Basic difference between GiFi and WiFi
GiFi technology

Following are the features of GiFi technology:
This is the world's first transceiver developed on a single chip using a CMOS process.
- It works at 60GHz. (using unlicensed band 57 to 64GHz).
It enables wireless audio / video transmission at 5Gbps over a range of 10 meters with very low power consumption.
- It was developed by NICTA (National Center for Information Technology and Communication Research) Australia.
The main component of the GiFi architecture is a subscriber station (transceiver that converts radio signals into digital signals, which can be routed to and from communication devices) that communicate. with an AP (Access Point).
It is defined in the IEEE 802.15.3C standard, which constitutes a wireless PAN network in the millimeter wave frequency range.
Usually rooftop antennas support LOS communication.
It uses TDD topology to transmit and receive with an antenna.
- It can be used with FDD topology using 3 antennas.
Advantages
- GiFi offers very high data rates (7Gbps, BPSK) and low noise.
- Complex modulation schemes are not required.
- An antenna distance of about 1.25mm is needed.
- GiFi technology is about ten times faster than WiFi technology.
Defect
- Supports short distances (about 10 meters) due to high frequency-dependent attenuation.
- It can be blocked by an object very easily.
- RTS / CTS doesn't work in GiFi technology unlike WiFi.
WiFi technology
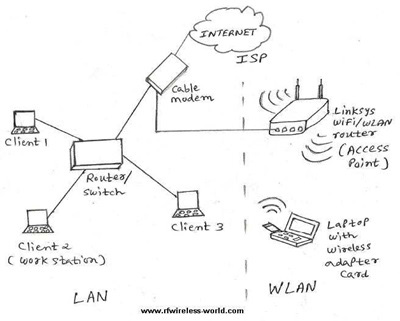
The following are the features of WiFi technology.
- WiFi AP (Access Point) or router connected with Internet broadband cable or to mobile network. All WiFi-compatible mobile phones, tablets or laptops are connected to the AP (or router) to get to the Internet.
- WiFi networks operate in one of two modes: Adhoc (ie BSS - Basic Service Set) and infrastructure (ie ESS - Extended Service Set).
In BSS WLAN compliant stations (ie STAs) communicating directly. In ESS WLAN, the compliant STAs communicate with APs (access points) to access the Internet.
WiFi supports different speeds and ranges according to standards deployed in devices (STA, AP). 802.11a max support 54Mbps, 11b upto 11Mbps, 11n supporting 72Mbps / 150Mbps by BW (20MHz / 40MHz), 802.11ac wave-1 supporting up to 1.3Gbps (80MHz, 3 streams, 256QAM), 802.11 ac wave-2 max support 3.5Gbps (160MHz, 4 streams, 256QAM), etc. The coverage distance from 70 meters (indoor) to 250 meters (outdoor) can be achieved.
WiFi networks operate in different frequency bands: 2.4GHz and 5GHz.
- The PHY and MAC layers of the WiFi system are defined according to the IEEE 802.11 standard. There are different versions of 802.11 including 11a, 11b, 11g, 11n, 11ac, etc. Refer to the WLAN guide for more information.