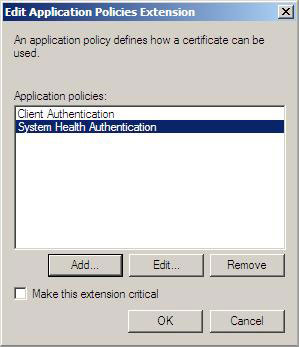
Figure 16
9. Click the Security tab and click Add . In the Select Users dialog box, Computers or Groups , enter NAP Exempt in the text box Enter the object name to select and click Check Names . Then click OK .
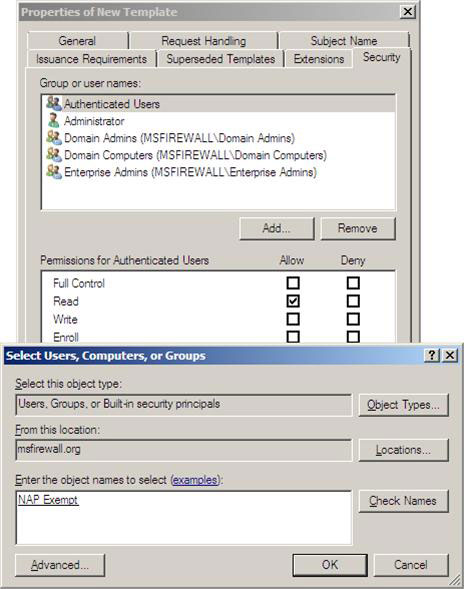
Figure 17
10. Click IPsec NAP Exemption , then check the box next to Allow , Enroll and Autoenroll and then click OK .

Figure 18
11. Close the console of the certificate templates.
Make the certificate template available for publication in Group Policy
Follow the steps below to enable the certificate template to become available in Active Directory Group Policy. After doing so, we will be able to make the certificate available to members of the NAP Exempt group through automatic enrollment.
Perform the following steps on WIN2008DC computer:
1. Click Start , click Run , type certsrv.msc, and then press ENTER .
2. Open the server name in the left pane of the console, in the console tree, click Certificate Templates , point to New , and then click Certificate Template to Issue .
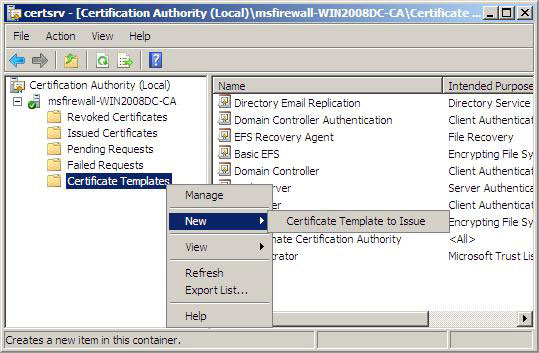
Figure 19
3. Click System Health Authentication , and then click OK
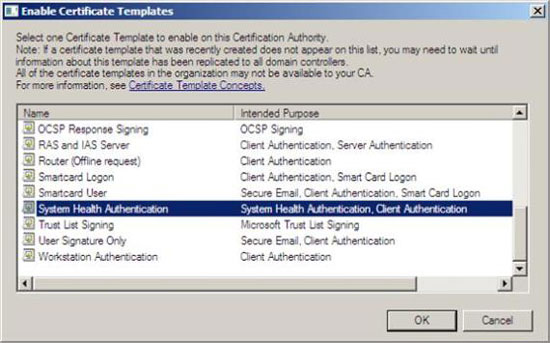
Figure 20
4. In the left pane of the console, click Certificate Templates, in the details pane located in the Name section, verify that the System Health Authentication is displayed.
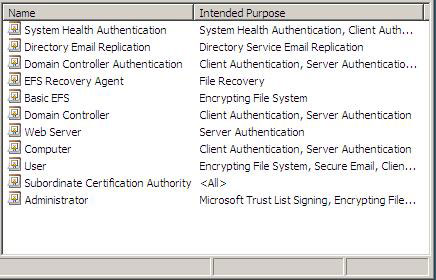
Figure 21
5. Close the Certification Authority interface
Distribute the NAP Exemption health certificate in Group Policy Autoenrollment
We have published the certificate template, so it can now make it available to machines belonging to the NAP Exempt group. We will do that by using autoenrollment.
Follow the steps below on the machine to activate the autoenrollment of this certificate:
1. Click Start and then click Run . Enter gpmc.msc in the Open text box and click OK .
2. In the Group Policy Management console, click to open the msfirewall.org domain name and right-click the Default Domain Policy and click Edit .
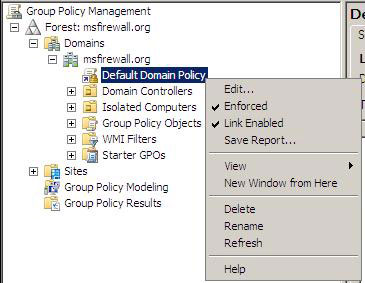
Figure 22
3. In the left pane of Group Policy Management Editor, open Computer ConfigurationWindows SettingsSecurity SettingsPublic Key Policies . In the middle of the console, double-click Certificate Services Client - Auto-Enrollment .
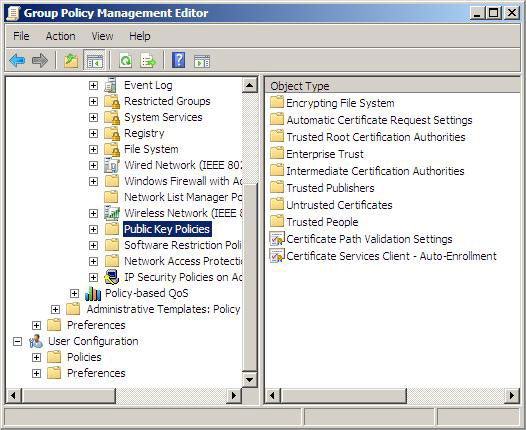
Figure 23
4. In the Certificate Services Client dialog box - Auto-Enrollment Properties , select the option from the Configuration Model list. Check the Renew Expired certificates box, update pending certificates, and remove revoked certificates and Update certificates that use certificate templates . Click OK .
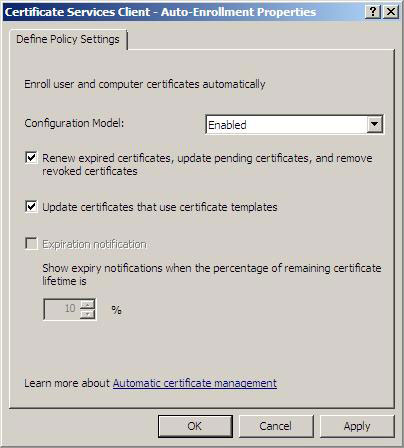
Figure 24
5. Close Group Policy Management Editor
6. Close the Group Policy Management console
Conclude
In this article, I have explained the configuration requirements for computers that are used as domain controllers. In this article, I will show you how to validate the enterprise CA root configuration, creating the NAP CLIENTS and NAP Exempt security groups, creating and configuring certificate templates for example NAP computers, making the certificate template current. property to publish in Group Policy, followed by distributing 'health' NAP exemption certificates to Group Policy. In the next article in this series, we will install the Network Policy Server and Health Registration rights as well as create a NAP policy.
You should read it
- ★ Deploying IPsec Server and Domain Isolation with Windows Server 2008 Group Policy - Part 4
- ★ Overview of Windows Server 2008 Firewall with advanced security features - Part 3
- ★ Overview of Windows Server 2008 Firewall with advanced security features (continued part 3)
- ★ Learn the new Network Policy Server feature in Windows Server 2008
- ★ Fix the problem when removing Windows Server 2008 Server Core from the domain