Boot and run Ubuntu from the USB drive
The TipsMake article below will show you how to boot and run Ubuntu from a USB drive and other Linux distributions. You can automatically save changes and settings on the USB drive and restore each boot using the 2nd partition.

This way you can run Ubuntu and its settings and files even on other computers. Continue reading the article below.

Note: The instructions below do not require Ubuntu 8.10 because USB Ubuntu Creator is already integrated.
Boot and run Ubuntu from the USB drive
Request

- USB 2.0 drive with minimum capacity of 1GB.
- Computer with CD drive (must be able to boot from USB drive. Devices with new motherboards will meet the requirement. BIOS update from good computer manufacturer).
- Ubuntu LiveCD (if your computer has Ubuntu installed, you do not need the Ubuntu LiveCD).
- Have knowledge of Terminal.
You can visit ubuntu.com to download the Ubuntu LiveCD. Download the Ubuntu Desktop LiveCD ISO file and burn it to CD using Nero or another program.
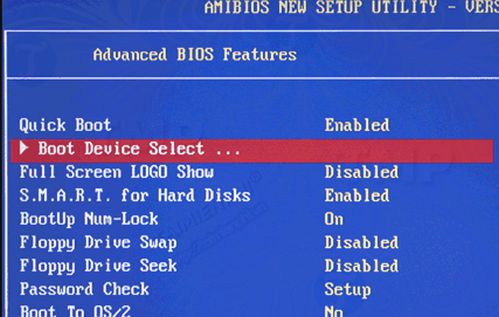
Change BIOS boot order
The next step to do now is to change the BIOS boot order. Turn on your computer, during the boot process press the button to access the BIOS Setup Utility. Depending on your computer, the keys may vary, but are usually F2 or Delete.
Navigate around the settings until you find the boot order setting. You can change the boot order to choose to boot from your device first.
Also on boot you will have the option to temporarily boot from the specific device. You can use the option if you want to boot from one device at a time.
Boot from Ubuntu LiveCD
Turn off your computer, then insert the CD drive into the CD/DVD tray on the computer. Next, open your computer and set up the BIOS to boot from the CD drive. It will load and you will see Ubuntu.
If your computer already has Ubuntu installed, you can skip this step. Just open your computer and log in.

Format the USB drive
The next step now is to format the USB drive. In this tutorial we will create 2 partitions, one for the actual Ubuntu operating system and one for the other operating system to automatically save changes and settings in the USB drive and restore these settings every time. startup times. In addition, you can also store personal data on the 2nd partition.
Back up all your data on the USB drive before performing the steps. This operation will delete all files and data on your USB drive.
Step 1 : Back up data on your USB drive.
Step 2: Open Terminal located in Applications.
Step 3: Enter sudo su there.
Step 4: Enter fdisk -l there and determine which device is your USB. Suppose if your USB drive is sda, enter " format sda1 " there.
Step 5 : Enter the command " umount /dev/sdb1 ".
Step 6: Enter the command " fdisk /dev/sdb ".
- Enter p to display existing partitions and d to delete that partition.
- Enter p again to display the remaining partitions (if the partition exists, perform the above step to delete the partition).
- Enter n to create a new partition.
- Enter p for primary partition.
- Enter 1 to number the first partition.
Press Enter to use partition 1 as the default partition.
- Enter +750M to set the partition size.
- Enter a to activate the partition.
- Enter 1 to select partition 1.
- Enter t to change file system partition.
- Enter 6 to select fat16 file system.
- Enter n to create a new partition.
- Enter p for primary partition.
- Enter 2 to mark the 2nd partition.
- Press Enter to use the default partition.
- Press Enter again to use the last partition as the default partition.
- Enter w to write a new partition table.
Step 7 : Enter the command umount /dev/sdb1 , then enter umount /dev/sdb2.
Step 8 : Enter the command mkfs.vfat -F 16 -n Ubuntu /dev/sdb1 . This command to format the first partition.
Step 9 : Next enter the command mkfs.ext2 -b 4096 -L casper-rw /dev/sdb2 to format the second partition.
Step 10: Close the Terminal window and remove the USB drive.
Install Ubuntu to the USB drive
After completing the USB drive formatting process, the next step is now to install Ubuntu onto the USB drive partition.
Step 1: Plug the USB drive into the computer.
Step 2: Open Terminal.
Step 3 : Enter the command apt-get update.
Step 4 : Access Ubuntu Packages, download Mtools to your computer and install. Next, download Syslinux and install.
Download Mtools to your computer and install here: Download MTools
Download Syslinux to your computer and install it here: Download Syslinux
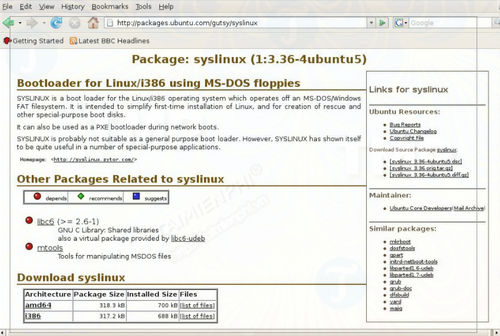
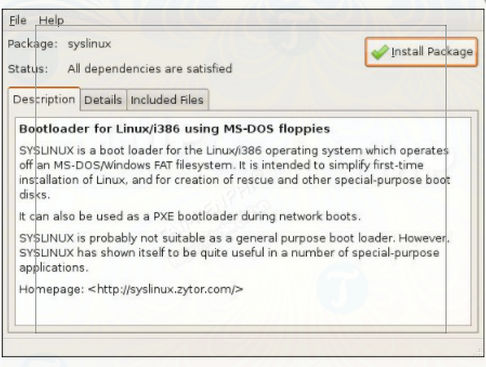
Step 5 : On the Terminal window, enter the command syslinux -sf /dev/sdb1 .
Step 6 : Enter cd /cdrom.
Step 7: Enter the command " cp -rf casper disctree dists install pics pool preseed .disk isolinux/* md5sum.txt README.diskdefines ubuntu.ico casper/vmlinuz casper/initrd.gz /media/Ubuntu/".
Ignore any "cannot create symbolic link" errors.
Step 8 : Access the first partition on the USB drive and rename isolinux.cfg to syslinux.cfg .
Step 9 : Edit syslinux.cfg like the file attached HERE
Completed
Just restart the computer, and set it to boot from the USB drive in the BIOS.
If you cannot boot and run Ubuntu from the USB drive, it is likely that your USB drive has an MBR error. To fix MBR errors on a USB drive, in the Terminal window on Ubuntu, enter the command below:
sudo apt-get install lilo
Then enter the command lilo -M /dev/sdb .

From now on you can run Ubuntu anywhere and have all the necessary settings and files available.
Above TipsMake has just shown you how to boot and run Ubuntu from a USB drive. If you do not want to continue running Ubuntu from a USB drive but want to install it directly on your computer, you can choose to install Ubuntu in parallel with Windows 10, 8, 7 UEFI and GPT which is also quite simple and easy.
 What is Linux Kernel? Application functions of Linux Kernel in computer systems
What is Linux Kernel? Application functions of Linux Kernel in computer systems What is Bash in Linux? What can it be used for?
What is Bash in Linux? What can it be used for? New free malware scanning tool for Linux
New free malware scanning tool for Linux How to use Scrcpy to control Android on Linux
How to use Scrcpy to control Android on Linux Everything you need to know about the DNF package manager
Everything you need to know about the DNF package manager 5 best Neofetch alternatives for Linux screen capture
5 best Neofetch alternatives for Linux screen capture