What to back up on a Linux Home Server system?
If you own a home server system that works with Linux, you will probably need to upgrade and update it regularly. Here, TipsMake.com will guide you some basic steps to back up the basic and most necessary components, helping users to save maximum time each time performing the upgrade process.
However, each home server system has a certain difference, so please adjust and change accordingly - this is a tutorial that should start.
/ Home directory:

Let's start with / home , the root directory for each account on the system. Here store all the music, video and document files (unless you leave the data on another partition), and this is also the place to store the configuration files of the program. Press Ctrl + H and you will see all the hidden files in this folder. Please backup any data needed, and apply to each account.
Apt source:

The list of software and applications used by apt is fixed at /etc/apt/sources.list , and gpg keys in the /etc/apt/sources.list.d/ directory. If you've ever had time to use Linux, surely people will want to install software from external repositories compared to the default system. After reinstalling, users only need to change the information of the corresponding distro (eg lucid to maverick ), and copy these lines to the new sources.list file. But depending on the repository, you must download the gpg key before using. Another thing to note is that users should also remember exactly what is on the old system, or use Ubuntu Tweak - 1 pretty good solution if you want to install the software and repository, as well as change the settings in the system.
Samba settings:

If you set up and use the Samba sharing feature (with Windows), you need to copy the /etc/samba/smb.conf file . There are actually very few differences between versions, so just keep the setup file in use. In case of a total reset, use gadmin-samba (on Gnome) and KSambaPlugin (on KDE) with smb.conf, both tools have a graphical console, making operations Much simpler and easier.
SSH:
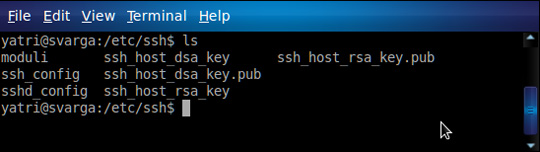
In case you use SSH to control and access remote computers, back up the setup file of this function at / etc / ssh / ssh_config and / etc / ssh / sshd_config.
fstab:

The entire file is fixed in the / etc / fstab directory , the main task is to specify the Linux file system file. Be careful when applying, because you will not be able to use the old fstab file on a new installation system. Because the UUIDs parameter will change every time the partition is reformatted. However, please keep the old configuration file in the fstab file, this is really useful if the system has multiple partitions, folders or shared connections, separate root / home directory . Besides You can also use pySDM (Gnome) or mountmanager (KDE) to adjust the fstab file (both have graphical interfaces).
Backup program:
If the server system is set up to automatically back up with rsync or Simple Backup , keep the configuration files of those tools, for example, the configuration file of Rsync at /etc/rsyncd.conf and Simple Backup is /etc/sbackup.conf.
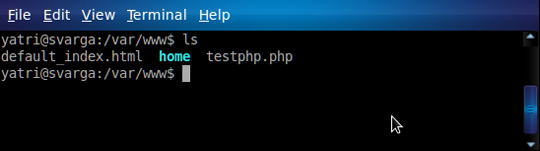
Website configuration files:
Many people use Apache, MySQL, or PHP on the system to use or research their personal websites. And backing up these configuration files is quite complicated, all in the directory / var / www:
But it would probably be better if you reconfigure all Apache, MySQL, and PHP when reinstalling the system, due to a change in user version or admin password. On the other hand, you can install it instead with the familiar LAMP combination:
sudo apt-get install lamp-server ^
Besides, please install phpMyAdmin to adjust MySQL database more easily:
sudo apt-get install libapache2-mod-auth-mysql phpmyadmin
And finally, remember to change the default passwords for these applications before using them. Good luck!