Balance downloading Web-Proxy Client with ISA Server 2004 Standard Edition
In this article we will modify the script configuration provided by ISA Server 2004 Standard Edition and deploy it to browser clients .
Load balancing of Web-proxies is often understood as one of the functions provided by ISA Server Enterprise Edition. But for many, the extra cost of the Enterprise Edition makes them hesitant, although the desire of organizations or companies is always in need of extra storage and load balancing. Up to now the Standard Edition business version has provided a number of tips and tricks to enable load balancing. If you intend to own two or three ISA Servers that work effectively together, this article can help you.
Introduce
With ISA Server 2004 (and 2000), if you want to have more than one Web-proxy server for your organization and let them work together, you should go out and buy an Enterprise version . Enterprise Edition supports Cache Array Routing Protocol (or CARP) and provides a mechanism to link proxies together. But is it really clear? If you only have a few hundred users and have to prepare a large amount of Web-proxy reserves, do you really need to take a significant extra cost for the Enterprise license couple?
In fact, people are more interested in CARP than reading about Enterprise Edition. Some aspects of CARP are still hidden in Standard Edition waiting for you to explore. With two or three proxy servers in the "array", you may find that you save a lot of cost effectively when using Standard Edition. If more than three and the protocol is not CARP, you need Enterprise Edition. This version manages more centers and other "Enterprise" components are supported.
So, when deciding to use two proxies to reserve, you want both to share the download activity and avoid the extra costs and complexity of Enterprise Edition: what are the options?
DNS Round-Robin and Network Load Balancing (NLB)
Both of these mechanisms can be used to provide some functions such as fault-tolerance and load balancing. Surely many people will want to try them. In both cases you will have to configure a generic name, (as with NLB, a common IP) to point to all ISA servers. Before Standard Edition, Microsoft did not support the more complex NLB system.
You can configure your browser to use the generic proxy name directly, or configure "automatic detection" and "automatic configuration scripts". These "auto" options have a number of distinct improvements over static methods, in which you can describe backup routing routes when everything becomes pear-shaped.
Be careful because if you use "automatic" methods, the browser will download the configuration file from one of the ISA Servers (decided by NLB or round-robin) and this file will tell the browser to use only the proxy. during the process. This may not be the load balancing mechanism you want! To overcome errors faster when using the "automatic" method, you can configure the settings on each ISA Server, using another ISA Server as a backup method. ISA Server will then add this information to the configuration file of the browsers it receives.
The major drawback of these methods is that each ISA Server builds its own cache containing the information inherent on the other ISA Server. This is not an efficient use of resources.
Automatic proxy configuration files (Proxy Automatic Configuration - PAC)
If you configure "automatic detection" or "automatic configuration script" in the browser, the configuration file does not come from ISA Server. It can be pointed to another location containing the custom configuration "script" provided by you that is not ISA Server. This method opens the entire world to the ability to load balance and error tolerance.
What are these configuration scripts (scripts)? Nearly every browser currently supports the use of automated configuration scripts. They are written in JavaScript. The browser runs them and calls specific functions in the script every time a URL is found. The function will return the Web-proxy to the browser that is about to send the incoming URL request.
So how do these scripts load balance? The most common method is that the script runs a "hash" algorithm on the requested URL and uses the result obtained from the hash function to determine which Web-proxy will send the request (return algorithm). URL string is a unique number, called hash number). The great improvement of this method is that each browser runs the same hash function and determines the same Web-proxy for the provided URL, depending on the Web-proxy server. This means Web-proxies build a unique cache for its other Web-proxy "friends." Therefore, resources are exploited effectively.
The number of hashing algorithms used is not limited. There have been experts developing the "Super Proxy Script" model since 1996, you can refer to the address: http://naragw.sharp.co.jp/sps/. But for most people, this technology is often combined with CARP.
In this article we will examine the configuration configuration scripts using CARP. It sounds scary, but don't worry, any previous prejudices about Enterprise Edition support CARP and Standard Edition notes, ie ISA Server Standard Edition will be replaced. Everything 'scary' will be done automatically.
Cache Array Routing Protocol (CARP)
As mentioned above, people often talk about CARP rather than mentioning whether to sell the Enterprise Edition business version. CARP includes two types: client-side CARP (on the client) that we discussed and server-side CARP (on the server).
Server-side CARP
This CARP uses a similar hash function (if not quite the same) with the type mentioned above. But here it is for the server to determine if it has any required URLs in the cache memory, or if its "you" is there? This is great for clients that require a URL or will not support client-side CARP (ie "Secure NAT" clients in ISA Server speech), or if the server has proxy arrays in the opposite direction and must decide the largest proxy to send the request to.
ISA Server Enterprise Edition supports server-side CARP but you must enable this component. Standard Edition does not support CARP server-side.
Client-side CARP
If a browser supports client-side CARP, then it doesn't matter whether the Web proxy is Enterprise or Standard Edition (or even ISA Server). However, Enterprise Edition creates automatic configuration files with all necessary CARP client-sile components in place. It even does this even if you do not allow CARP in the configuration. Standard Edition is the same. The error that occurs in Standard Edition is because it does not understand if there is a 'partner', so it is not possible to configure this required information in the prepared script.
Why Microsoft does not allow Standard Edition to create non-functional client-side CARP code in configuration scripts. That means, just a little help, you can create a fully functional script.
Let's look at the script created by ISA Server Standard Edition. Just open the browser, type: http:/// myISAServer: 8080 / wpad.dat (use your server name). Write the file when requested, then open it in a text editor like Notepad.
See the code snippets in the dialog box below:
// Copyright (c) 1997-2004 Microsoft Corporation
BackupRoute = "DIRECT";
UseDirectForLocal = true;
function MakeIPs () {
}
DirectIPs = new MakeIPs ();
cDirectIPs = 0;
function MakeNames () {
}
DirectNames = new MakeNames ();
cDirectNames = 0;
HttpPort = "8080";
cNodes = 1;
function MakeProxies () {
this [0] = new Node ("10.245.10.254", 0.1.000000);
}
Proxies = new MakeProxies ();
function Node (name, hash, load) {
this.name = name;
this.hash = hash;
this.load = load;
this.score = 0;
return this;
}
FindProxyForURL function (url, host) {
var urlhash, urllower, ibest, bestscore, list, i, j, port = HttpPort;
urllower = url.toLowerCase ();
if ((urllower.substring (0.5) == "rtsp:") ||
(urllower.substring (0.6) == "rtspt:") ||
(urllower.substring (0.6) == "rtspu:") ||
(urllower.substring (0.4) == "mms:") ||
(urllower.substring (0.5) == "mmst:") ||
(urllower.substring (0.5) == "mmsu:"))
return "DIRECT";
if (UseDirectForLocal && isPlainHostName (host))
return "DIRECT";
if (cDirectNames> 0)
for (i = 0; i
return "DIRECT";
if (cDirectIPs> 0)
for (i = 0; i
return "DIRECT";
urlhash = HashString (url);
for (i = 0; i
list = "";
for (j = 0; j
bestscore = Proxies [i] .score;
ibest = i;
}
}
Proxies [ibest] .score = -1;
list = list + "PROXY" + Proxies [ibest] .name + ":" + port + ";";
}
list = list + BackupRoute;
return list;
}
function HashString (url) {
var h = 0;
var slashes = 0;
for (var i = 0; i
if (c == '/')
slashes ++;
if (slashes <3)
c = c.toLowerCase ();
h + = (((h & 0x1fff) << 19) | ((h >> 13) & 0x7ffff)) + CharToAscii (c);
h = MakeInt (h);
}
return h;
}
function Scramble (h) {
h + = ((h & 0xffff) * 0x1965) + ((((h >> 16) & 0xffff) * 0x1965) << 16) + (((h & 0xffff) * 0x6253) << 16);
h = MakeInt (h);
h + = (((h & 0x7ff) << 21) | ((h >> 11) & 0x1fffff));
return MakeInt (h);
}
var Chars = "!" # $% & '() * +, -. / 0123456789:; <=>? @ ABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRSTUVWXYZ [] ^ _ `abcdefghijklmnopqrstuvwxyz {|} ~ € ??????????? Ž ???????????? ž? ¡¢ £ ¤ ¥ ¦§¨ © ª «¬®¯ ° ± ²³´¶¶ · ¸¹º» ¼½¾¿¼½¾¿ÂÄÅÆÇÈËËËÎÏÎÏÎÏÎÏà ÓÕ
function CharToAscii (c) {
return Chars.indexOf (c) + 32;
}
function MakeInt (x) {
if (x <0) {
return x + 4294967296;
} else if (x> = 4294967296) {
return x - 4294967296;
}
return x;
}
So what does this code provide? Your browser configured for this script's location will download and execute it. The script is run with red code and set some extended variables, run some functions (purple). When the browser needs to request a URL, it will call FindProxyForURL (orange). This function returns a proxy server to send the request to the URL or the message "DIRECT", ie without Proxy for this URL.
What is all the blue code? FindProxyForURL calls these functions to create the hash table from the URL and calculate the value for each proxy it knows. The FindProxyForURL function actually returns a list of proxies with the highest score at the beginning and the backup direction configured at the end. The browser will use this highest-level proxy to send the incoming URL request. That is the operation of client-side CARP.
The script comes from ISA Server Standard Edition, so what are all these hash codes for? Absolutely not to do anything! If you take a closer look at the start section, you will see a function (purple) called MakeProxies , listing ISA Server to create the script. Only one proxy is listed here, so the script must always return the proxy. As we know, Microsoft likes to use microprocessors to run all unnecessary code. In this example, our poor browser has implemented most unused code over the entire URL request time, perhaps a few times for a Web page. Small help but not necessary for us but they do not intend to stop!
Create a basic configuration configuration script
Although it may seem hard, you can do it. Of course the real problem is getting the resulting script from the browser on the client but we will care about it later. We will also discuss the intelligent editing issues in Part 2, but now only create a basic function script.
Let's look at the following lines in the script downloaded from ISA Server:
cNodes = 1;
function MakeProxies () {
this [0] = new Node ("10.245.10.254", 0.1.000000);
}
"10.245.10.254" is our ISA Server address taken in this illustration example. When you do, this IP address will be replaced with your own ISA Server address. You may have a fully qualified domain name, both good.
Now fix the following lines, including your second ISA Server.
cNodes = 2 ;
function MakeProxies () {
this [0] = new Node ("10.245.10.254", 2032180928 , 1.000000);
this [1] = new Node ("10.245.10.253", 2843172549,1.000000);
}
Having a few numbers seems to be confusing. They are added so that the hashing algorithm chooses a proxy or another option in the 50/50 range, depending on the requested URL. In the next part, we will find out where those numbers come from, but now they are just temporarily accepted for use.
HTTP port
Look closely, you'll see the same line like this:
HttpPort = "8080";
This parameter states that the port of your ISA Server listening to the proxy request is 8080. There is only one entry, meaning all nodes must be configured to use the same port. The "8080" port is set by default and rarely needs to be changed.
Deploy an optional configuration script
There are two mechanisms for bringing scripts into the browser on the client: either configuring them using the "automatic detection" function, or providing the location for "automatic configuration scripts". Before that, you need to put your script on a suitable website that your browser can access.
If you want to have redundant proxies to reserve, you need a residual website to set the configuration file or have a single point of failure. To illustrate a required configuration, we will go through each step by creating a single IIS website. But you can absolutely use a fault-tolerant Intranet website or any other suitable form.
First, create a new IIS Manager website:

The next step in the Web Site Creation Wizard is to give the website a descriptive name. Here I use the name WPAD.
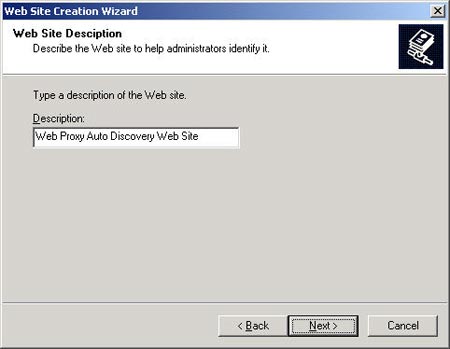
In the next page you can give a specific IP address (or leave it as it is here). You should attach this IP address to port 80 because there is one component that automatically detects this port (we will discuss in part two). A host header is necessary because port 80 can be shared by other virtual servers.
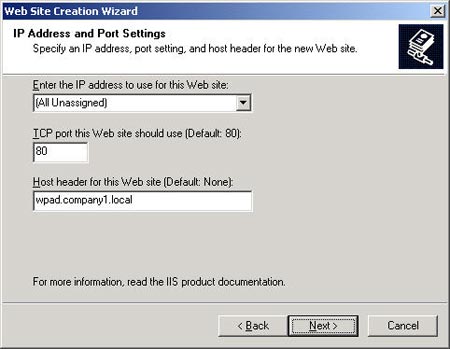
Remember that you must have a DNS (Domain Name System) solution on every host-header address. You may have two entry points pointing to two websites (DNS round-robin) or point the record to a balance of virtual IP downloads or otherwise use whatever fault-toterlant website you have.
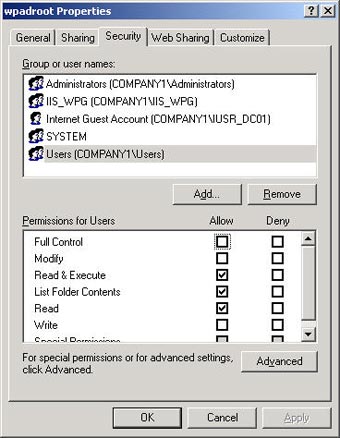
Accordingly, you need to provide the location for the file and note that this website must allow anonymous access. The next Wizard page is followed by permissions. With this website you only need read permission - "Read" (no scripts needed, executable or written).
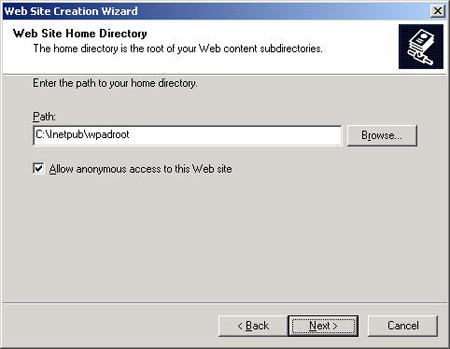
In the end, the Wizard will complete the essential configuration for the website. The next problem is to just copy your configuration script into the appropriate location (here is C: Inetpubwpadroot ) and make sure the anonymous access account (usually IUSR_ Servername ) has read access to this file location. .
You should check the whole page by including the link to the file and downloading it (in this example the URL will be http:///wpad.company1.local/wpad.dat ).
I named the configuration script WPAD.DAT even though there are no requirements that require you to call that.
Configure Internet Explorer to use Configuration Script
Configure Internet Explorer "manually" to use the configuration file without difficulty. Start by selecting the Internet Options component on the Tools menu.
We need the Lan Settings option, found on the Connections page.
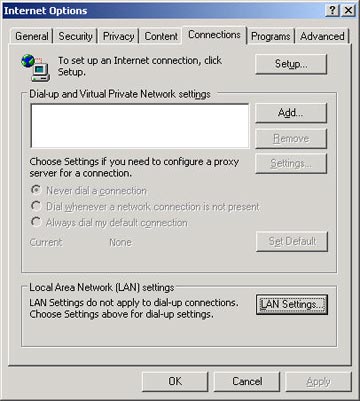
Enter the URL that points to the WPAD.DAT file you created and click OK .
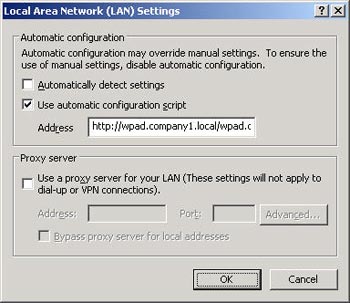
Finish. Point the link to an Internet website and the browser will start using the configuration script to select the proxy to send the request to, like this:
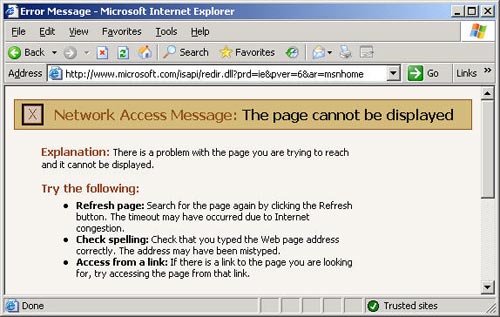
Perhaps I have configured my ISA Server according to the rules, but nothing proves most clearly that you will pass an ISA Server with this small page.
Of course, if there are up to 100 clients, you certainly won't want to "manually" configure these browsers. Group Policy is a good choice for you. But we will discuss it later in part two. In the second part, we'll look at Automatically detect settings , but please be warned that there will be some controversy about this issue.
Conclude
In this article we have edited the configuration script provided by ISA Server 2004 Standard Edition and deployed it to our client clients. As a result, there are two or more ISA Server Standard Edition Web proxies that can effectively load balance, using client-side CARP. If an ISA Server proxy is lost, it will be converted to its "friends" quickly.
The information above is all you need to install and run. In part two, we will look at some of the more advanced edits of custom scripts (optional scripts). We will illustrate some "manual" changes to other components in the script because ISA Server will not do anything more about them. We will also introduce the "CARP Exception" concept, an Enterprise Edition component to help you avoid problems with some websites.
But before you finish, you should .
Calculate hash value for Proxy buttons
If you remember, you will see two "magic" numbers entered in the script that the hashing algorithm will use to ensure each ISA Server has a fair share of load. These numbers are 2032180928 and 2843172549. In fact, we cannot know where these numbers are calculated from.
I tested and installed the 120-day version of ISA Server 2004 Enterprise Edition onto some virtual machines and checked the value in the WPAD.DAT file downloaded from one of the servers. Although somewhat "cheating", but very effective!
You can use some tricks to explore other values in the script, but you cannot install ISA Server 2004 Service Pack 2. SP2 to introduce changes in Enterprise Edition, including the advanced hashing algorithm in configuration script. Therefore, you should use previous versions of SP2 to avoid having a headache with its changes.
Anyway, the "magic" number of ISA Server is in array 3804533832 and the other numbers are the same.
See next section II